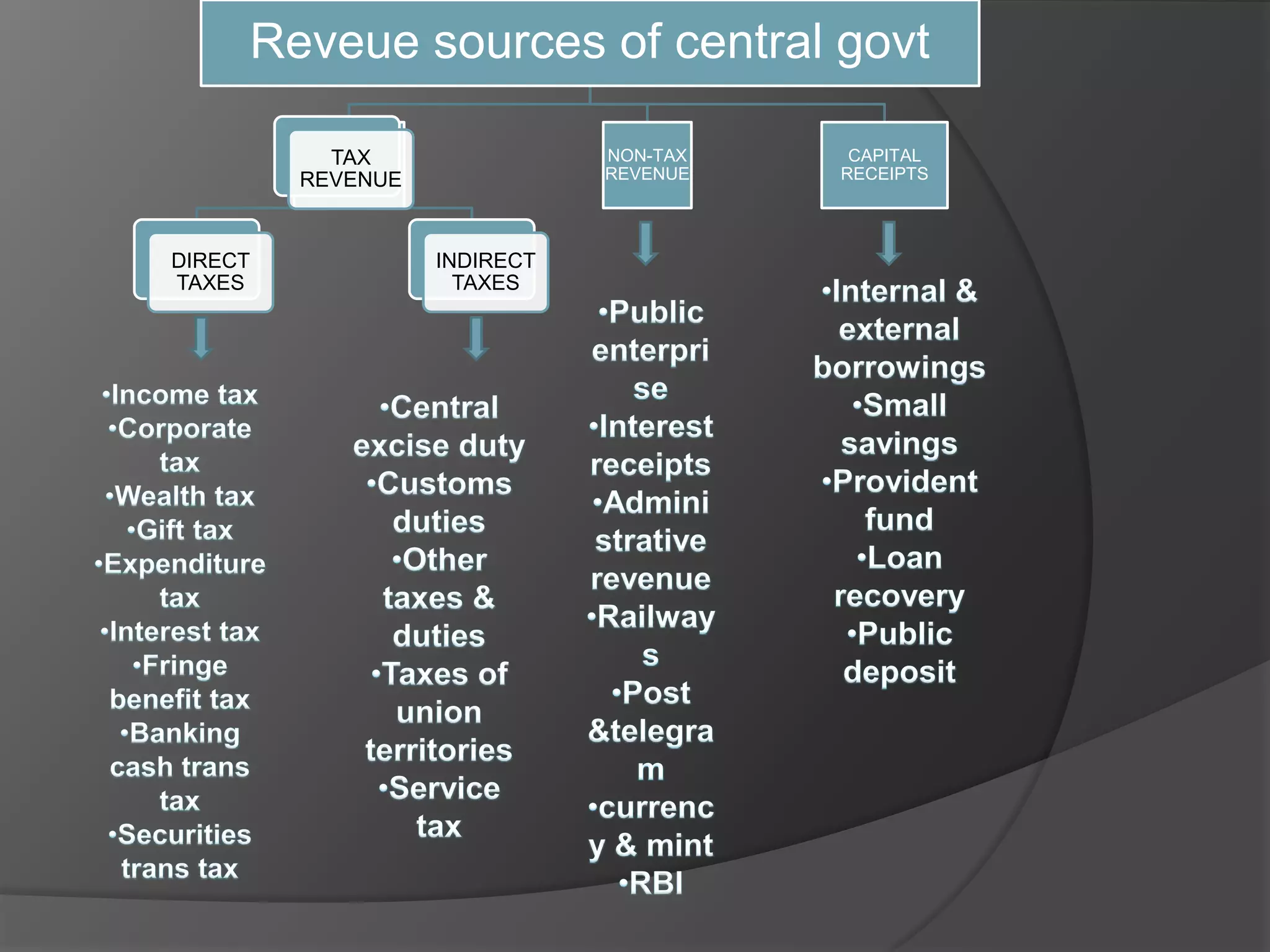
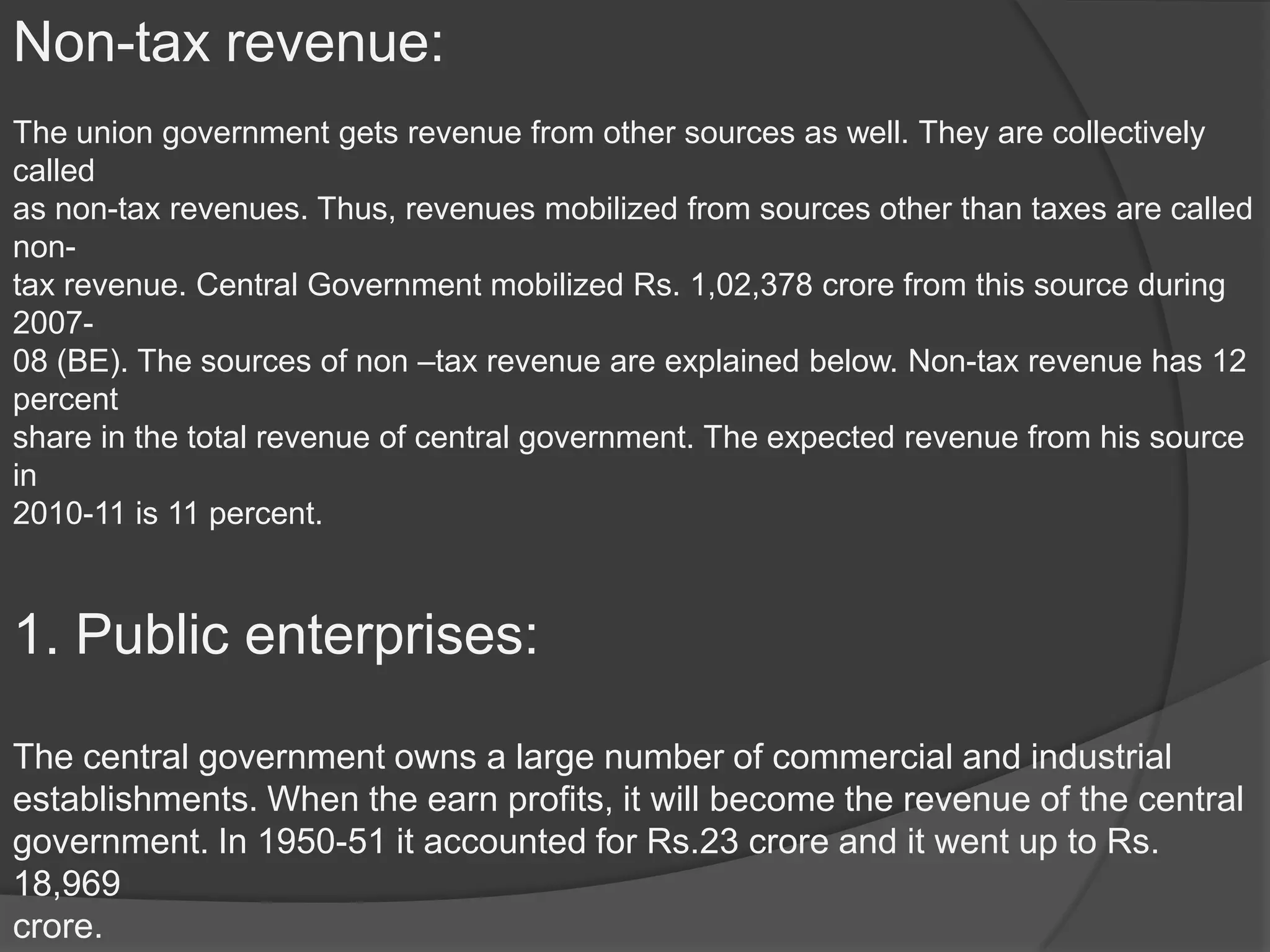
Government needs resources to perform political, social, and economic activities to maximize welfare. It obtains resources through public revenues, which come from tax revenue and non-tax revenue. Tax revenue includes direct taxes like income tax paid directly to the government by taxpayers, and indirect taxes like sales tax where the burden is passed on to consumers. Non-tax revenue sources include profits from public enterprises, railways, postal services, the Reserve Bank of India, and income from currency and mint. Together, tax and non-tax revenues make up the central government's primary source of funding.