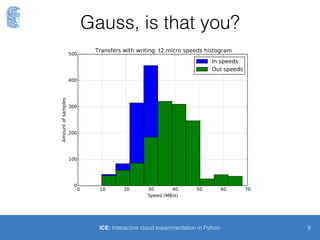
The document discusses the Interactive Cloud Experimentation (ICE) project developed by George Lestaris as part of his bachelor thesis at the University of Athens. It focuses on measuring and predicting intra-cluster network performance within the AWS cloud environment through automated experimentation and classification of virtual machine pairs. The ICE tool allows for easy orchestration and execution of Python scripts across multiple VM instances, facilitating the analysis and validation of network performance data.







![Creating VMs
18iCE: Interactive cloud experimentation in Python
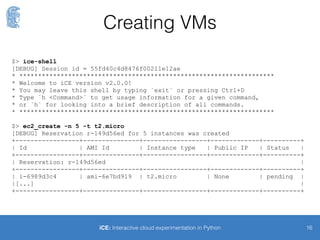
$> ice-shell
[DEBUG] Session id = 55fd40c4d8476f00211e12ae
* ********************************************************************
* Welcome to iCE version v2.0.0!
* You may leave this shell by typing `exit` or pressing Ctrl+D
* Type `h <Command>` to get usage information for a given command,
* or `h` for looking into a brief description of all commands.
* ********************************************************************
$> ec2_create -n 5 -t t2.micro
[DEBUG] Reservation r-149d56ed for 5 instances was created
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| Id | AMI Id | Instance type | Public IP | Status |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| Reservation: r-149d56ed |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| i-6989d3c4 | ami-6e7bd919 | t2.micro | None | pending |
|[...] |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
Experimentation
session](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ice-pycon-uk-150919141725-lva1-app6891/85/PyCon-UK-iCE-Interactive-cloud-experimentation-18-320.jpg)
![Waiting for VMs to come up
and register
19iCE: Interactive cloud experimentation in Python
$> inst_wait -n 5
[DEBUG] 0 instances found, sleeping for 5 seconds...
[...]
[INFO] Instances are ready!
$> inst_ls
[INFO] Found 5 instances
+--------------------------+--------------+----------------------------------+
| Id | Public IP | Cloud Id |
+--------------------------+--------------+----------------------------------+
| 55fd45b2d8476f00211e12b5 | 54.77.34.67 | eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com |
| [...] |
+--------------------------+--------------+----------------------------------+
$> ec2_ls
[DEBUG] Reservation r-149d56ed for 5 instances was created
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| Id | AMI Id | Instance type | Public IP | Status |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| Reservation: r-149d56ed |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+
| i-298cd684 | ami-6e7bd919 | t2.micro | 54.76.34.228| running |
| [...] |
+-----------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+----------+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ice-pycon-uk-150919141725-lva1-app6891/85/PyCon-UK-iCE-Interactive-cloud-experimentation-19-320.jpg)
![A simple experiment (1/2)
20iCE: Interactive cloud experimentation in Python
import ice # iCE package
from fabric import api as fab # Fabric API
@ice.Runner
def run(hosts):
"""A sample iCE runner. It gets the hostnames of all instances and
prints them out.
:param dict hosts: Dictionary of ice.entities.Instances objects.
"""
# Get hostnames of all instances, through fab.execute
# First argument: Python function
# Second argument: List of hosts
# It returns a dictionary with the task result as value.
hostnames = fab.execute(get_hostname, hosts)
# Prints
for key in hostnames:
print hostnames[key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ice-pycon-uk-150919141725-lva1-app6891/85/PyCon-UK-iCE-Interactive-cloud-experimentation-20-320.jpg)

![Loading and running an experiment
22iCE: Interactive cloud experimentation in Python
$> exp_load ./experiments/simple.py
[DEBUG] About to load module 'simple' from path '/Users/george/di_dev/Thesis/iCE/
experiments'
[INFO] Module `./experiments/simple.py` is successfully loaded!
$> exp_ls simple
> Module `simple`:
Runners:
* run: A sample iCE runner. It gets the hostnames of all instances and
prints them out. [...]
Tasks:
* get_hostname: A simple iCE task. It returns the FQDN hostname of the remote
instance. […]
$> exp_run simple
[ec2-user@ec2-54-77-17-214.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com] run: hostname -f
[ec2-user@ec2-54-77-17-214.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com] out: ip-172-31-6-35.eu-
west-1.compute.internal
[...]
ip-172-31-6-35.eu-west-1.compute.internal
ip-172-31-6-36.eu-west-1.compute.internal
[...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ice-pycon-uk-150919141725-lva1-app6891/85/PyCon-UK-iCE-Interactive-cloud-experimentation-22-320.jpg)
