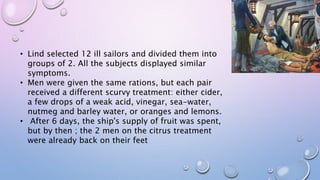
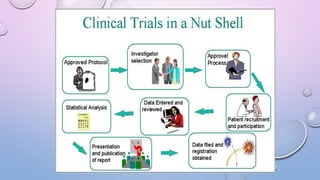
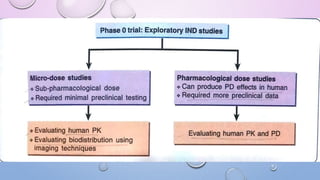
Clinical trials involve research studies that assign participants to medical interventions to evaluate their effects. There are various phases of clinical trials. Phase 0 involves micro-dosing to determine pharmacokinetics. Phase I tests safety on healthy volunteers. Phase II evaluates dosing and efficacy on patients. Phase III tests larger groups to confirm efficacy and monitor safety compared to standard treatments. Phase IV occurs after approval to further monitor long-term safety and efficacy. The document outlines the goals and timeline of each phase in the drug development and approval process.