Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics, like superposition and entanglement, to perform computations, potentially solving problems far beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
Key Concepts:
Qubits:
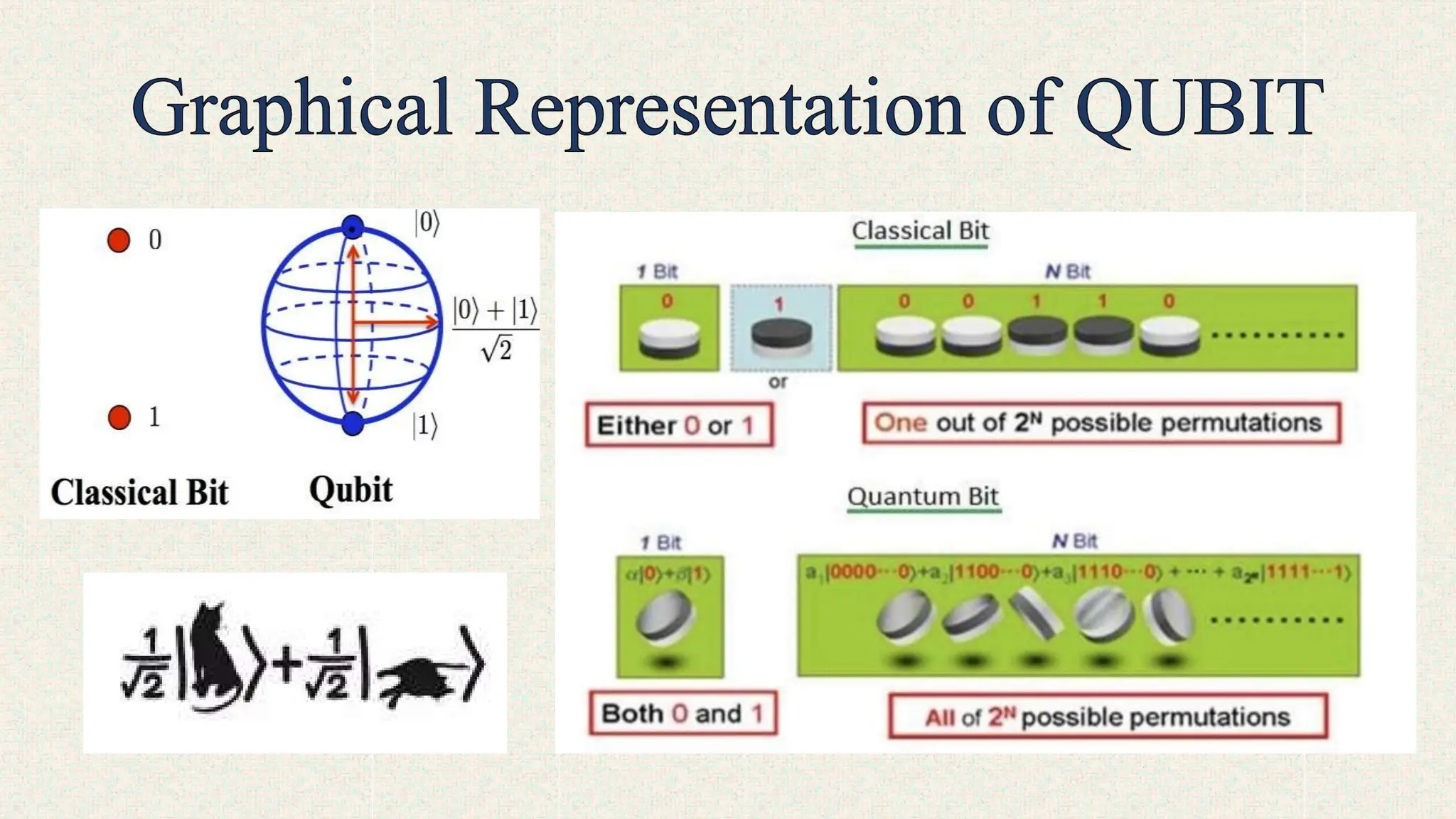
Unlike classical bits that represent 0 or 1, qubits can exist in a "superposition" of both states simultaneously, allowing for parallel processing and the potential for faster calculations.
