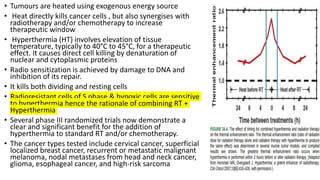
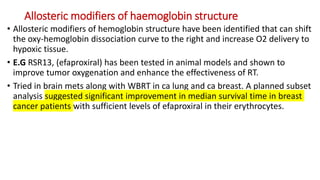
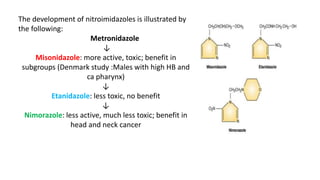
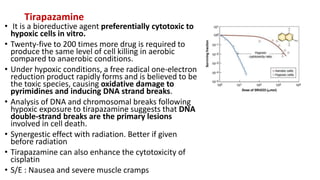
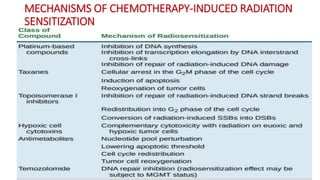
Radiosensitizers are agents that increase the lethal effects of radiation when administered with radiotherapy. They work through various mechanisms like increasing DNA damage, inhibiting repair, and modulating biological response. Common types include physical agents like hyperthermia, chemical agents like nitroimidazoles to target hypoxic cells, and biological modifiers like cetuximab. Effective radiosensitizers improve the therapeutic ratio by increasing tumor cell killing while minimizing harm to normal tissues. Combining radiosensitizers with radiotherapy can improve outcomes for many cancer types.




![Hyperthermia
• Hippocrates (470–377 BC), in one of his aphorisms,
states, “Those who cannot be cured by medicine can
be cured by surgery. Those who cannot be cured by
surgery can be cured by fire [hyperthermia]. Those
who cannot be cured by fire, they are indeed
incurable.”
• Heat kills cells in a predictable and repeatable way.
Figure shows a series of survival curves for cells
exposed for various periods of time to a range of
temperatures from 41.5° to 46.5° C.
• The cell survival curves for heat are similar in shape
to those obtained for x-rays (i.e., an initial shoulder
followed by an exponential region) except that the
time of exposure to the elevated temperature
replaces the absorbed dose of x-ray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiosensitizers-200601150625/85/Radiosensitizers-5-320.jpg)