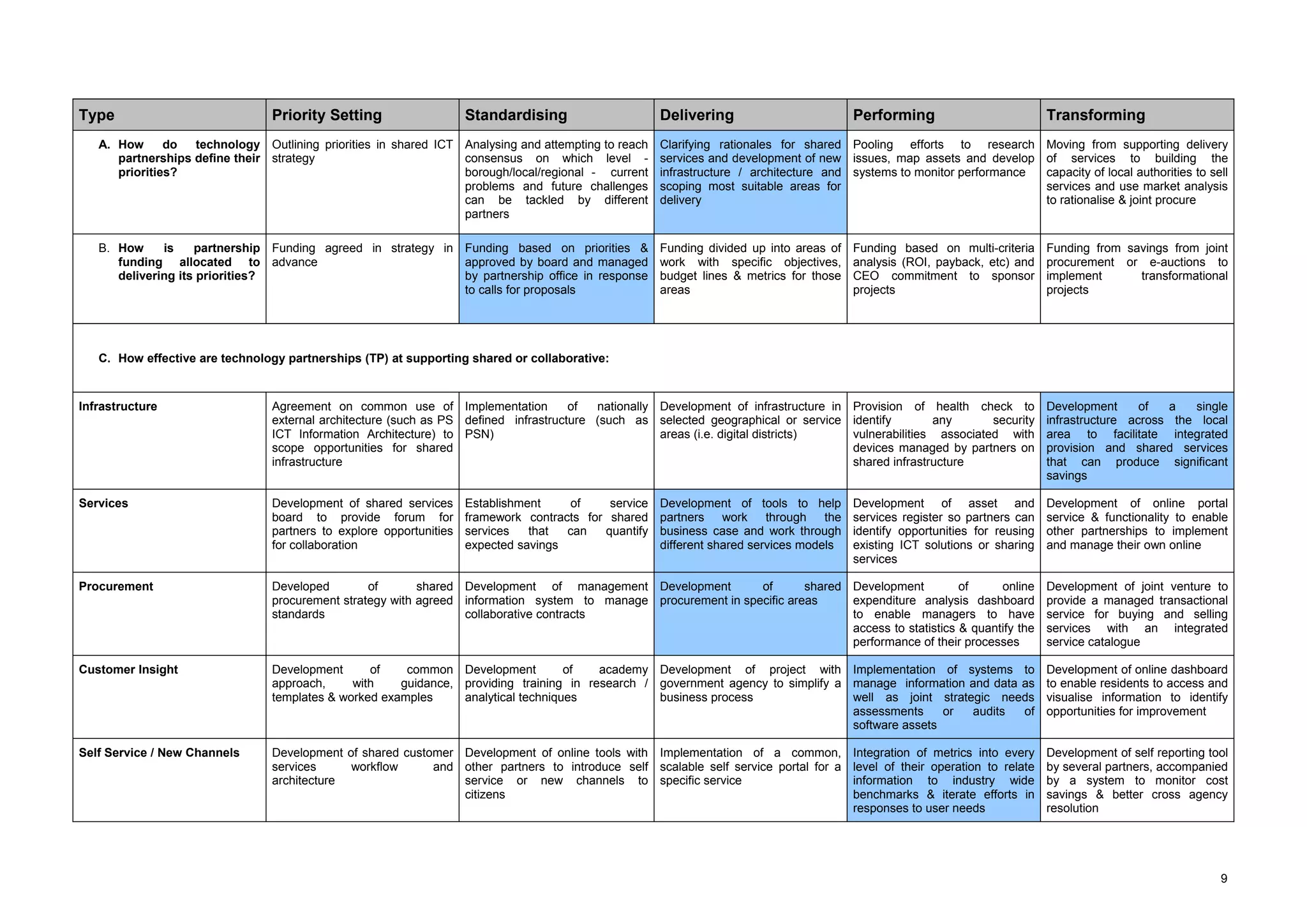
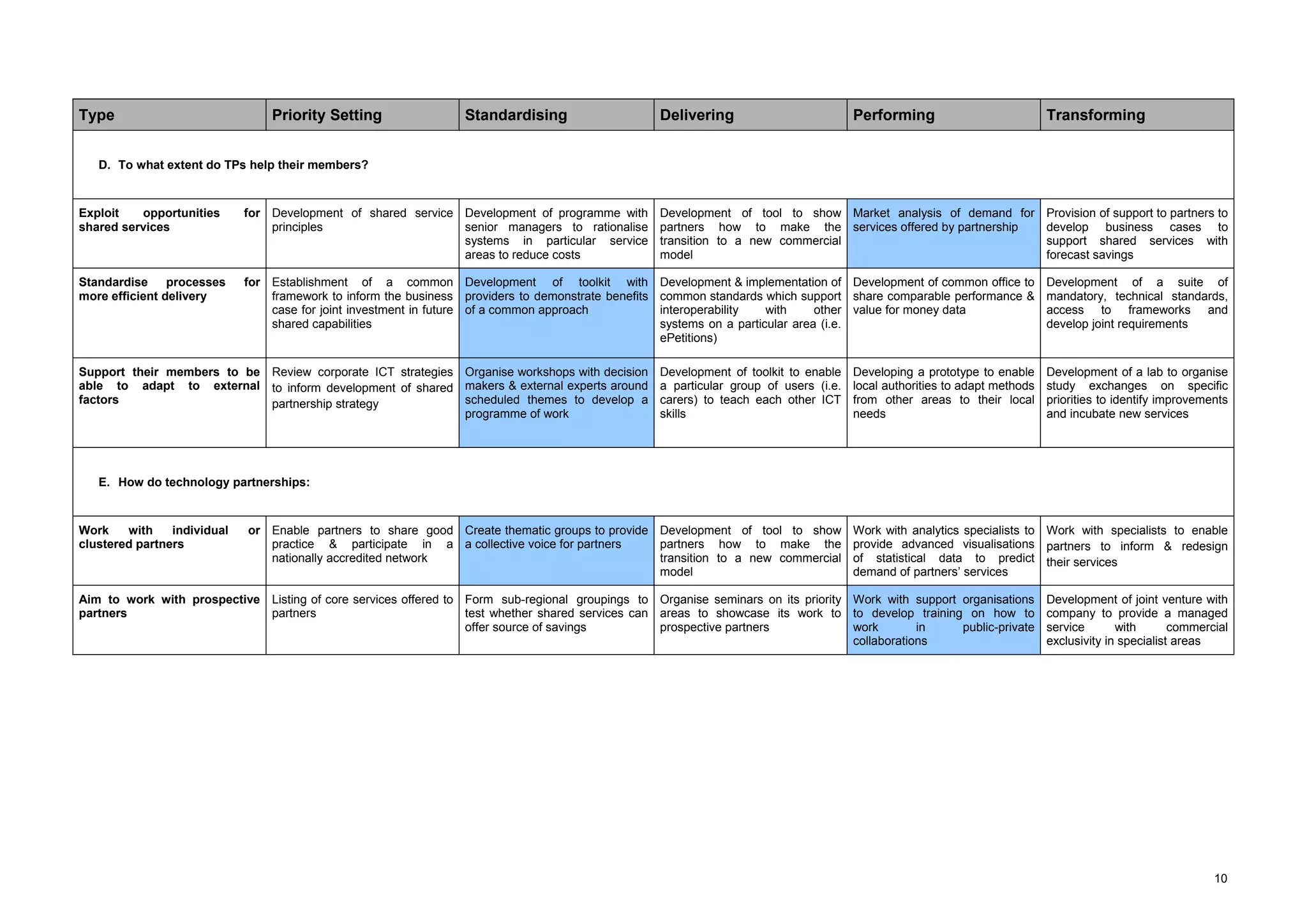
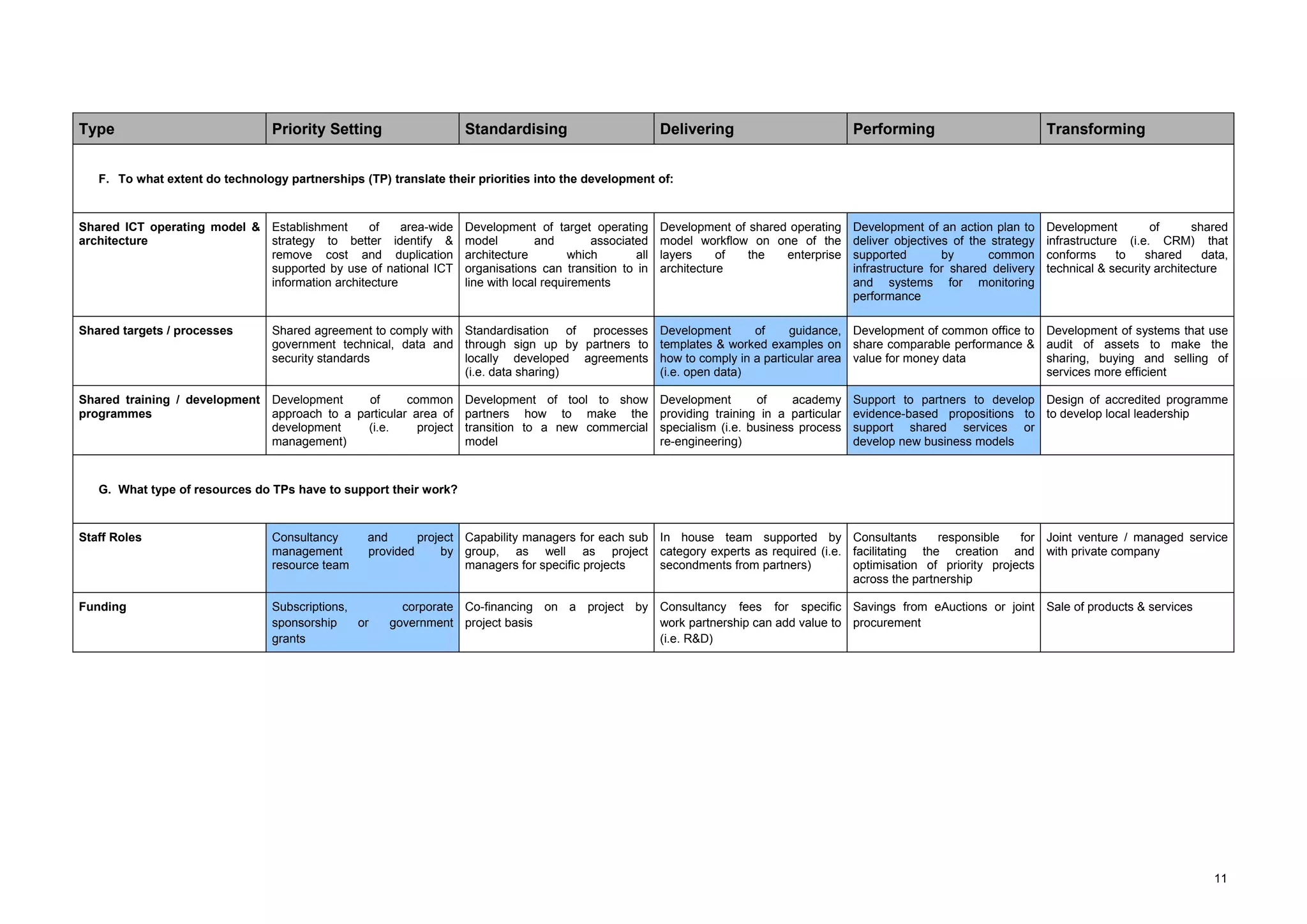
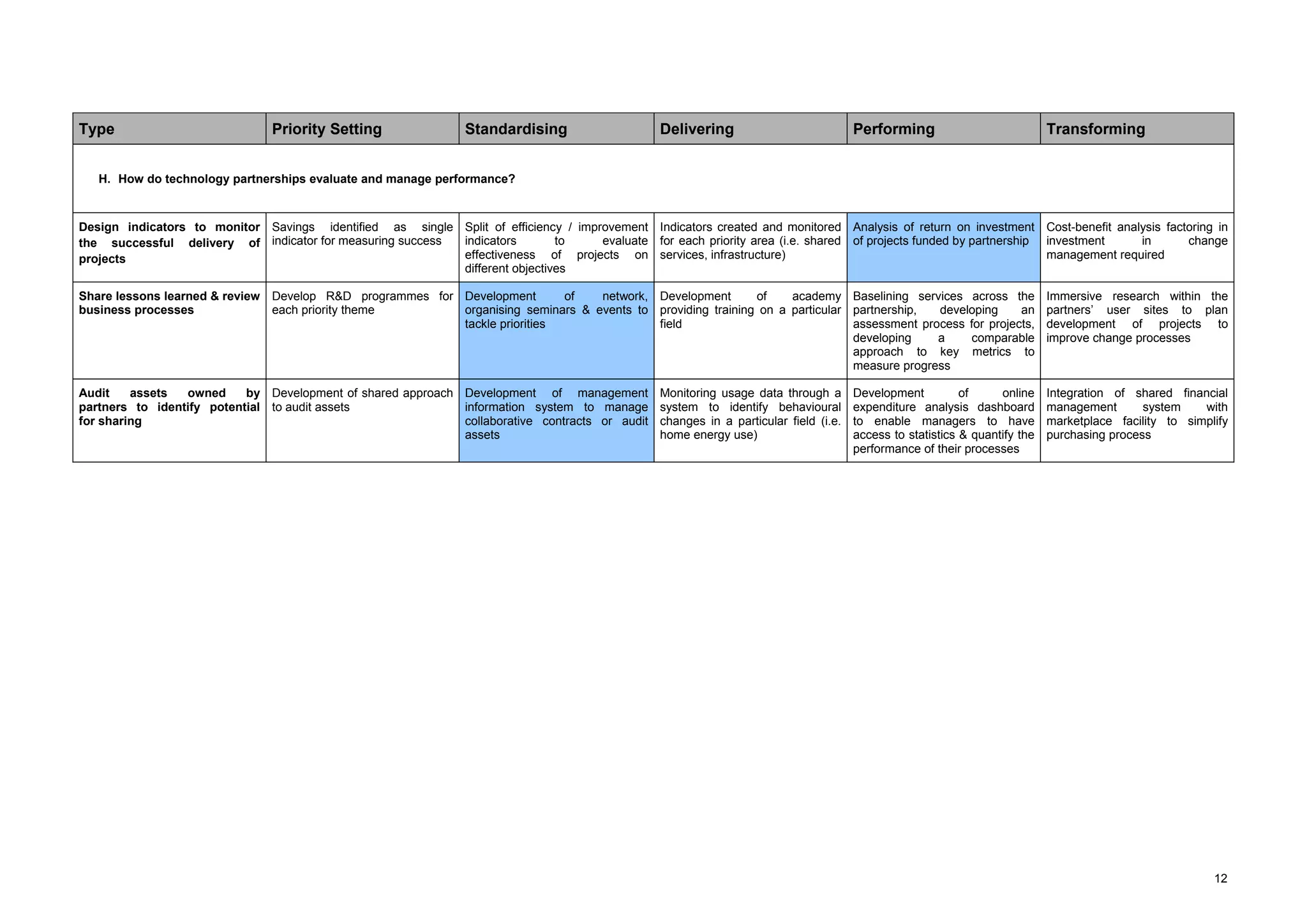
The document describes a maturity model for public service ICT partnerships. It outlines 5 levels of maturity: 1) priority setting, 2) standardizing, 3) delivering, 4) performing, and 5) transforming. For each level, typical processes, characteristics, and capabilities of partnerships at that level are defined. The document also provides recommendations for how the described partnership can apply the maturity model to benchmark itself and identify areas for improvement.