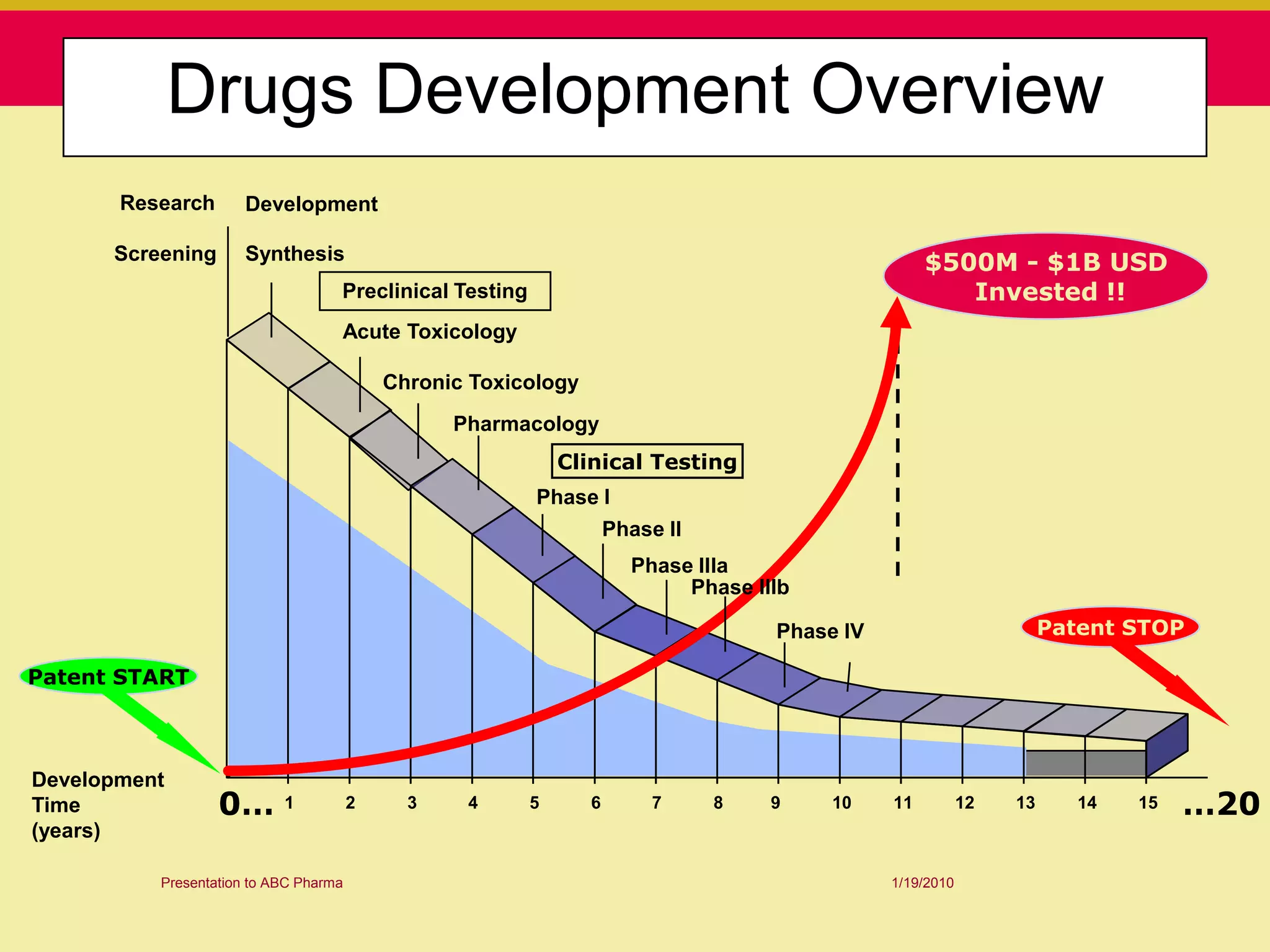
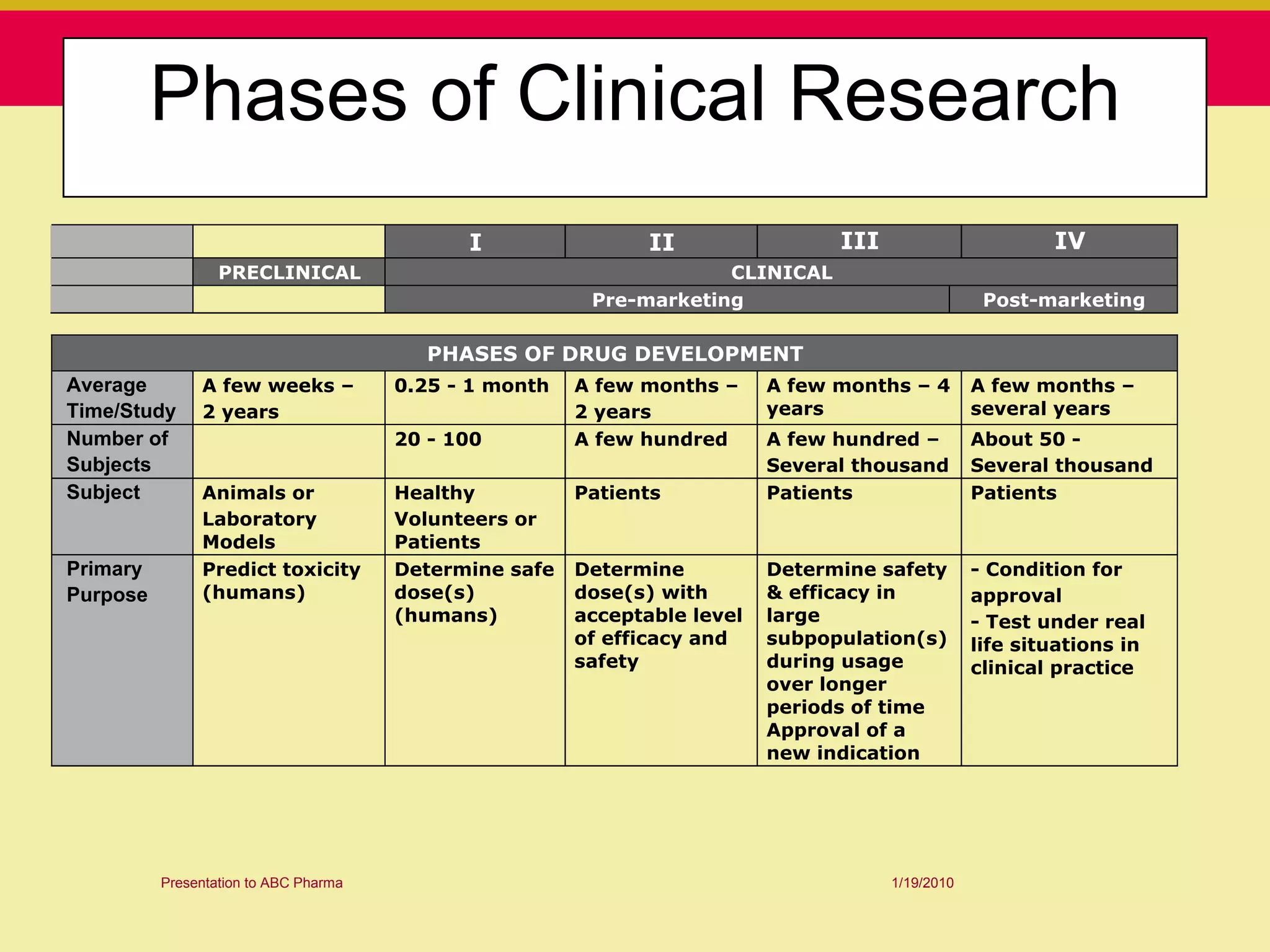
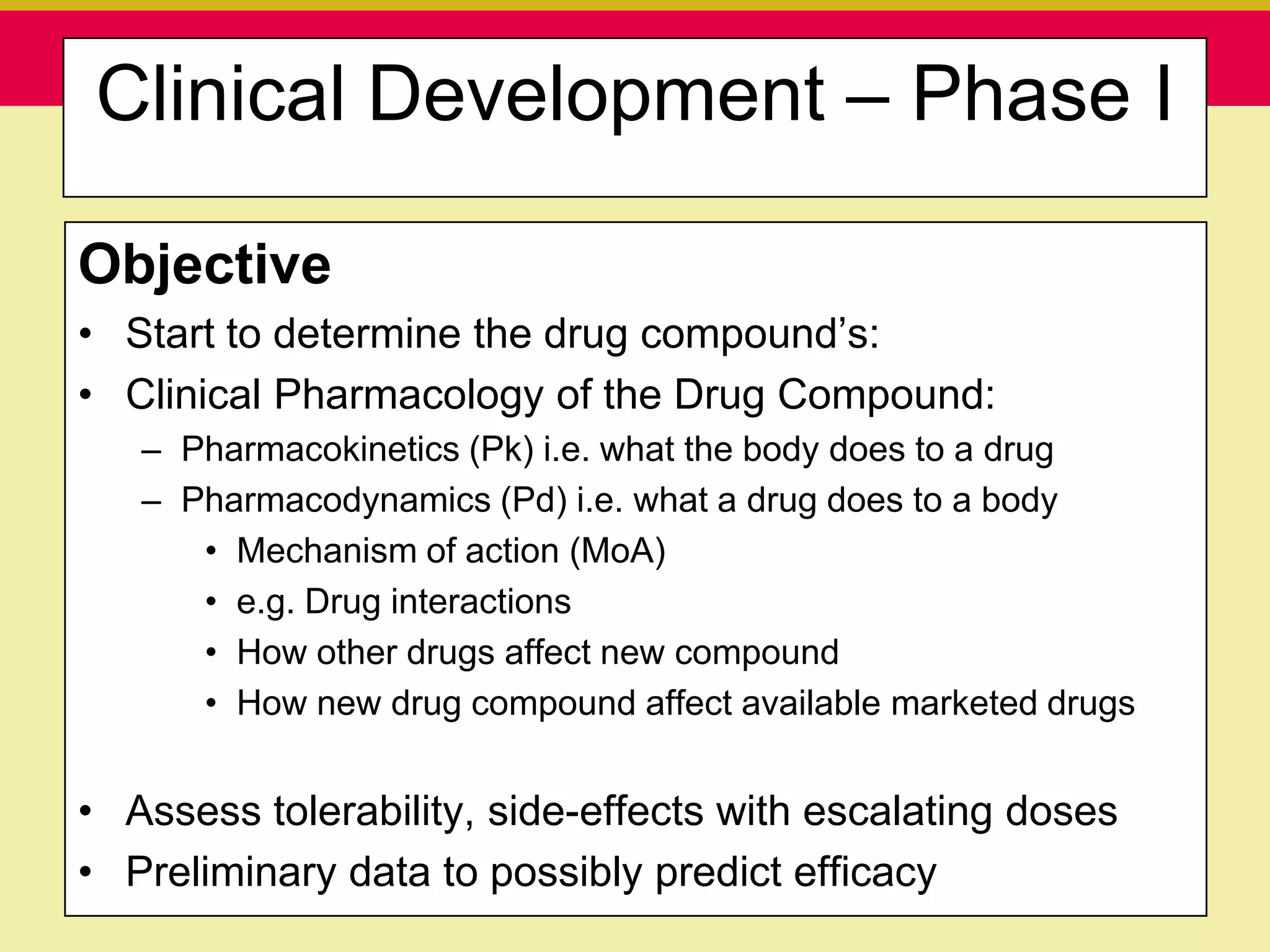
