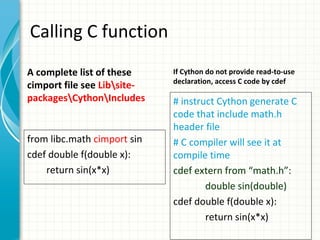
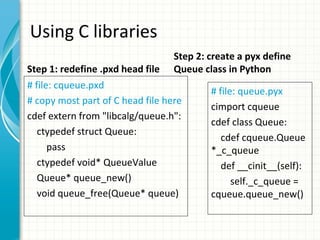
Cython allows Python code to be compiled to C/C++ extensions for improved performance. It is a superset of Python that adds static type declarations for variables and functions. This allows Cython code to be compiled to efficient C/C++ code while retaining the syntax and functionality of Python. The document provides an overview of Cython and examples demonstrating how to install Cython, write basic Cython modules, optimize Python code with static types, call C functions from Cython, and interface with C/C++ libraries.



![First example: Building a Cython
module “hello”
hello.pyx
def say_hello_to(name):
print (“Hello %s!” %
name)
setup.py
from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Distutils import build_ext
ext_modules = [Extension("hello",
["hello.pyx"])]
Run command line build the module
$ python setup.py build_ext --inplace
--compiler=mingw32 --inplace
# How to run the function:
>>> from hello import say_hello_to
>>> say_hello_to(“John”)
Hello John
setup(
name = 'Hello world app',
cmdclass = {'build_ext': build_ext},
ext_modules = ext_modules
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocython-131221115551-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-cython-4-320.jpg)


![Using C libraries - cont
or step 3.2: include the lib in
step 3.1: change the setup.py
the option
$ CFLAGS="change
I/usr/local/otherdir/calg/include"
ext_modules =
[Extension("queue
LDFLAGS="", ["queue.pyx"])]
L/usr/local/otherdir/calg/lib" python
setup.py build_ext -i
to
ext_modules =
[ Extension("queu
e", ["queue.pyx"],
libraries=["calg"]) ]
calg lib see Simon Howard, C Algorithms library,
http://c-algorithms.sourceforge.net/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocython-131221115551-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-cython-9-320.jpg)
![Using C++ in Cython
• Brief overview of C++ support in Cython(Cython
v0.13)
– C++ objects can now be dynamically allocated
with new and del keywords.
– C++ objects can be stack-allocated.
– C++ classes can be declared with the new
keyword cppclass.
– Templated classes are supported.
– Overloaded functions are supported.
– Overloading of C++ operators (such as operator+,
operator[],...) is supported.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocython-131221115551-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-cython-10-320.jpg)