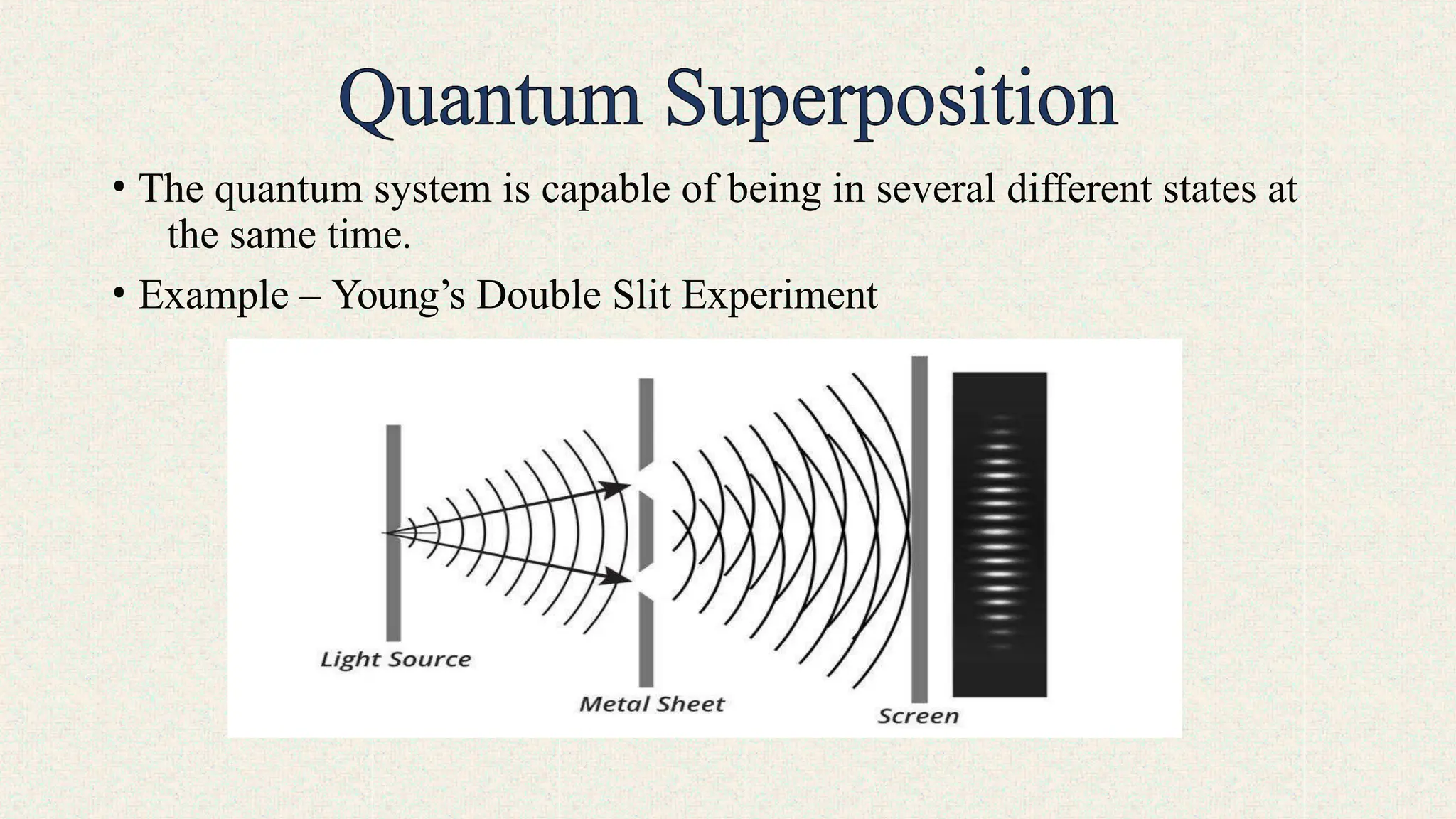
Superposition:
A qubit can exist in a combination of both 0 and 1 states until measured, enabling quantum computers to explore multiple possibilities at once.
Entanglement:
The states of two or more qubits can become linked, meaning that measuring one qubit instantly influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them.
