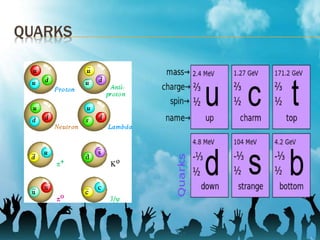
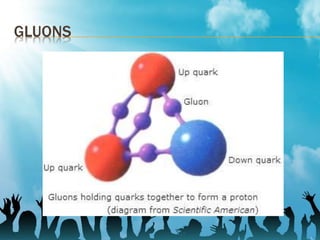
Quantum electrodynamics (QED) describes the interaction between matter and light. It was the first theory to show the relationship between quantum mechanics and special relativity. QED was developed in the 1920s-1970s through the work of scientists like Dirac, Fermi, Feynman, Politzer, Coleman, Gross, and Wilczek. Feynman diagrams provide a visual representation of interactions like photons being emitted or absorbed by electrons. QED explains phenomena like annihilation and pair production and is the basis for other theories like quantum chromodynamics.