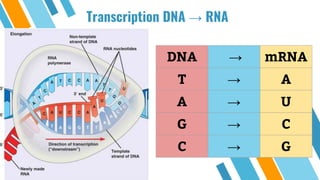
The document discusses protein synthesis, which involves DNA providing instructions in the form of mRNA that are read by ribosomes to assemble amino acids in the correct sequence. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. The instructions start as DNA and are transcribed into mRNA through base-pair matching, then the mRNA travels to ribosomes where the codon sequences are translated to select the corresponding amino acids using tRNA. Mutations can occur that change the amino acid sequence and prevent proper protein formation.