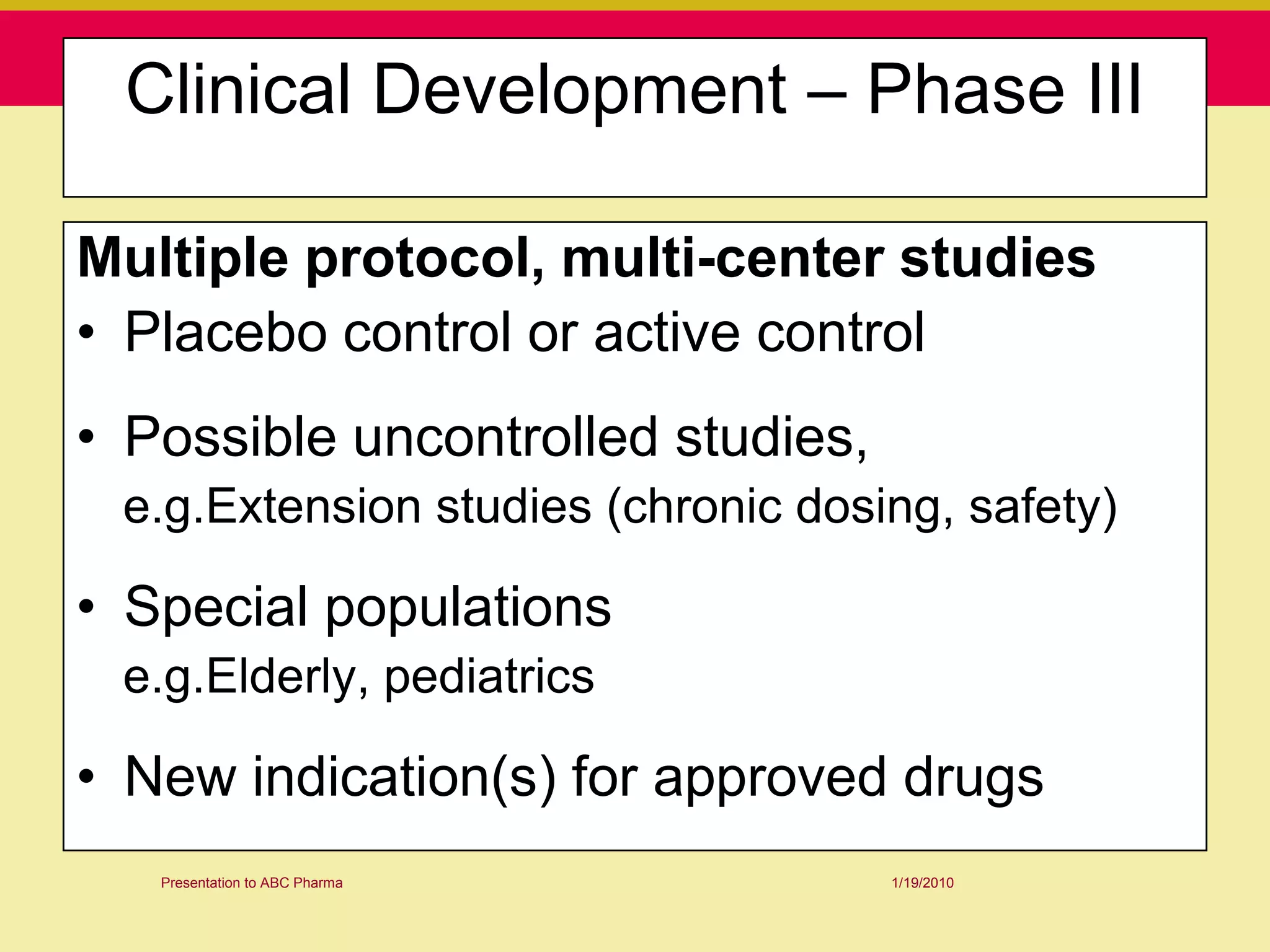
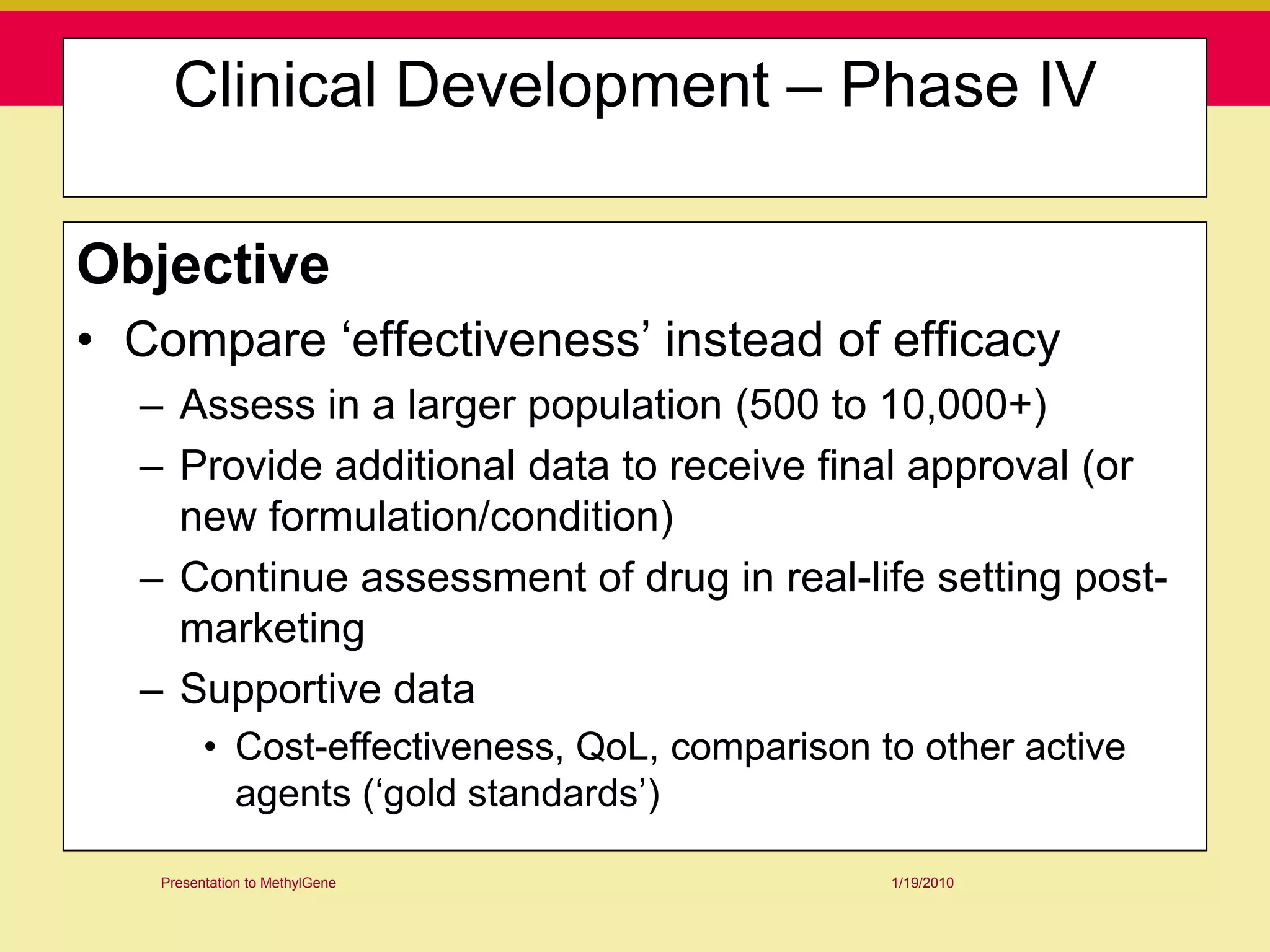
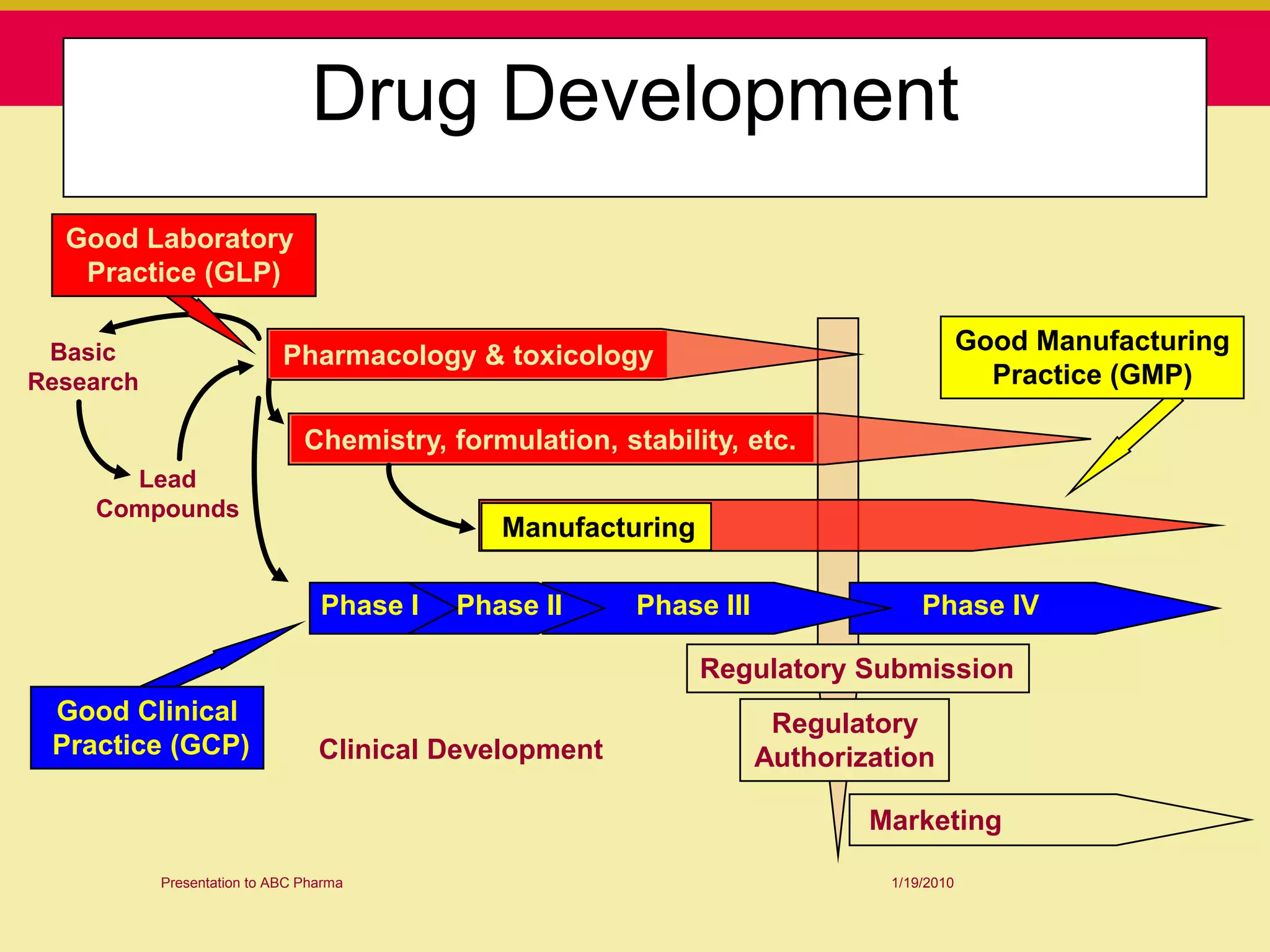
