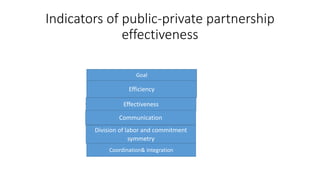
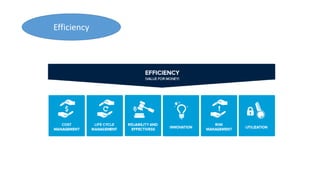
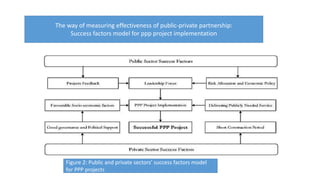
The document presents an overview of public-private partnerships (PPPs), defining them as agreements where private partners deliver public services aligned with government objectives. It discusses the importance of PPPs in enhancing public service delivery, the effectiveness of various models, and key success factors for implementation, while also identifying potential problems and solutions related to these partnerships. The emphasis is on the need for careful planning, risk management, and effective communication to achieve desired outcomes in various sectors.