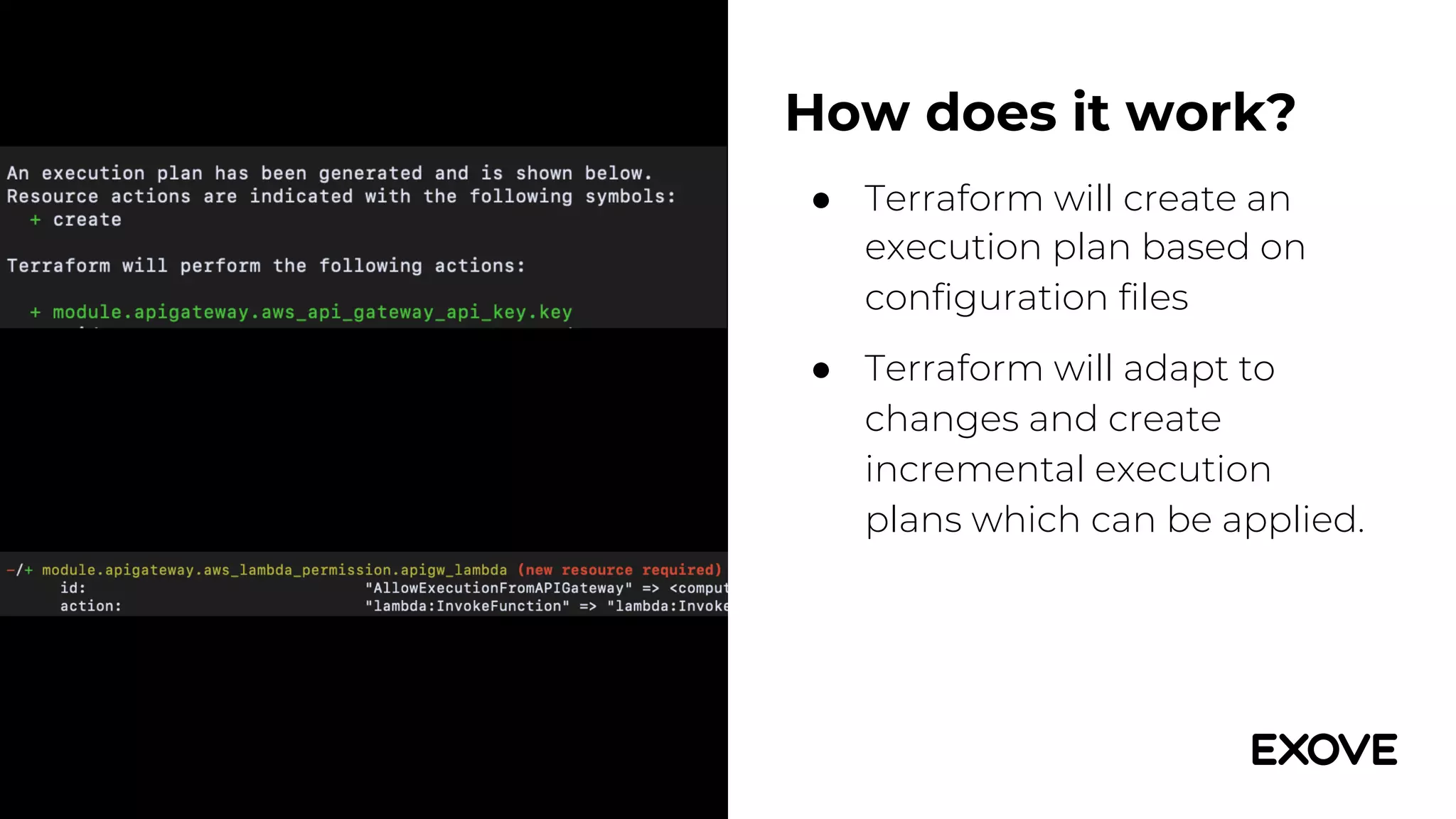
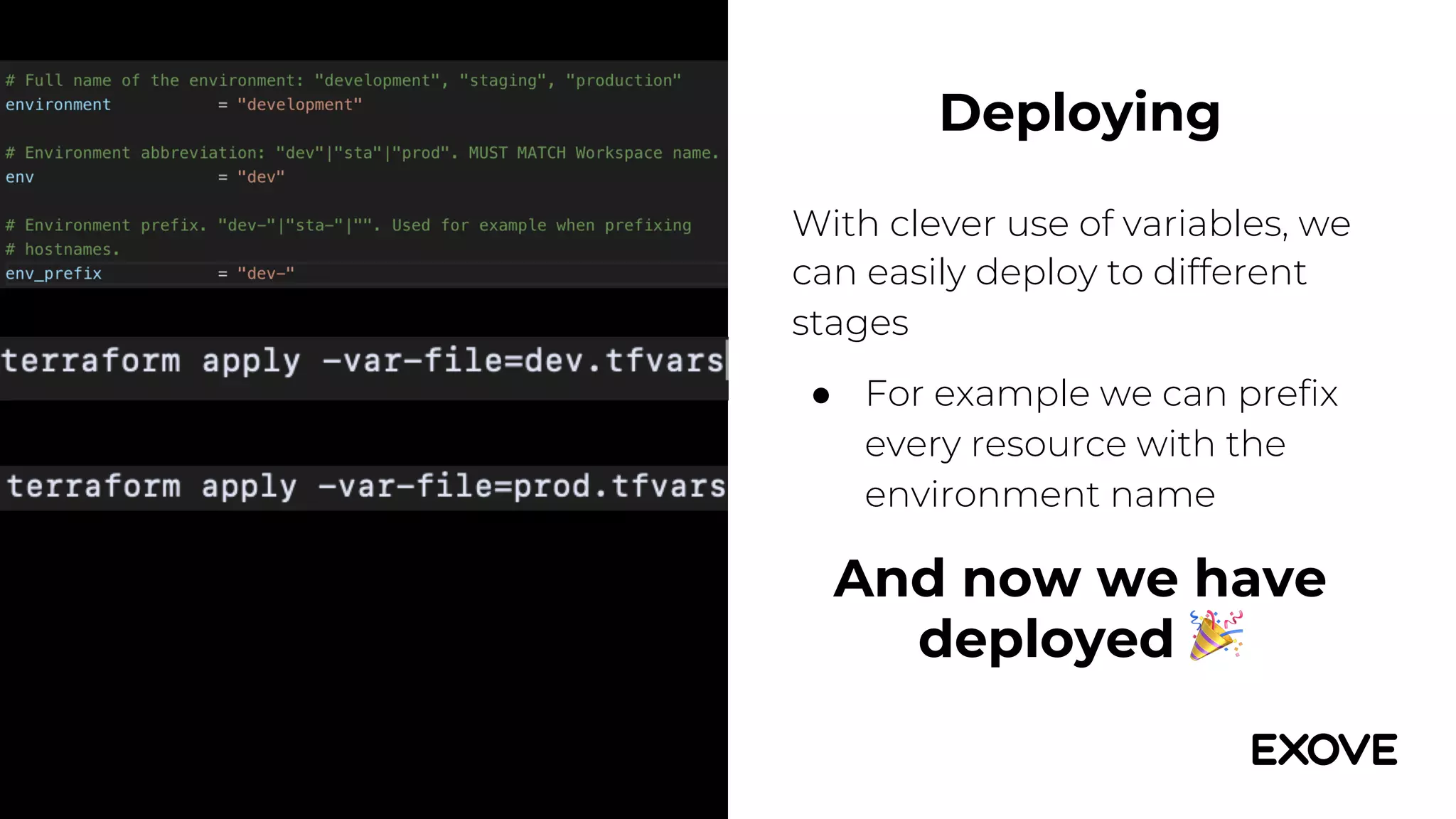
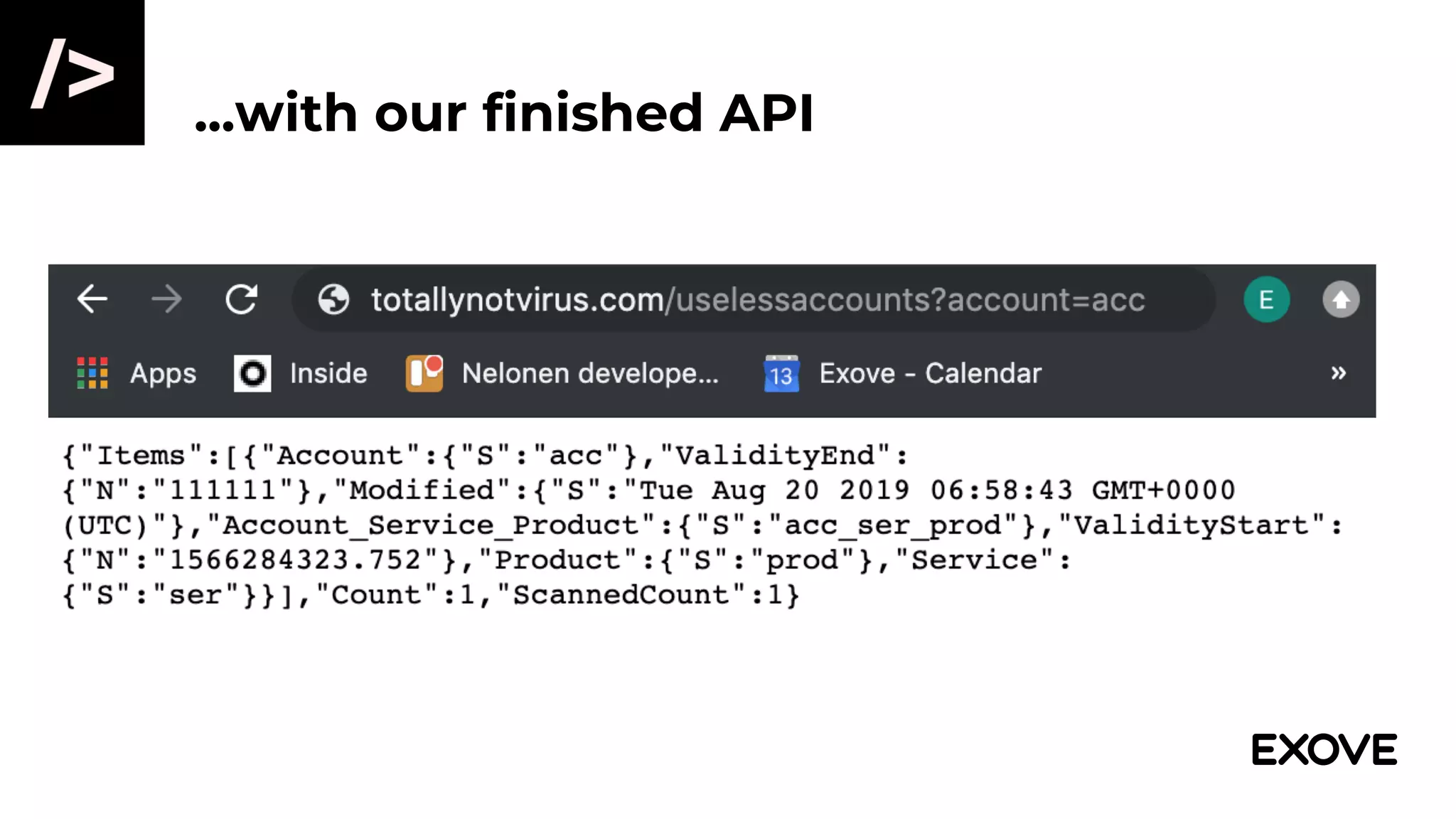
