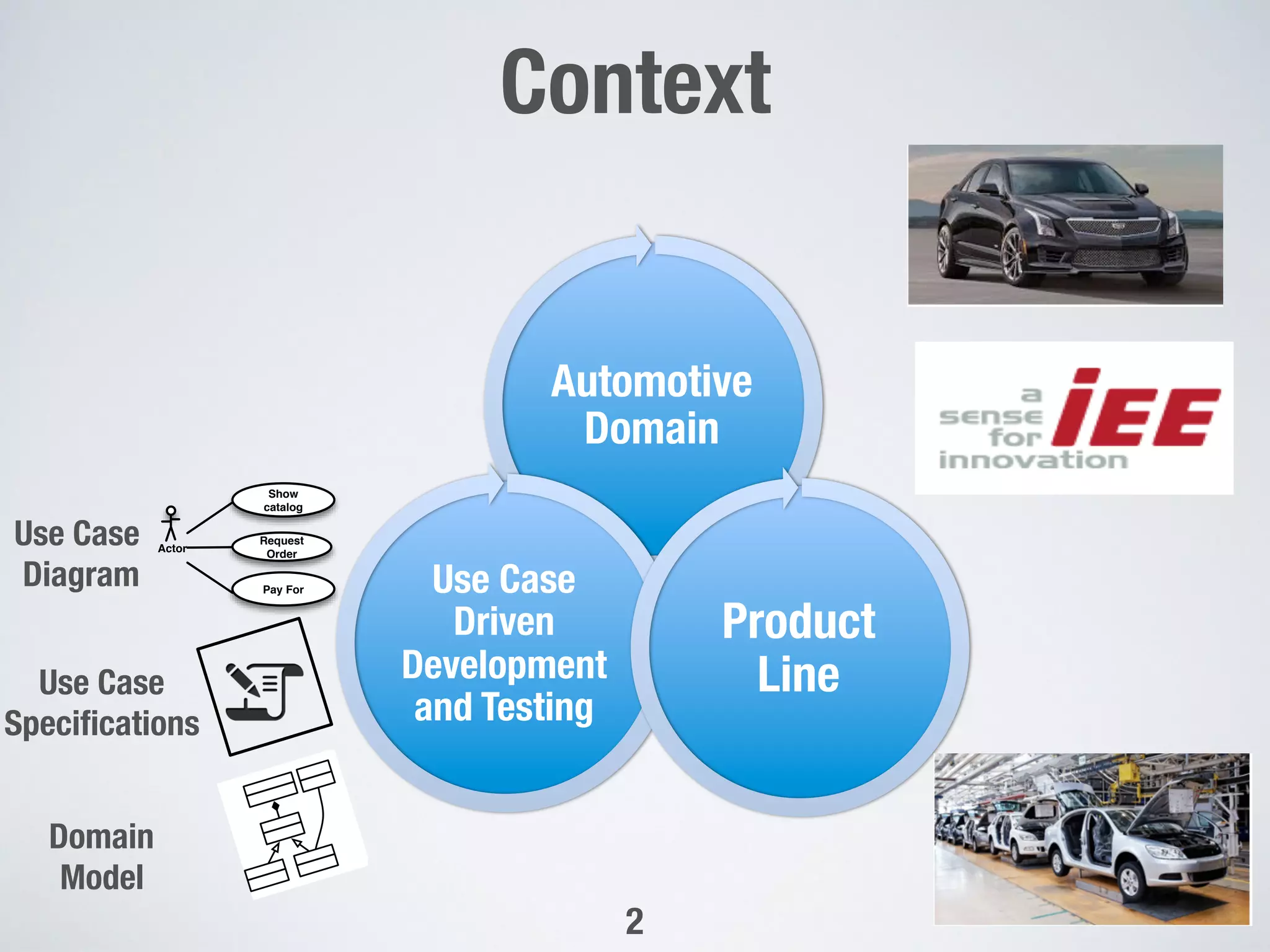
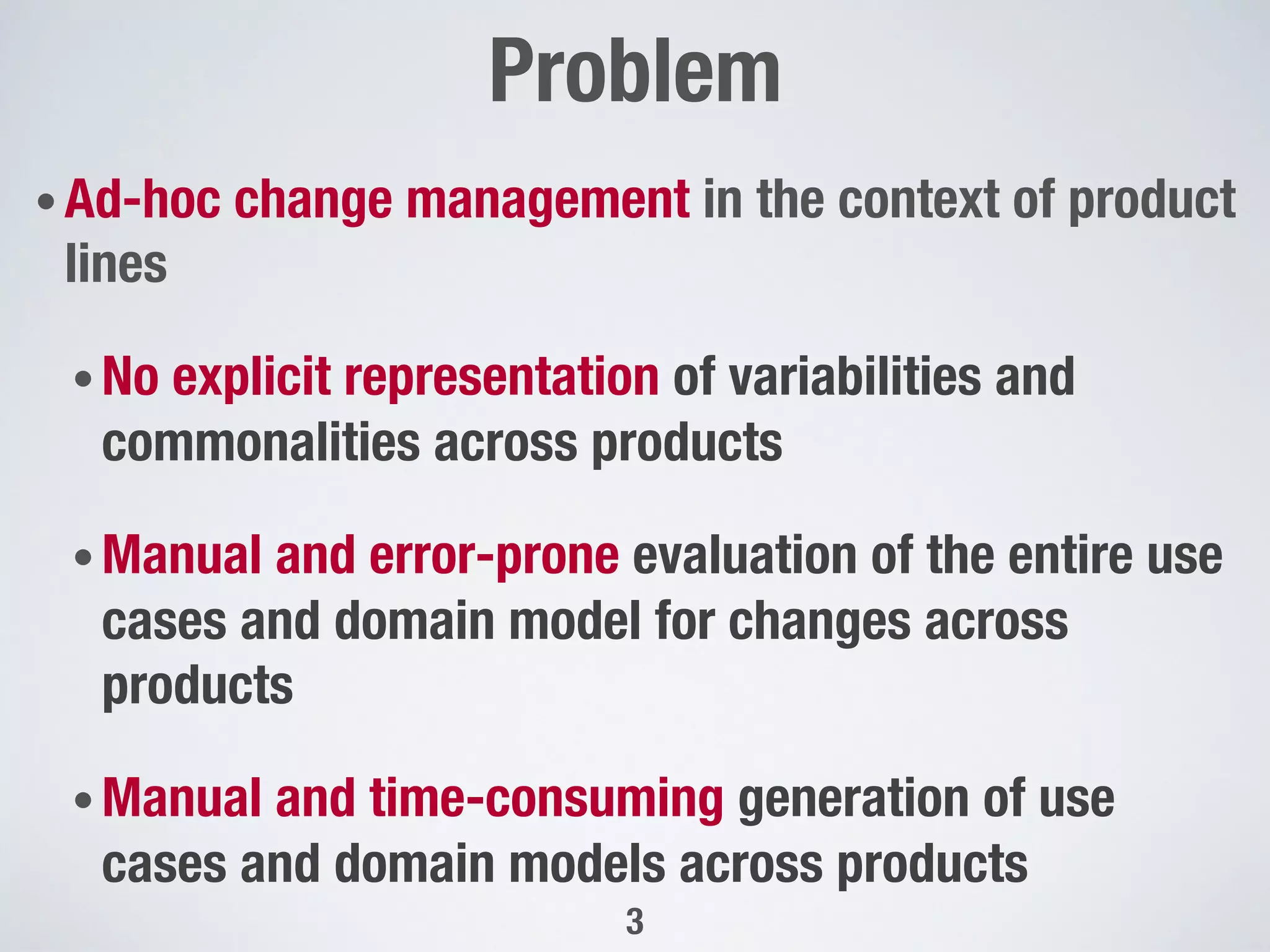
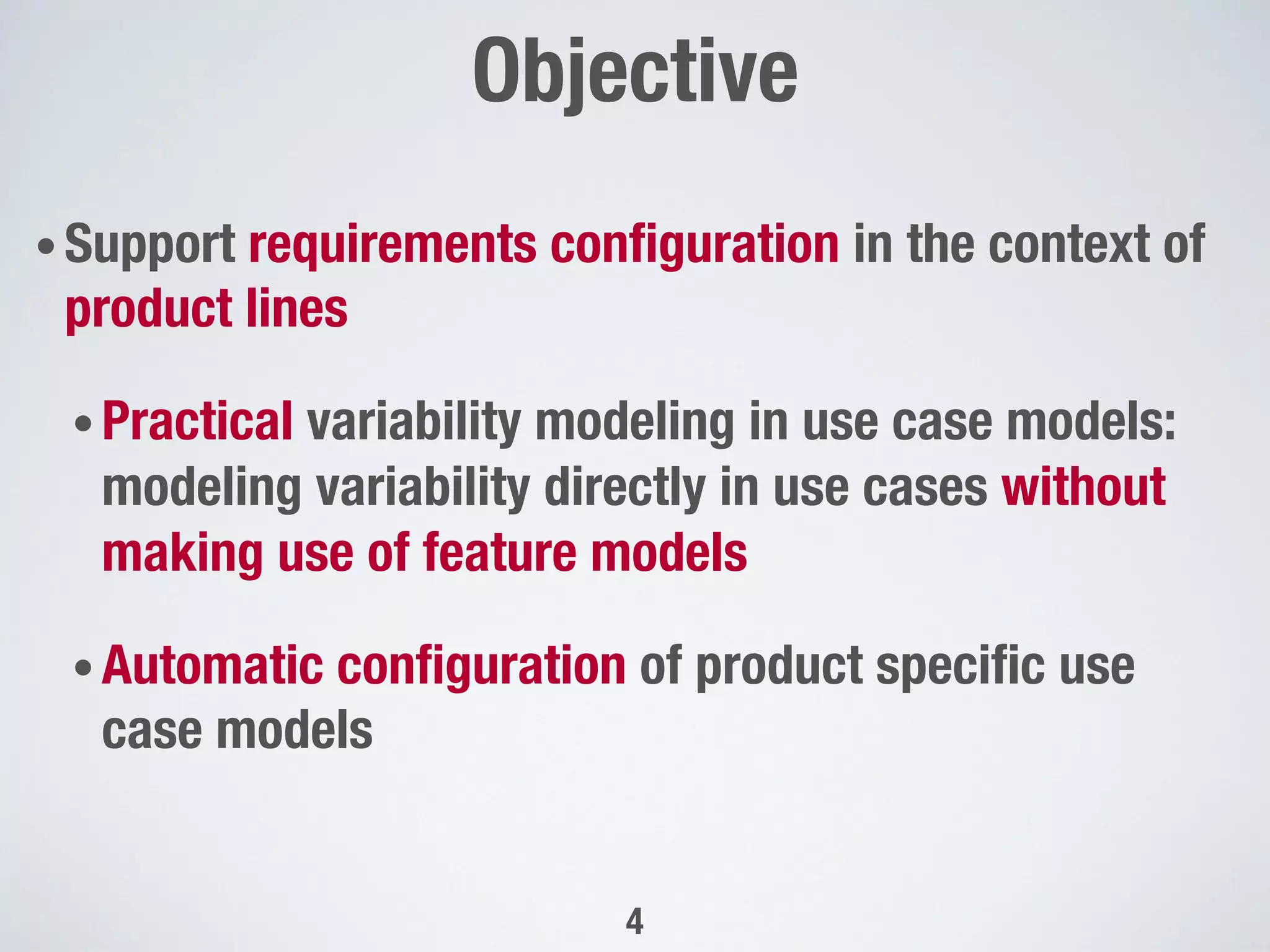
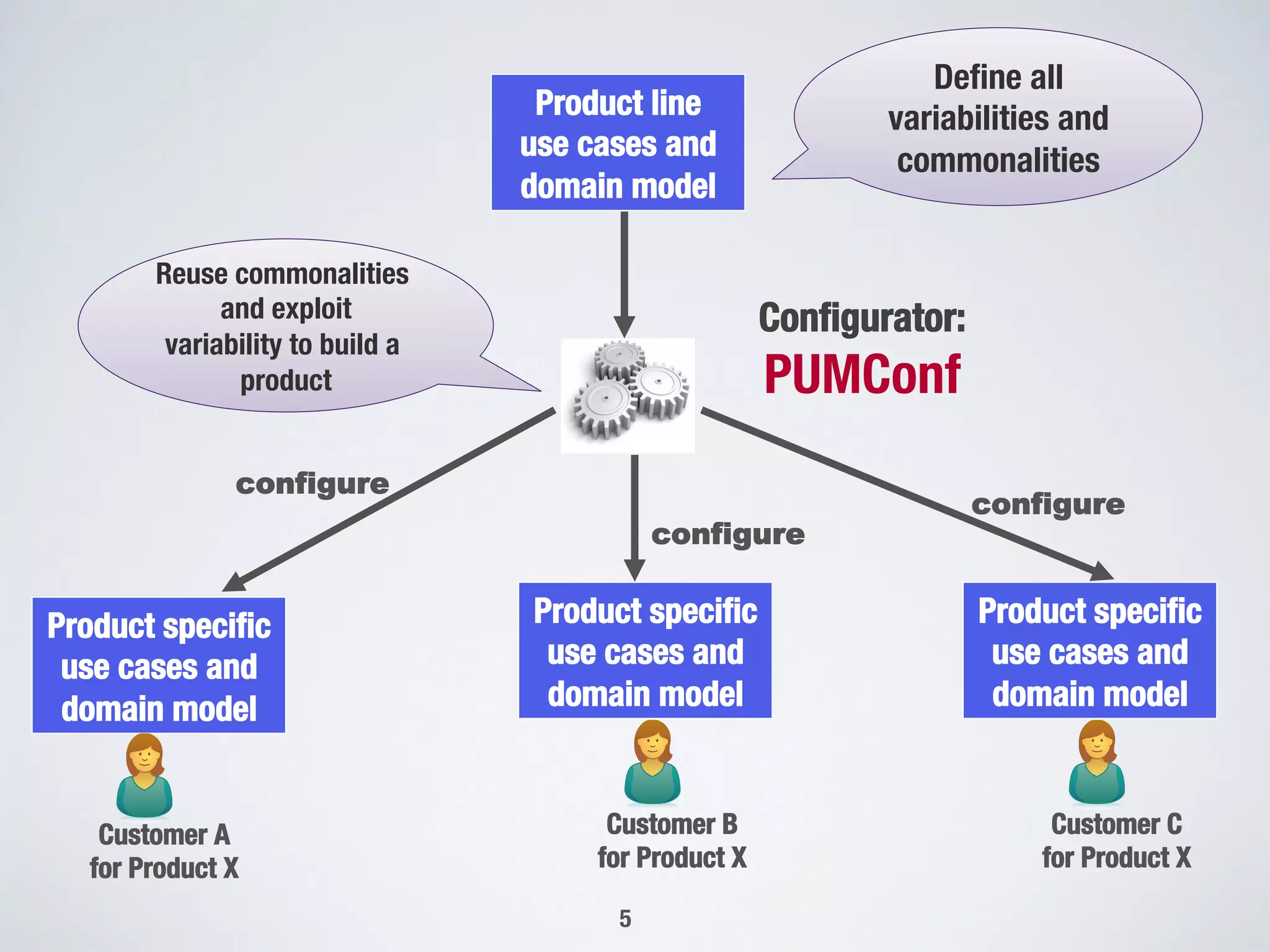
