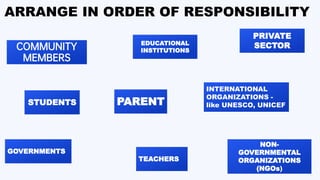
The document discusses the importance of quality education as a means to combat economic hardship, emphasizing its role in enhancing employability, promoting entrepreneurship, and breaking the cycle of poverty. It outlines the key components and characteristics of quality education, including accessibility, equity, qualified teachers, and relevant curriculum, while also highlighting the roles of various stakeholders in delivering effective education. Furthermore, the document details the negative effects of poor education and the benefits that quality education provides to individuals, communities, and governments.