This document provides an overview of using Terraform to provision infrastructure on AWS. It discusses how Terraform allows defining infrastructure as code through configuration files, enabling reliable and repeatable deployments. Key points include:
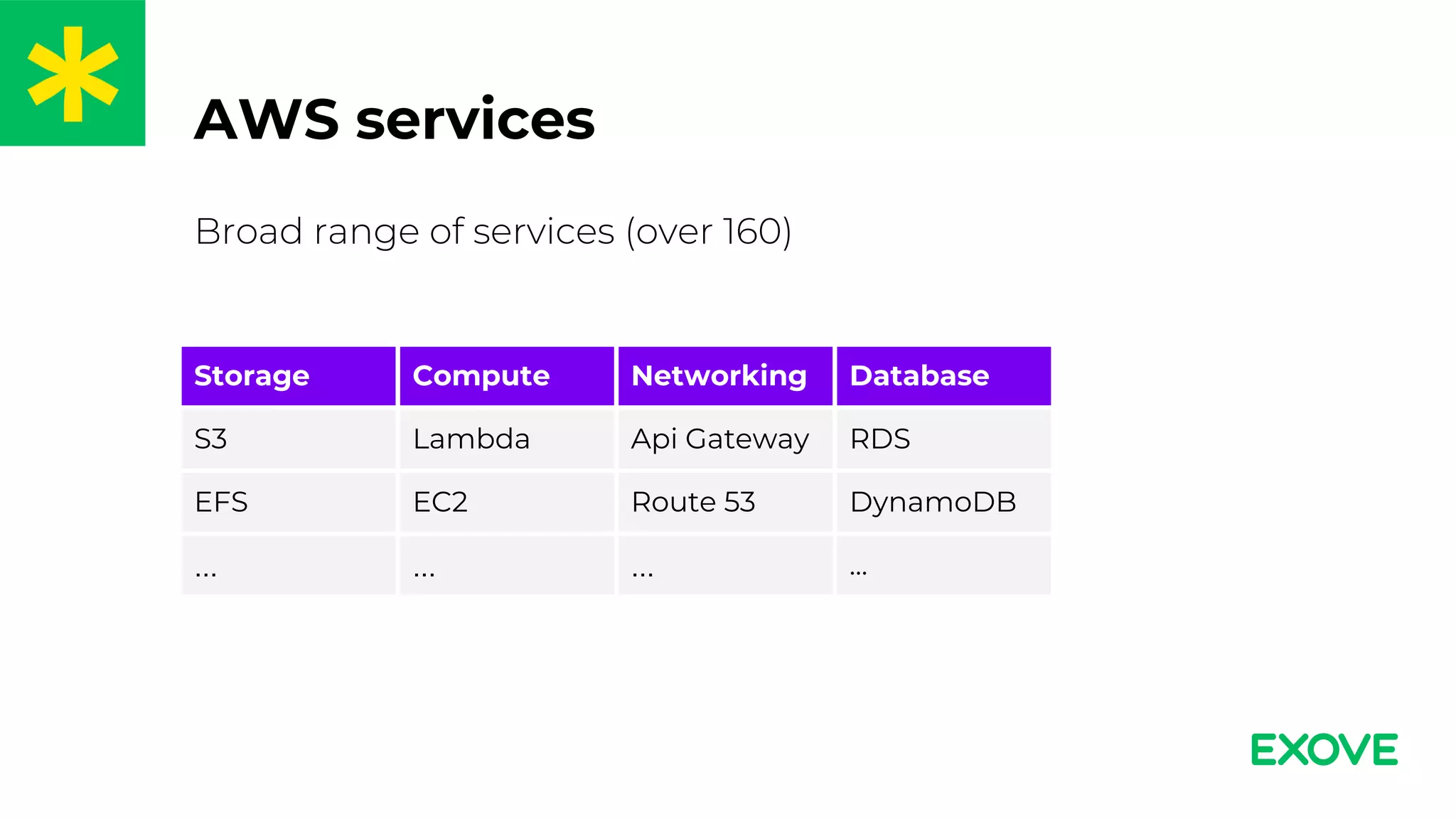
- Terraform can provision AWS services like Lambda, DynamoDB, API Gateway to build a serverless REST API on AWS.