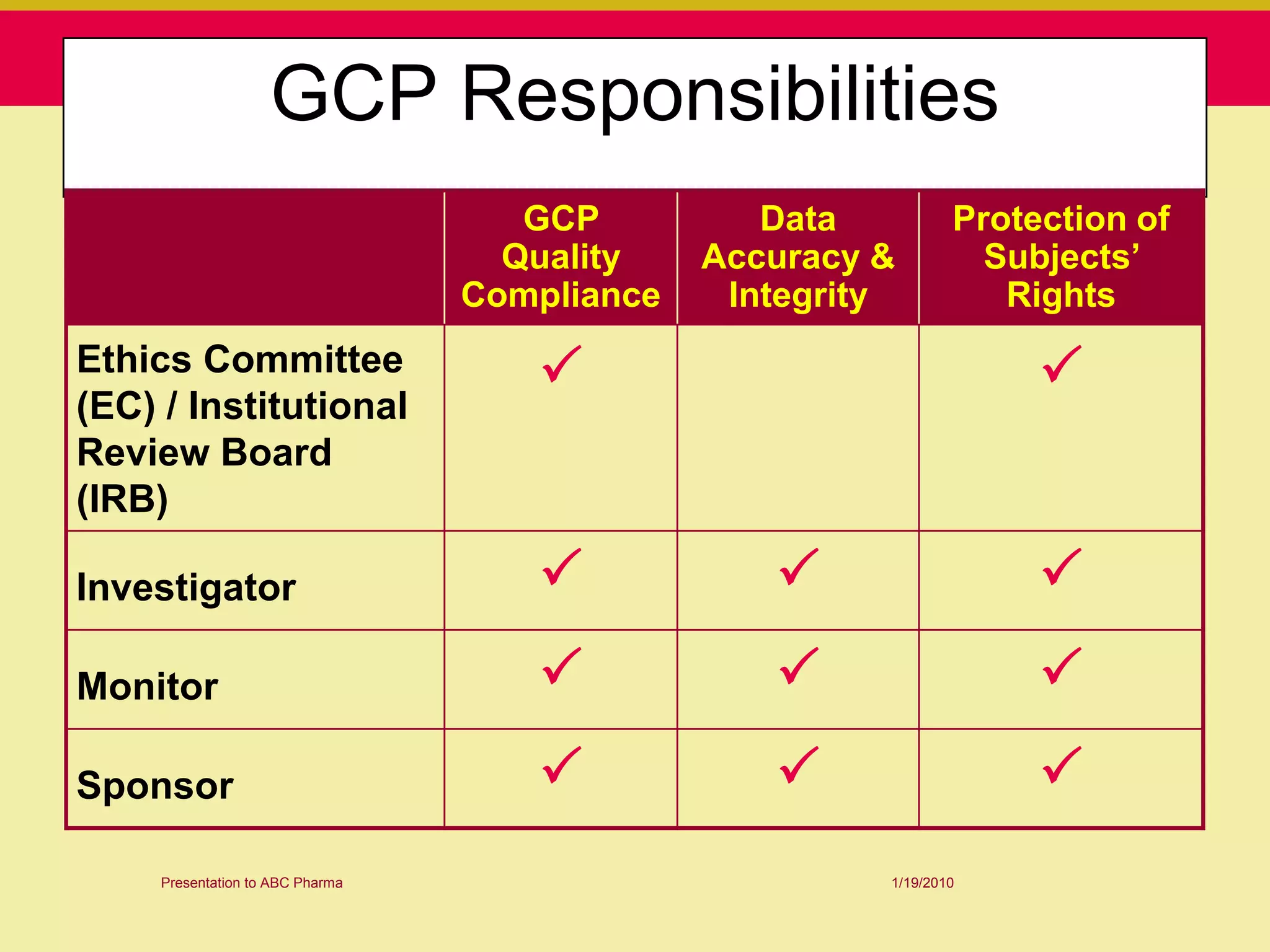
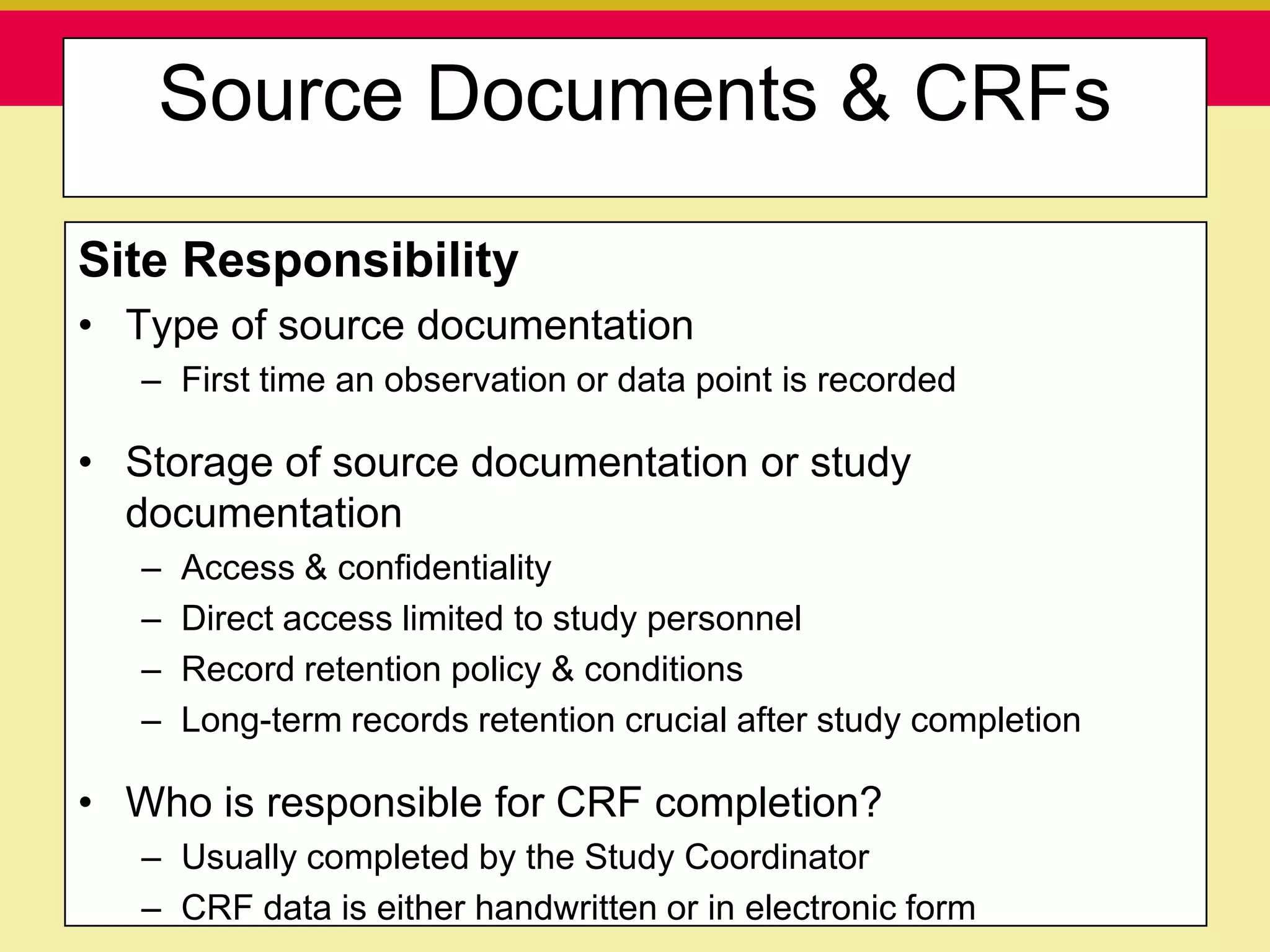
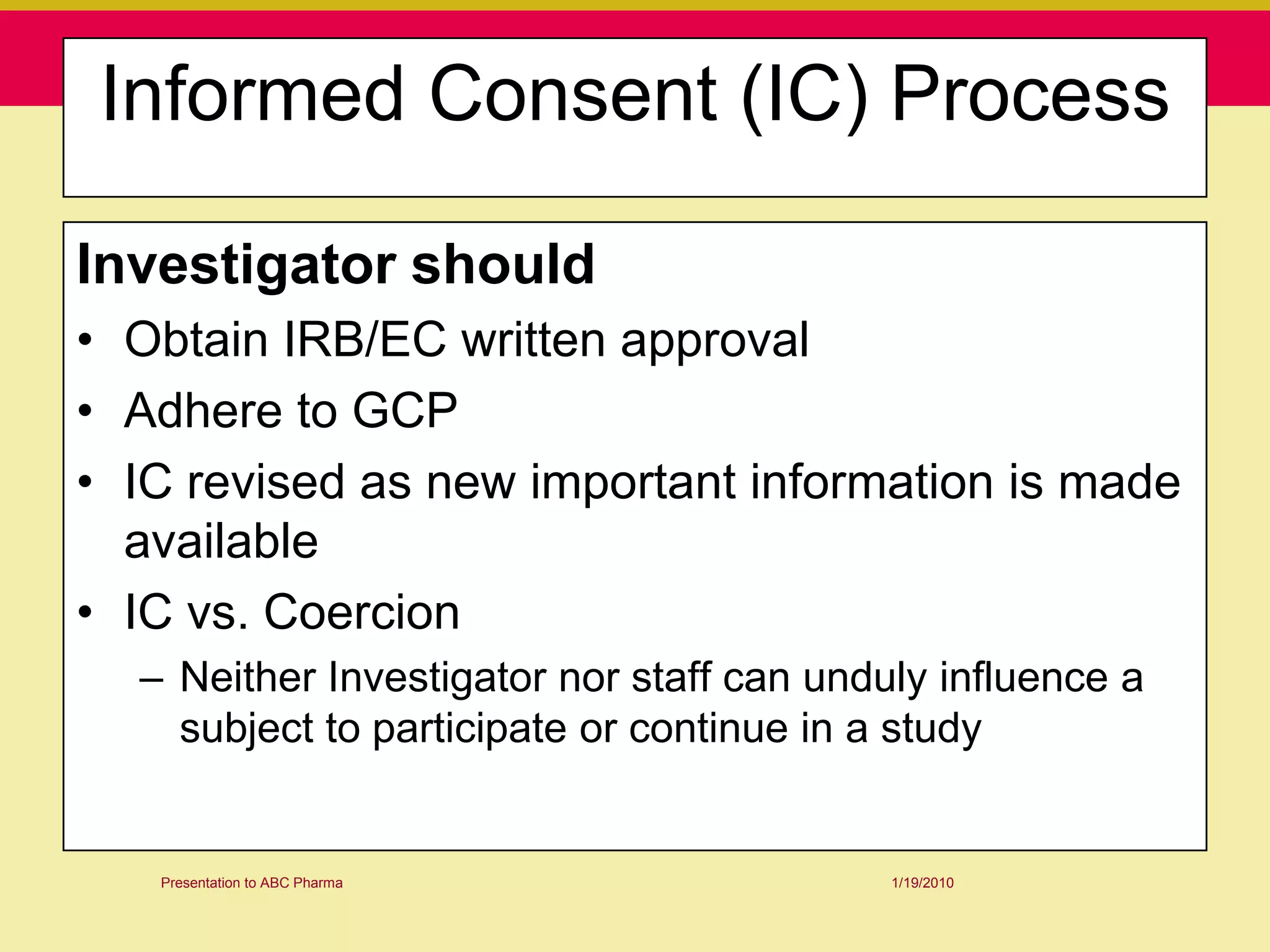