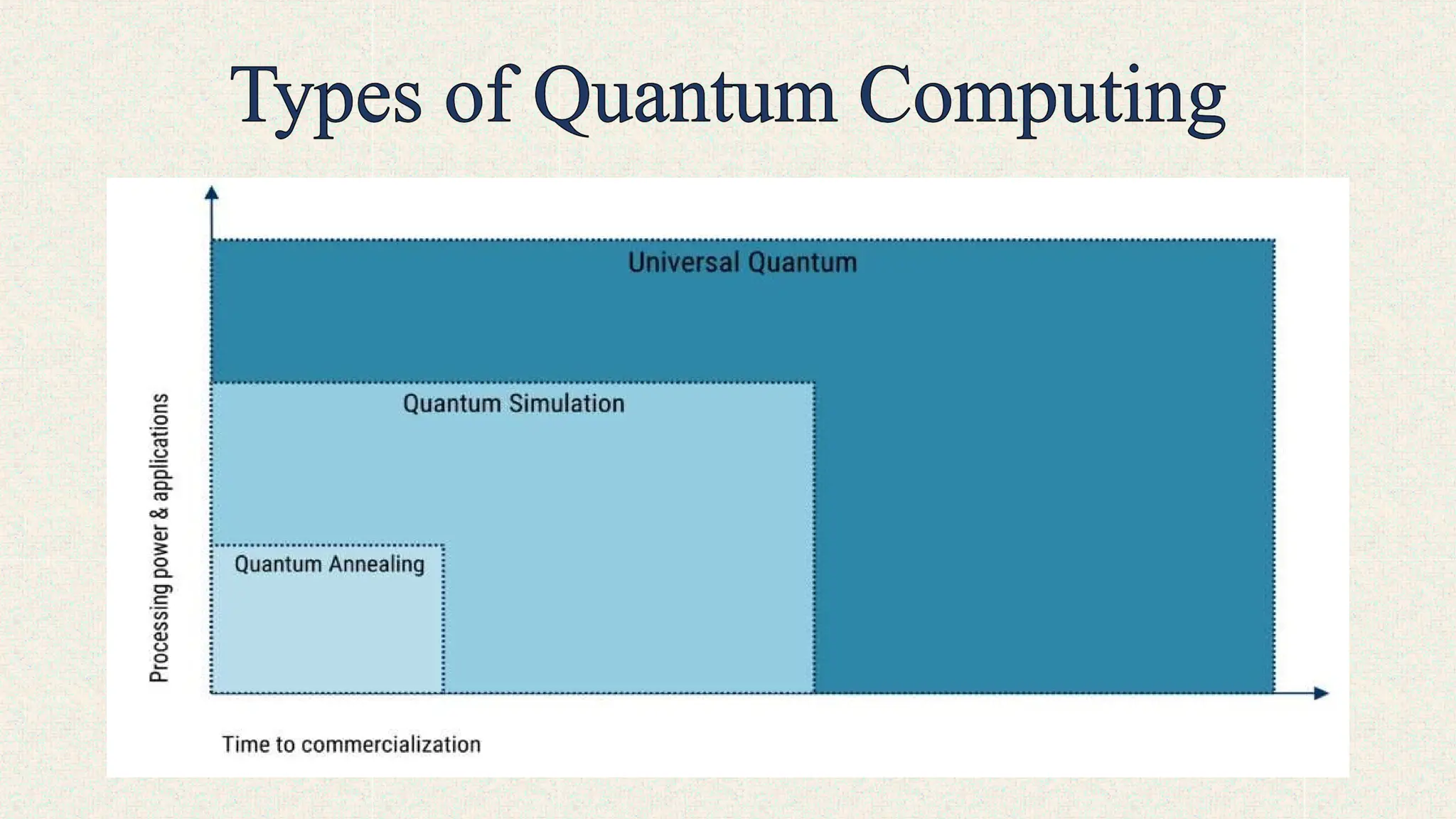
Quantum Algorithms:
These algorithms are designed to take advantage of quantum phenomena to solve specific problems more efficiently than classical algorithms.
Quantum Hardware:
Quantum computers are built using specialized hardware, such as superconducting circuits or trapped ions, to create and manipulate qubits.
Potential Applications:
Drug Discovery:
Quantum computers could simulate molecular interactions to accelerate the development of new drugs and therapies.
Materials Science:
They could help design new materials with specific properties, leading to advancements in areas like energy storage and electronics.
Cryptography:
Quantum computers could potentially break current encryption methods, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant cryptography.
Financial Modeling:
Quantum algorithms could be used to optimize investment portfolios and detect fraud.
Artificial Intelligence:
Quantum machine learning could lead to breakthroughs in areas like pattern recognition and natural language processing.
Challenges:
Scalability:
Building and maintaining stable quantum computers with a large number of qubits is a significant engineering challenge.
Error Correction:
Quantum systems are highly sensitive to noise and errors, requiring sophisticated error correction techniques.
Coherence:
Maintaining the quantum state of qubits for long enough to perform computations is crucial, but qubits are easily affected by their environment.
Quantum computing - Wikipedia
The basic unit of information in quantum computing, the qubit (or "quantum bit"), serves the same function as the bit in classical...
Wikipedia
What Is Quantum Computing? - IBM
5 Aug 2024 — Ian Smalley. Senior Editorial Strategist. What is quantum computing? Quantum computing is an emergent field of cutting-e...
IBM
What is Quantum Computing? How it Works and Examples
Organizations today use traditional computers to encrypt their data. They use large, complex prime numbers to encrypt data, which ...
TechTarget
Show all
Show more
हिन्दी में
In English
Quantum computing is a multidisciplinary field comprising aspects of computer science, physics, and mathematics that utilizes quantum mechanics to