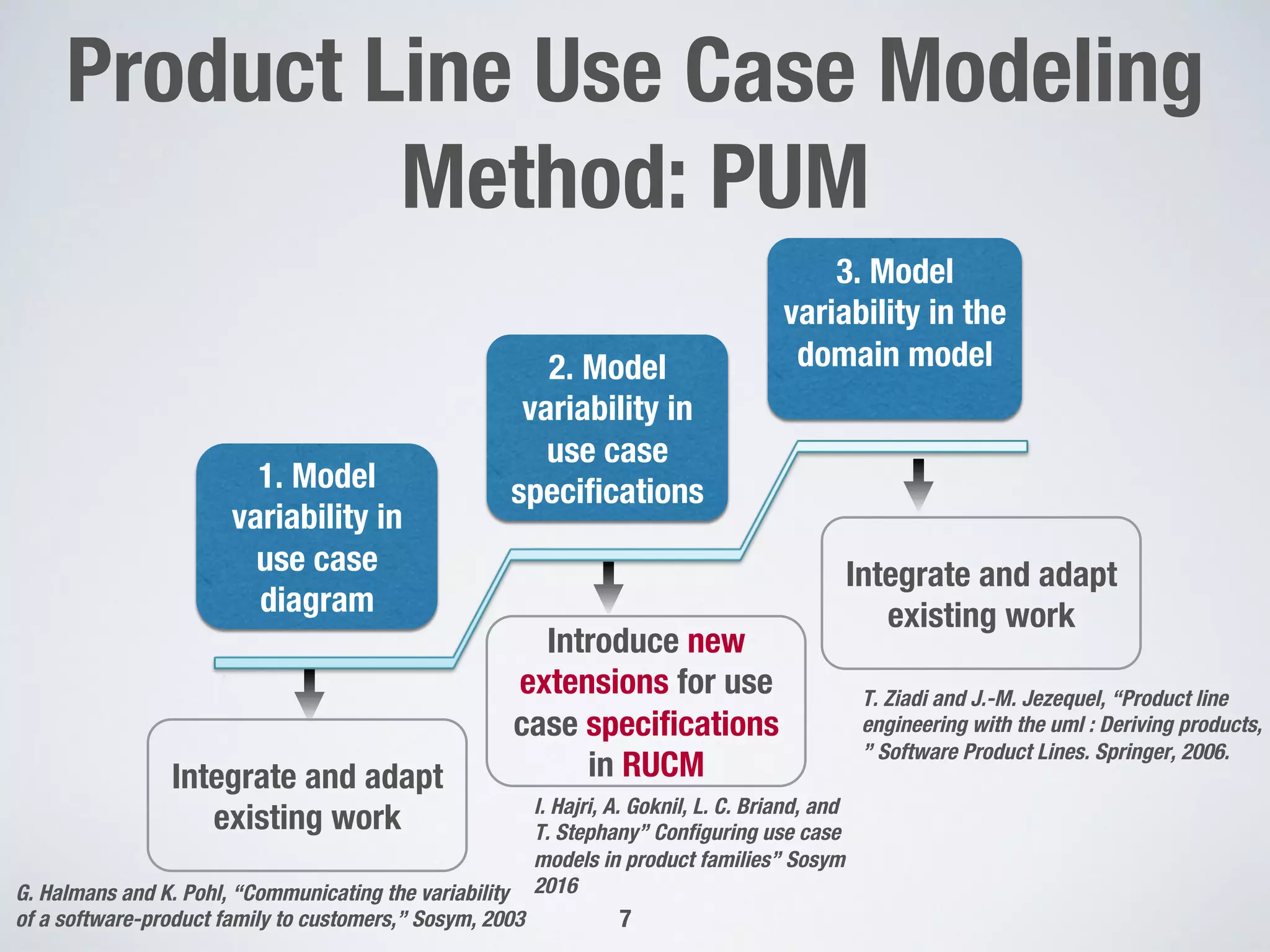
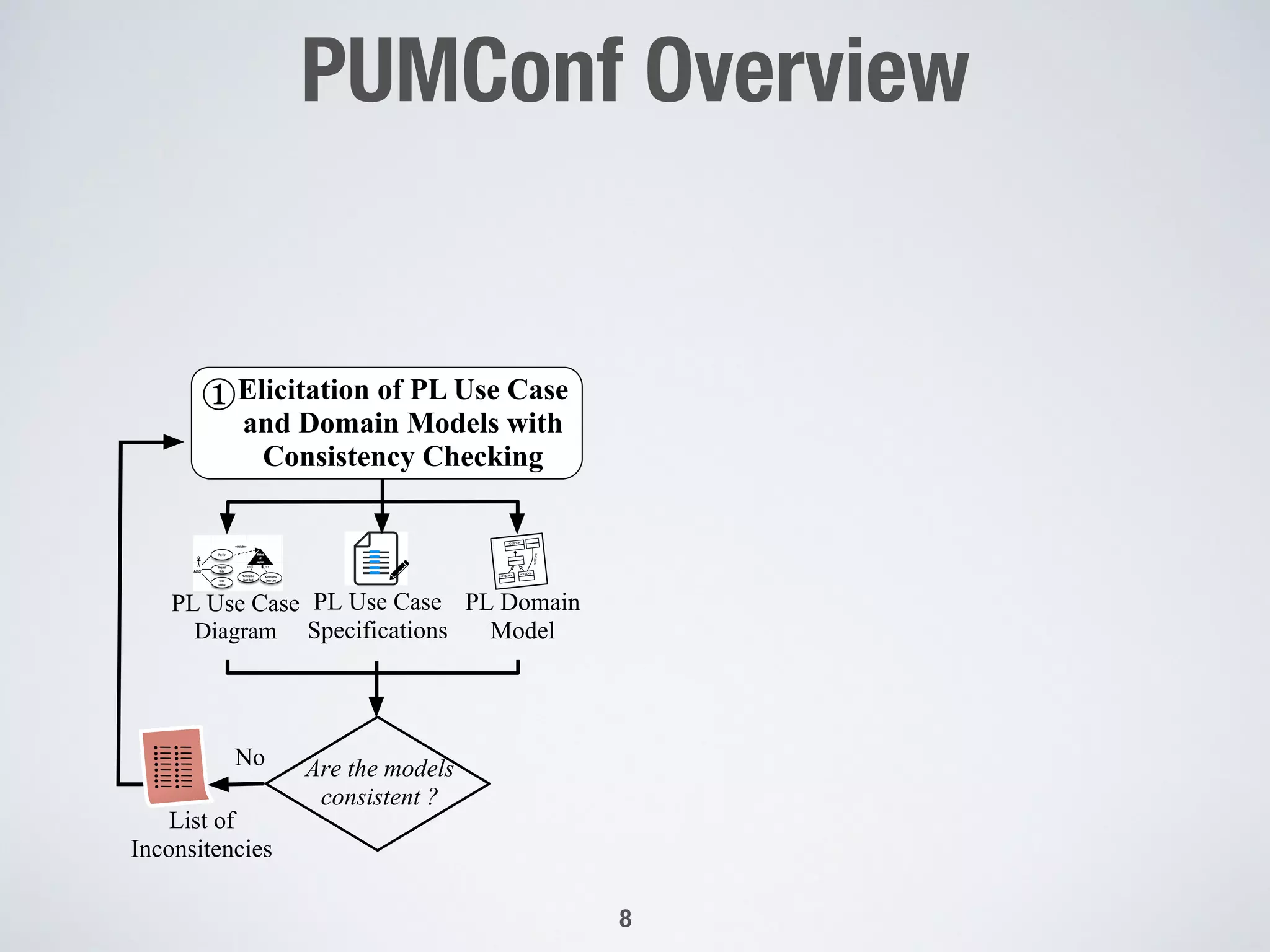
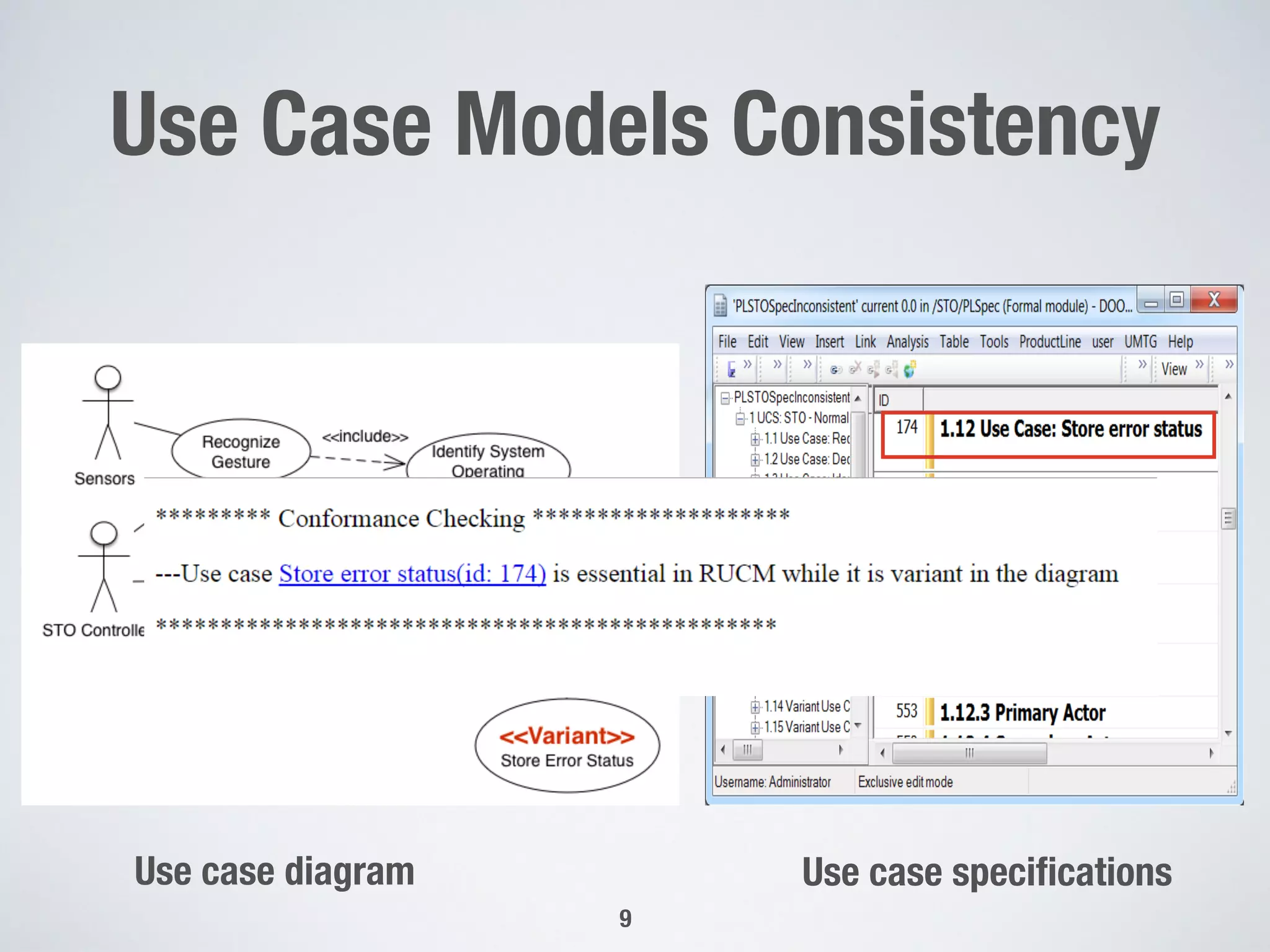
