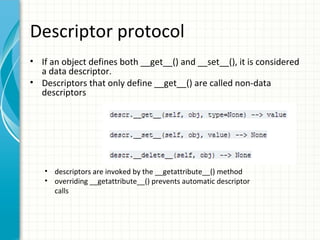
This document provides an overview of exception handling, generators, decorators, and descriptors in Python. It discusses how to handle exceptions with try-except blocks and raise user-defined exceptions. Generators are introduced as a way to create iterators using yield. Decorators allow functions to be passed as arguments to wrapper functions, modifying their behavior. Descriptors are object attributes that define binding behavior through __get__, __set__, and __delete__ methods, and can be used to implement properties.











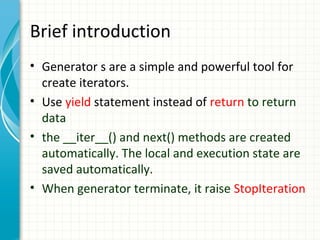
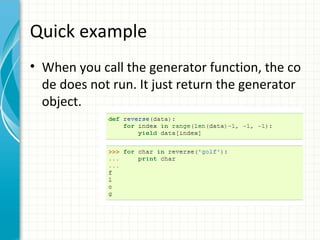
![The difference between generator
and sequence type
>>> mylist = [x*x for x in range(3)]
>>> mygenerator = (x*x for x in range(3))
•Both mylist and mygenerator are iterable
•But you can only read
generator once.
•Generator do not store all
the values in memory, they
generate the values on the
fly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonadvanced1-131221115011-phpapp01/85/Python-advanced-1-handle-error-generator-decorator-and-decriptor-14-320.jpg)