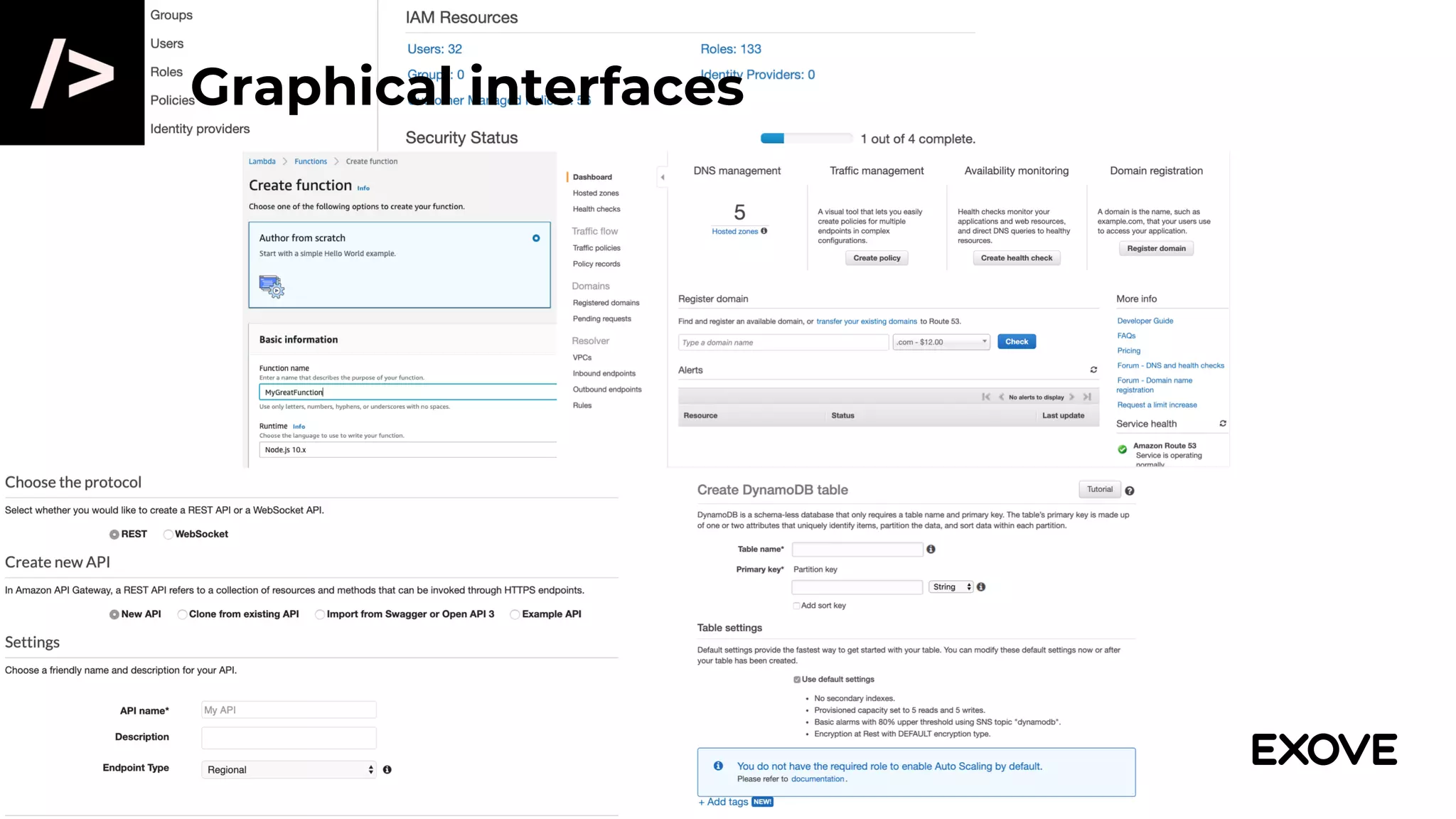
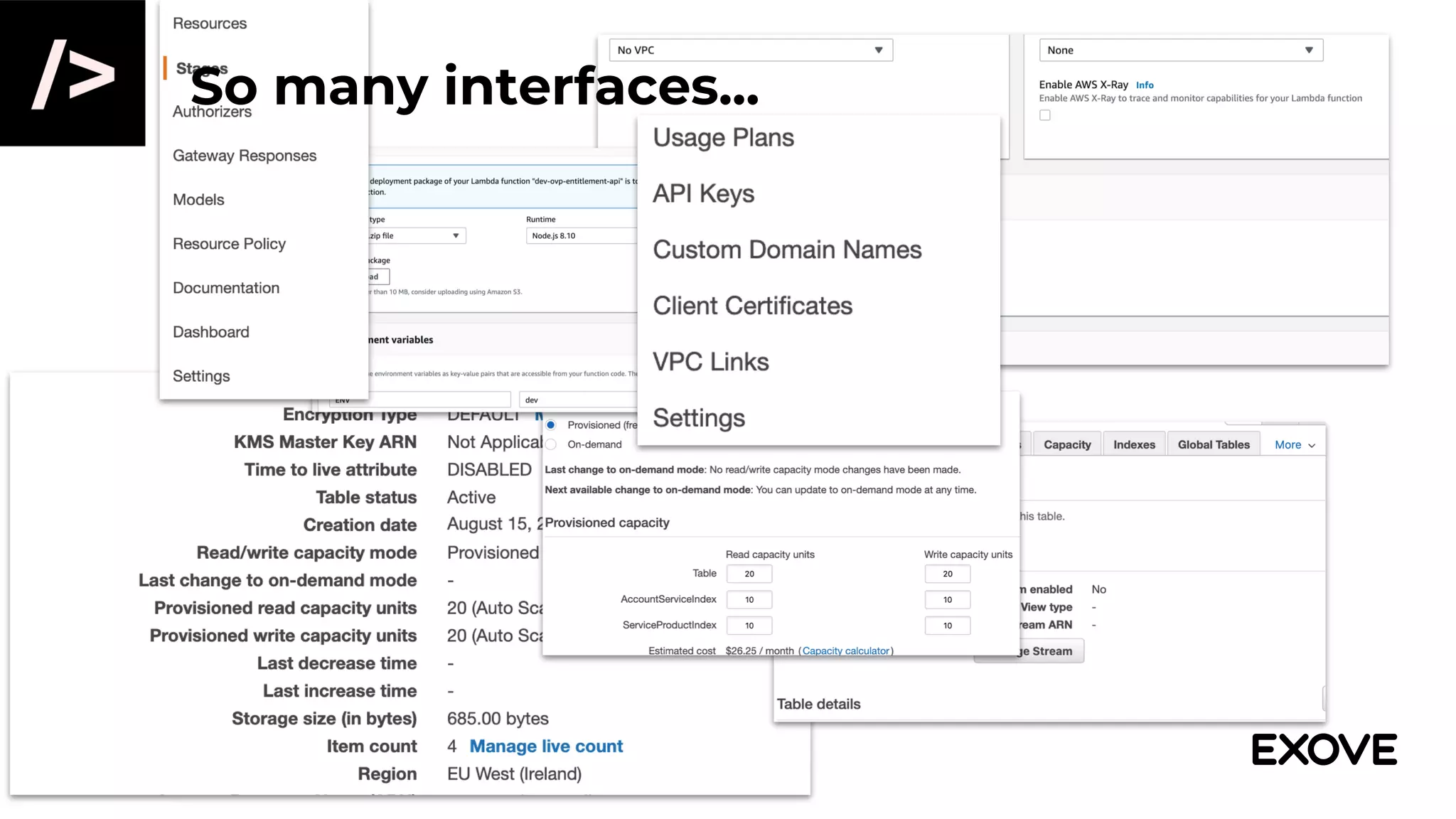
- Managing infrastructure through graphical interfaces becomes complex and error-prone for non-trivial configurations.
- Terraform addresses this by defining resources and dependencies through configuration files, then deploying the necessary infrastructure.
- This allows defining a standard structure for environments like development, test, and production through variables and modules.