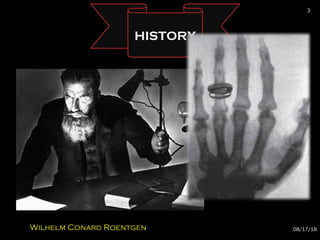
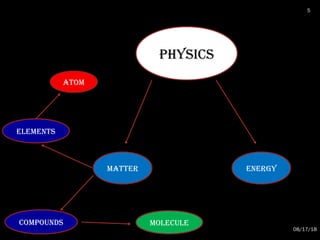
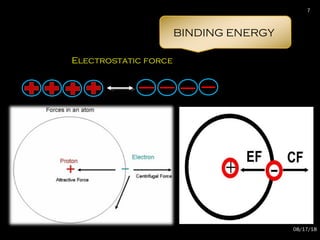
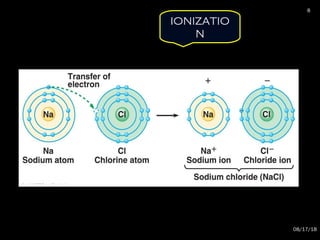
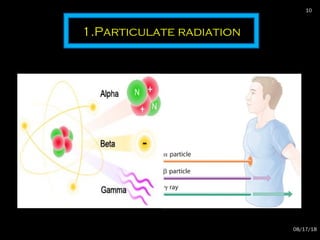
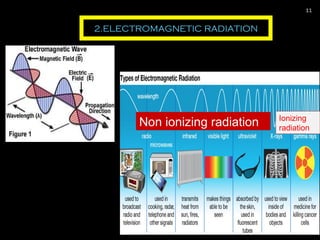
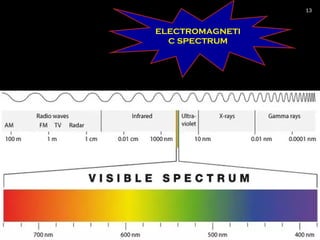
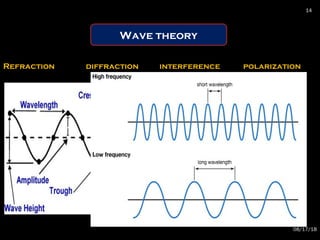
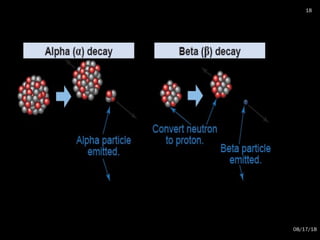
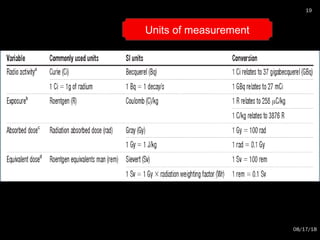
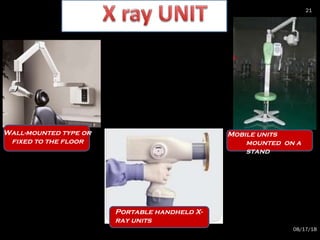
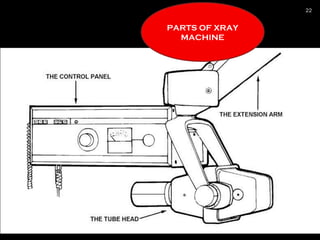
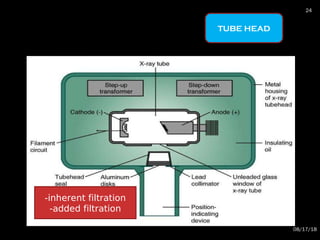
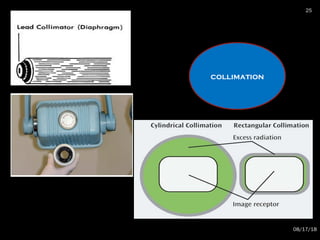
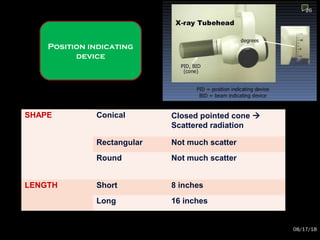
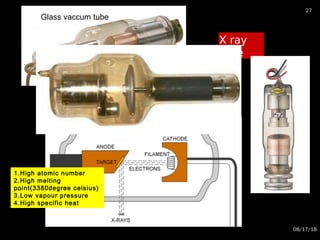
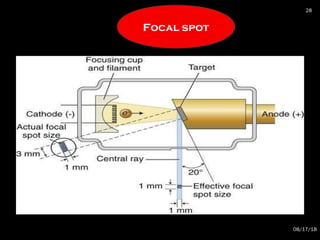
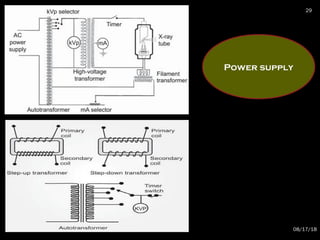
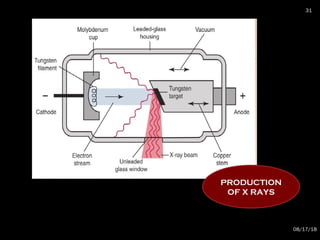
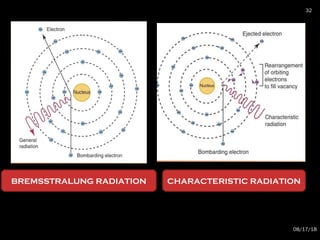
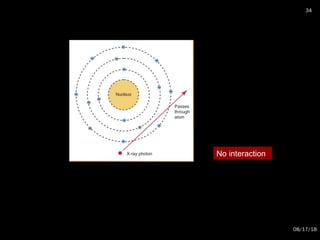
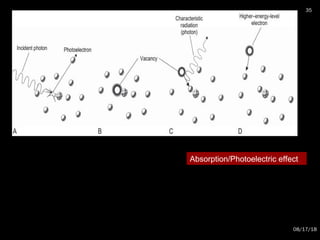
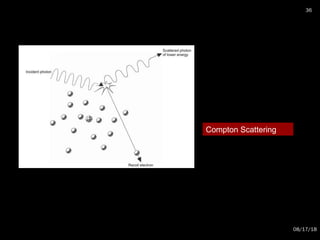
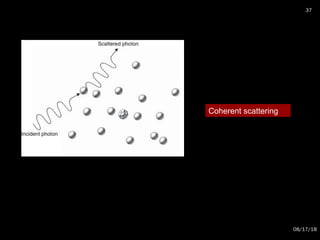
The document provides an overview of radiation physics, covering topics such as the history of x-rays, the basic model of an atom, types of radiation, radioactivity, dental x-ray units, and their interactions with matter. It discusses both natural and artificial radioactivity, as well as the components and operation of x-ray machines. References for further reading on dental and oral radiology are also included.