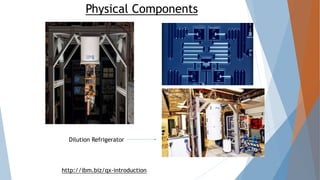
Quantum computing utilizes the unique properties of subatomic particles to perform faster and more energy-efficient operations than classical computers. It has a rich history marked by significant milestones including the development of key algorithms and the construction of working quantum computers. While it offers advantages in several fields, including security and medicine, it also faces challenges such as instability and incomplete technology development.