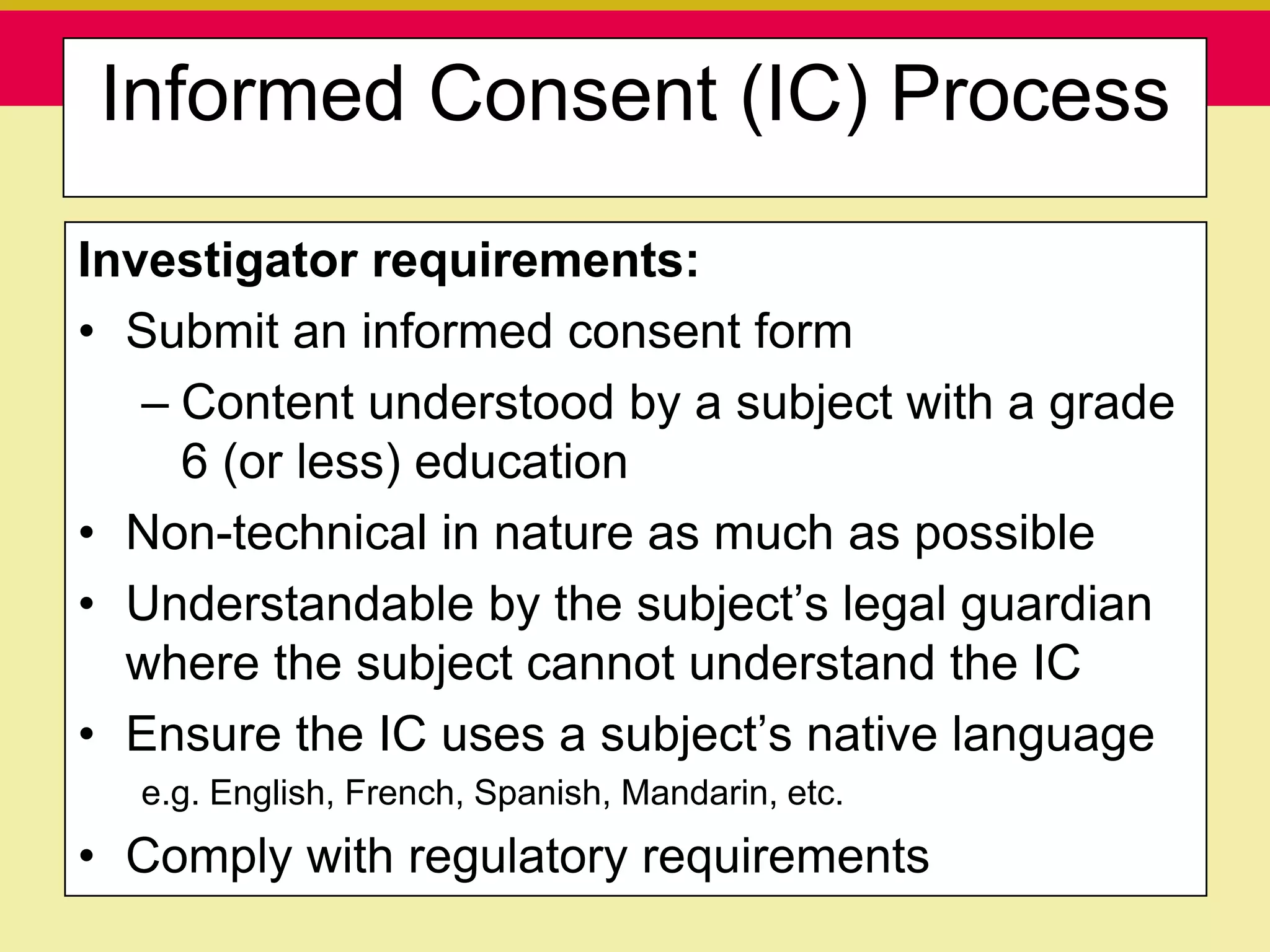
This document discusses guidelines for good clinical practice (GCP) and the drug development process. It provides an overview of the history and purpose of GCP, outlines the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders in clinical trials, and reviews the drug development phases from pre-clinical research through post-marketing studies. Key aspects of GCP covered include informed consent, responsibilities of investigators and sponsors, and requirements for ethics committee and regulatory approvals. The presentation aims to educate about current standards and regulations for clinical research.