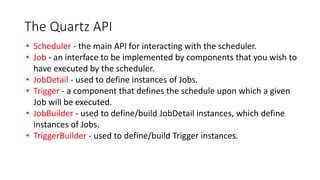
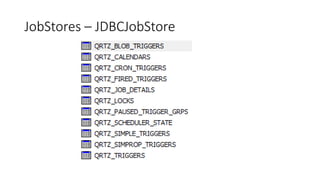
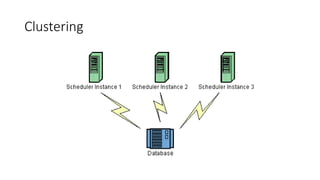
Quartz is an open source job scheduling library that can be integrated with Java applications. It allows scheduling of jobs to run at specific times, intervals, or based on a cron expression. Jobs are defined as Java classes and can be persisted in memory, a database like PostgreSQL, or with Terracotta for clustering. Triggers determine when and how often jobs are executed. Quartz provides listeners and plugins to monitor and customize job behavior.