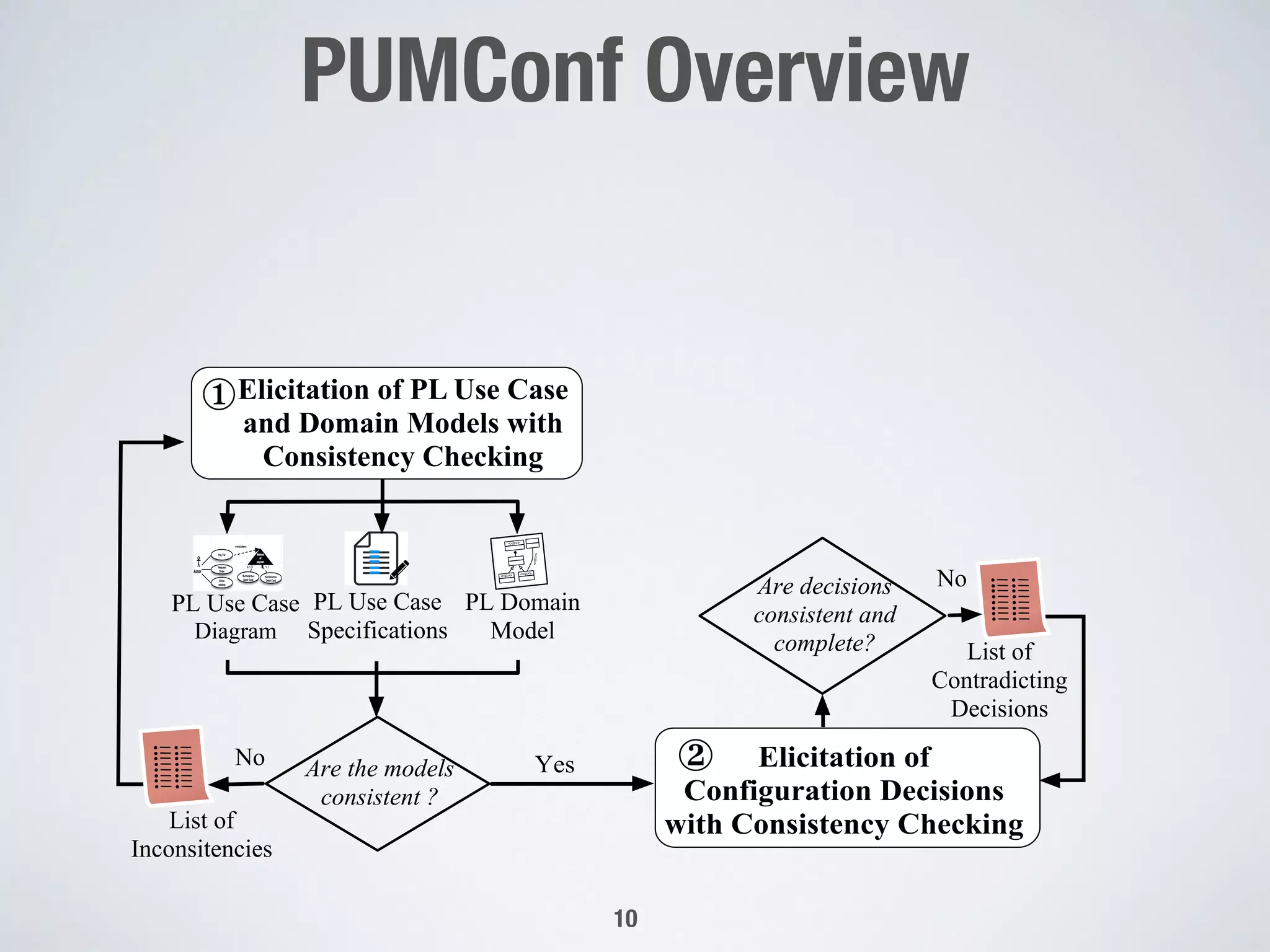
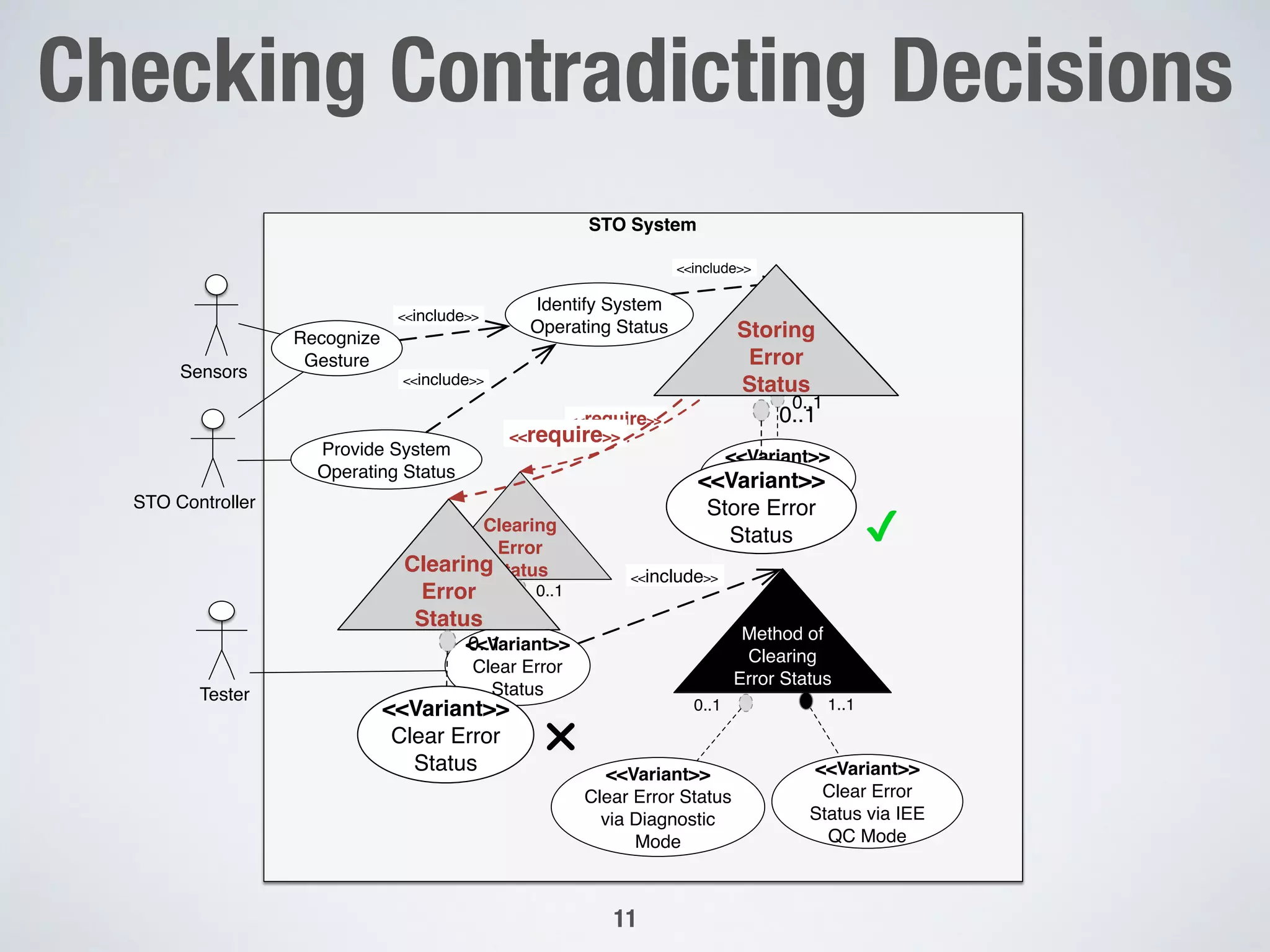
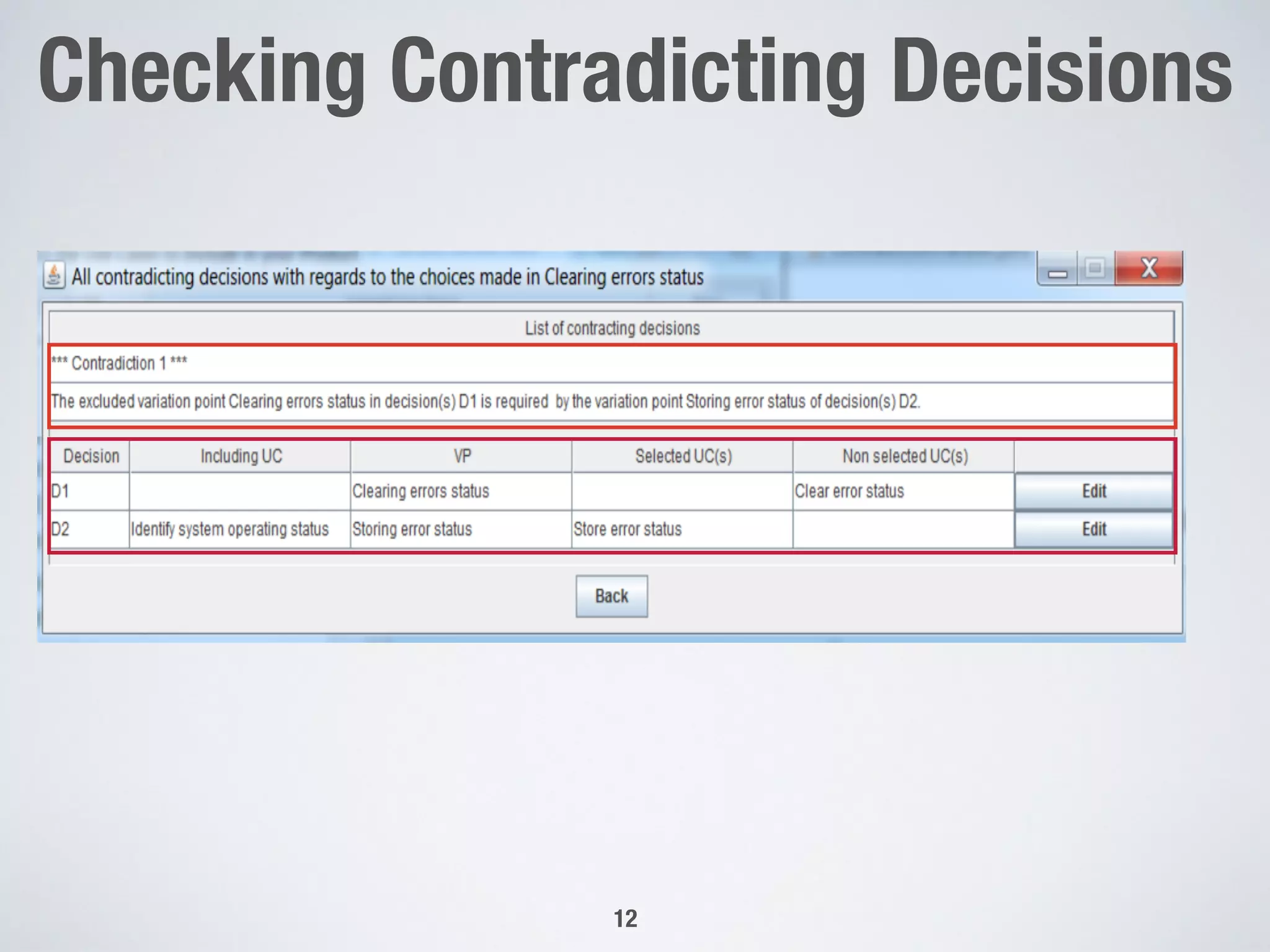
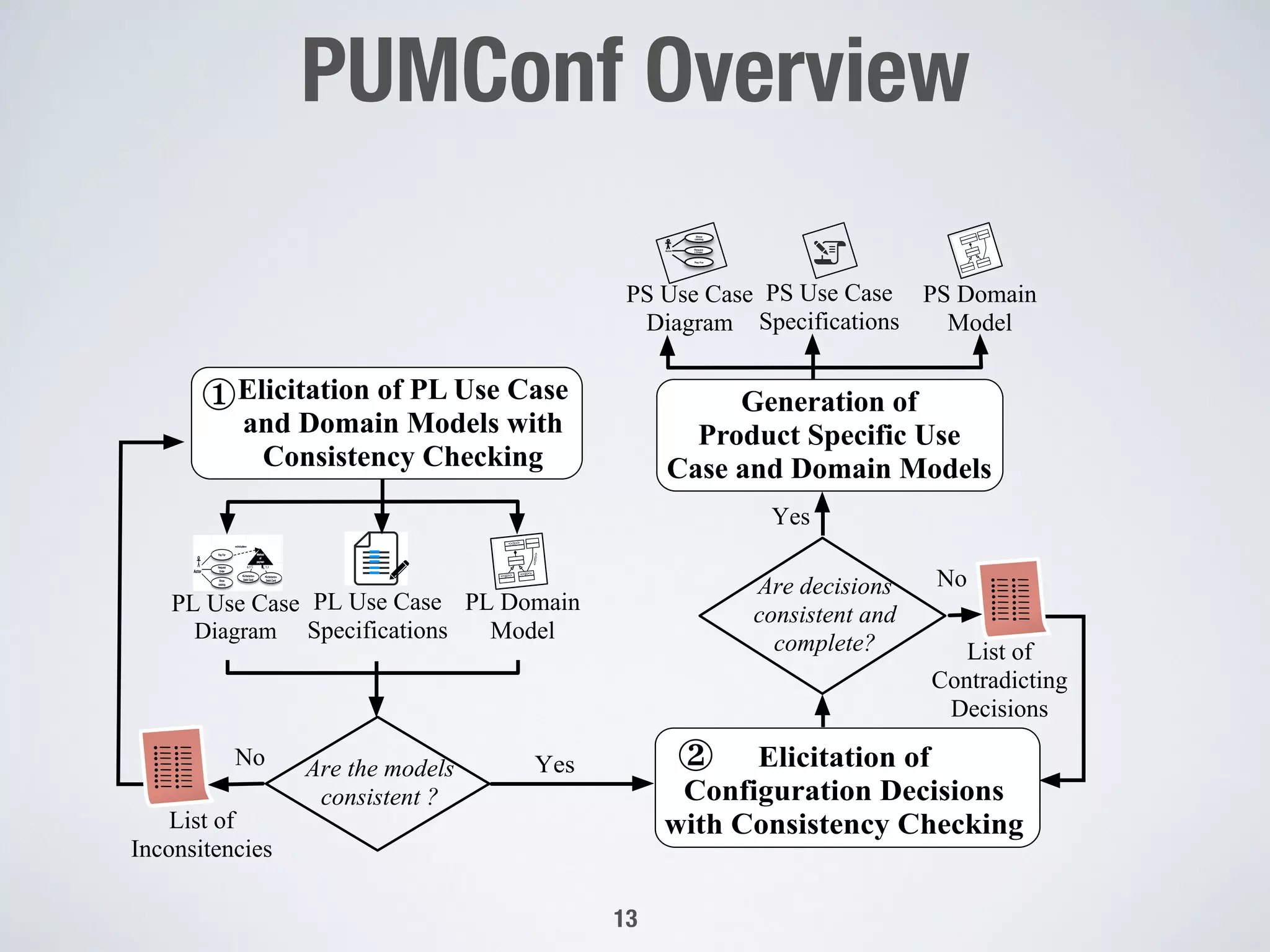
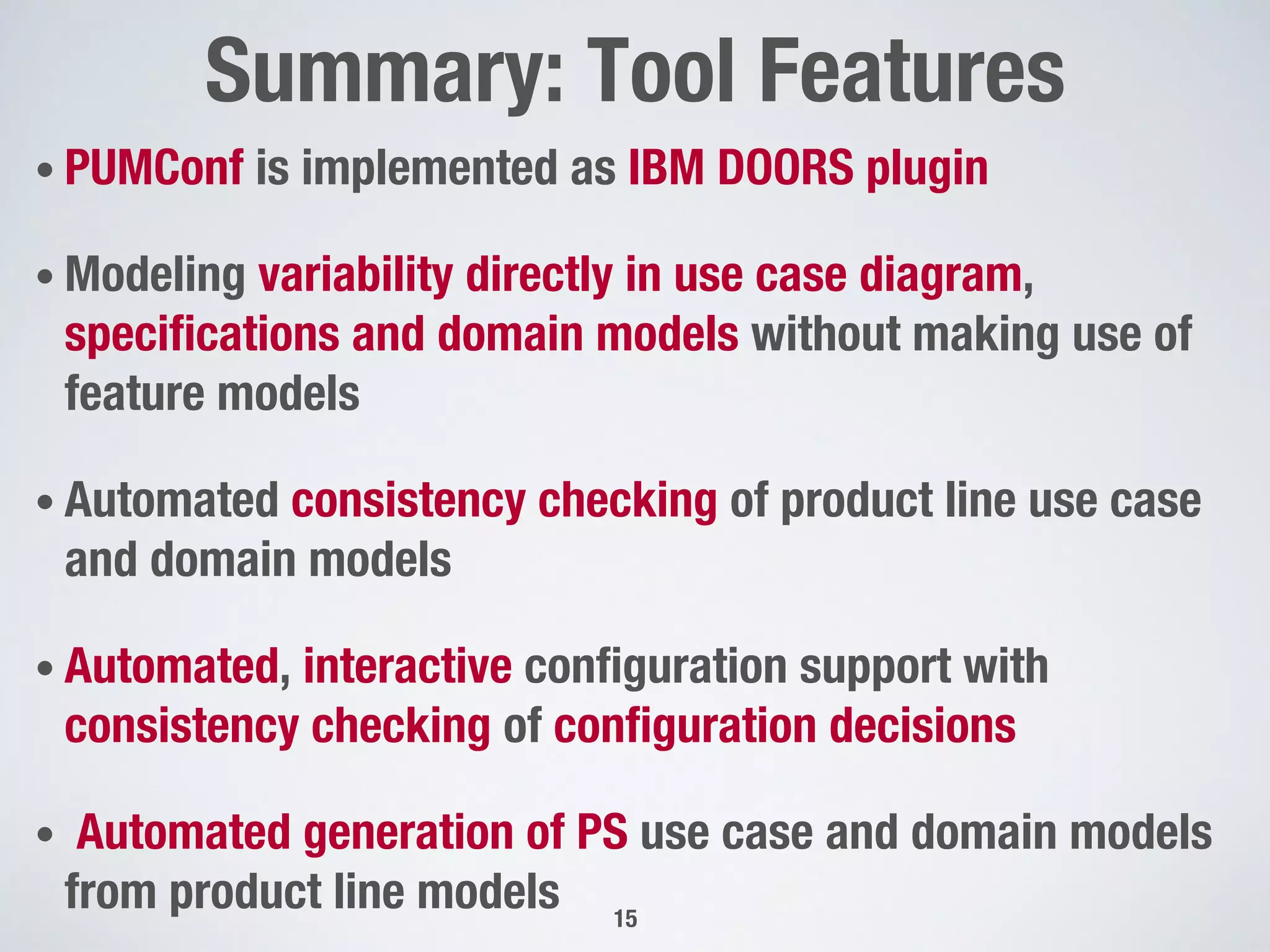
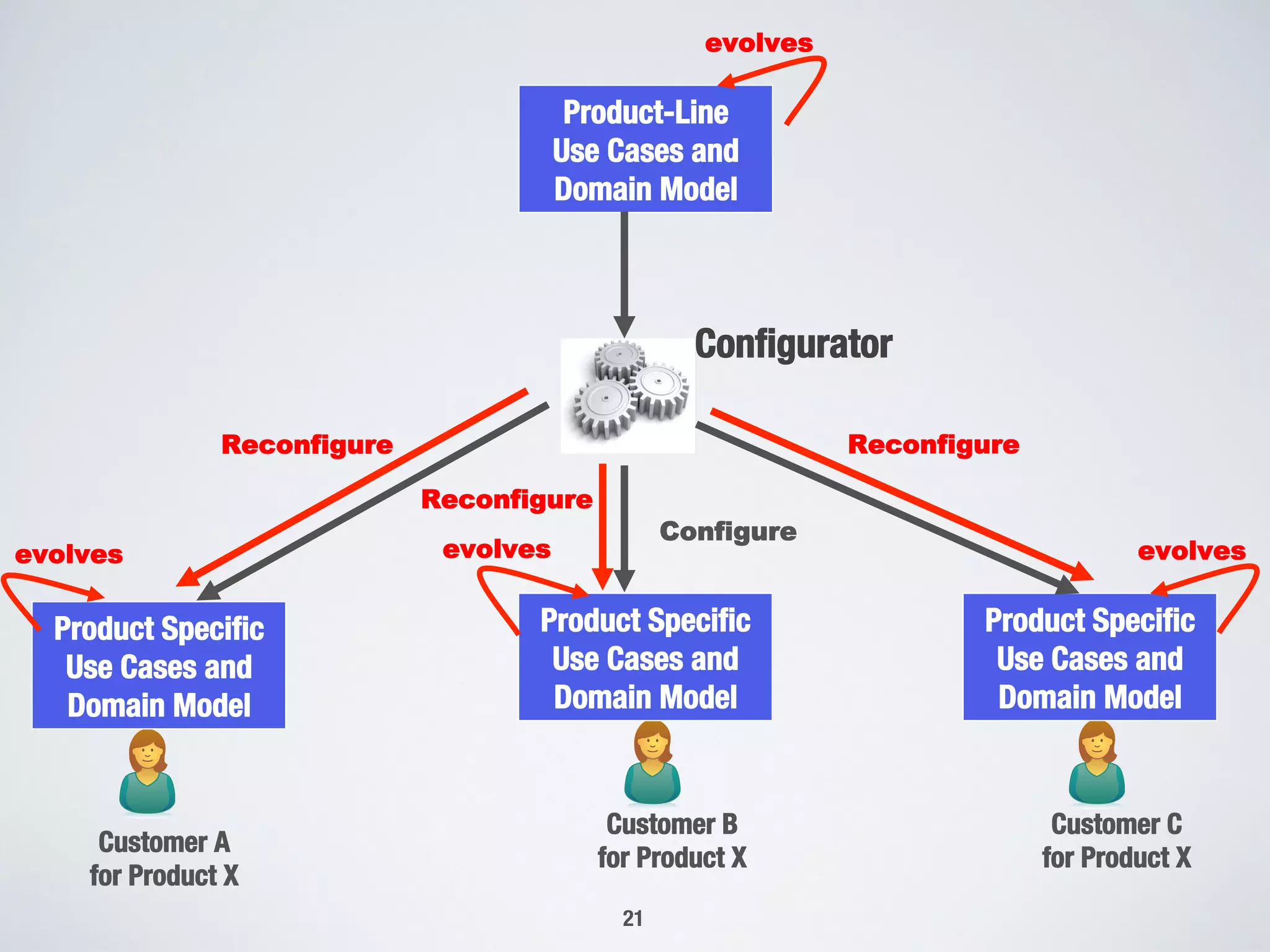
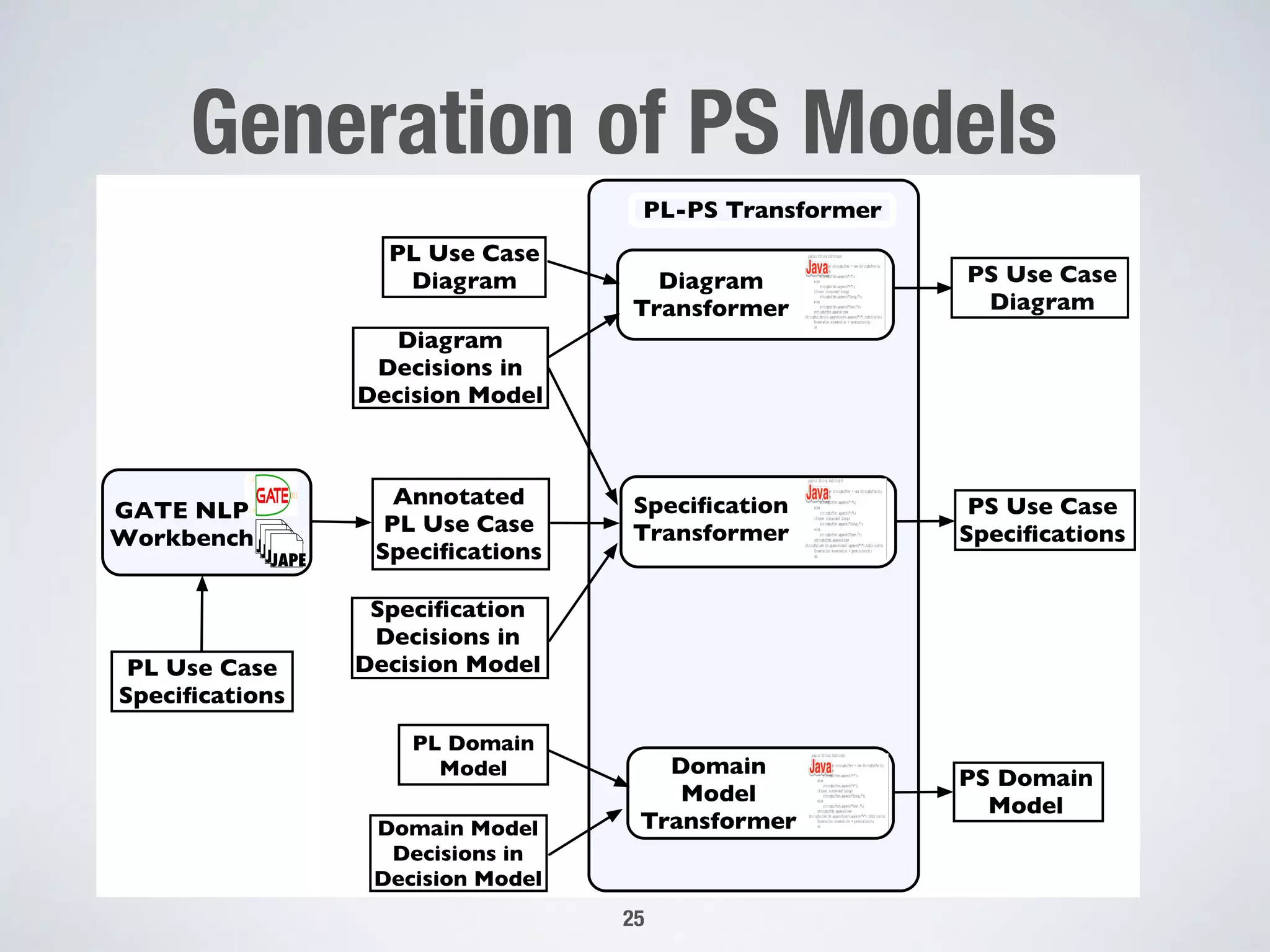
The document describes PUMConf, a tool that helps configure product-specific use case and domain models from product line models. PUMConf allows modeling variability directly in use case diagrams, specifications, and domain models without using feature models. It provides automated consistency checking of product line models, interactive configuration support with consistency checking of decisions, and automated generation of product-specific models from configured product line models. An evaluation in an industrial case study found the approach and tool to be practical and beneficial for configuring product models in industrial settings.