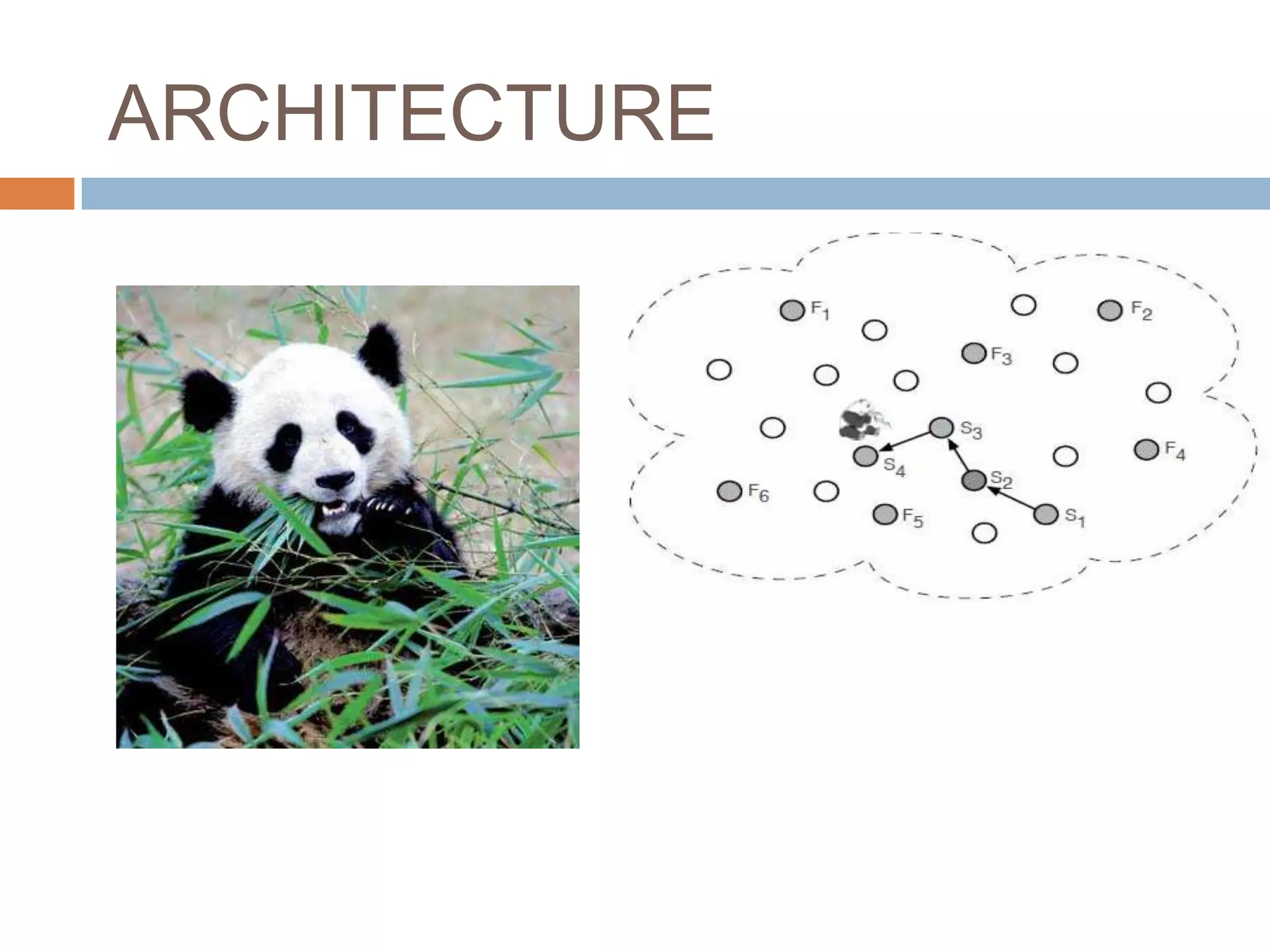
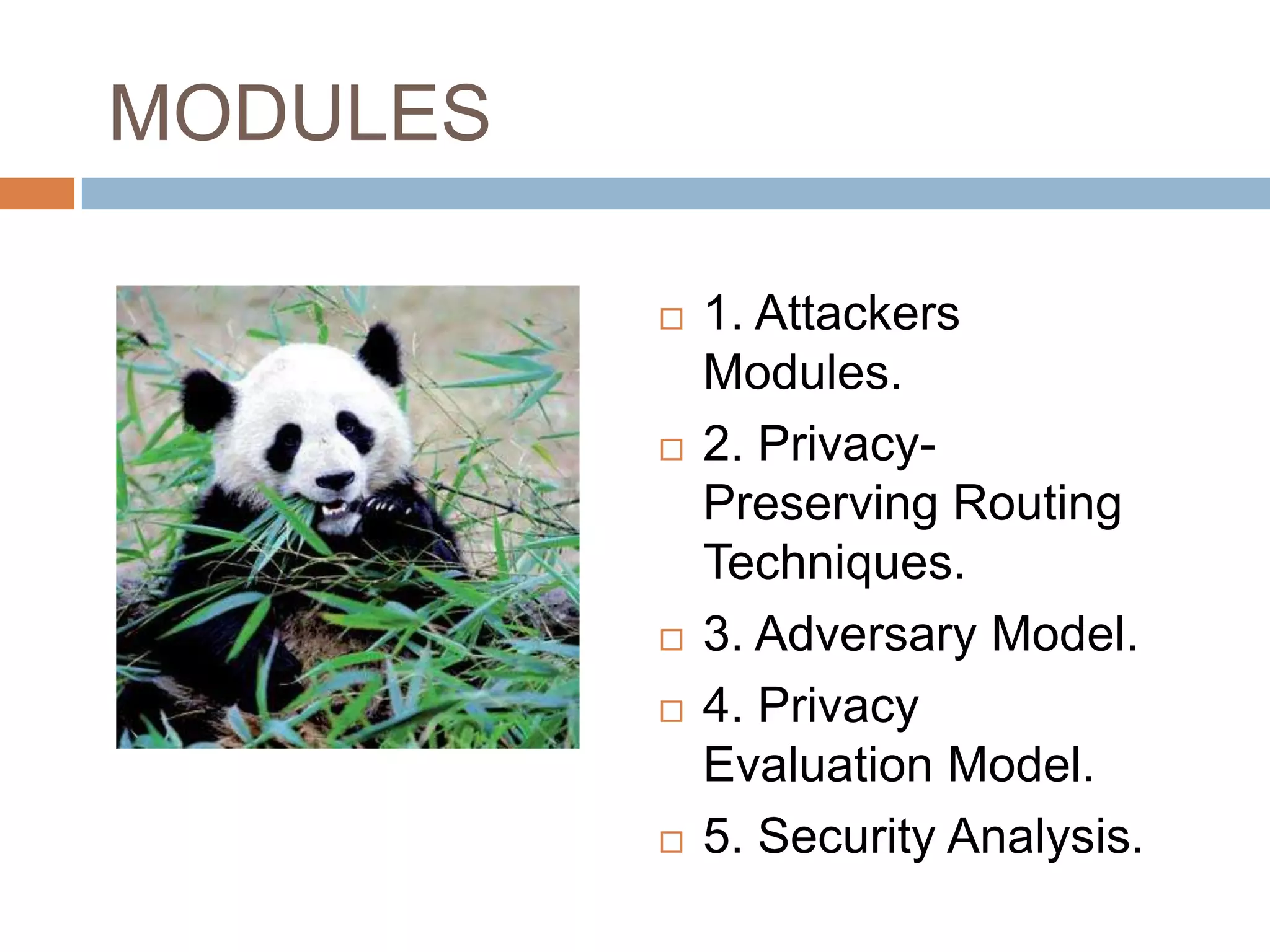
The document proposes two techniques - periodic collection and source simulation - to prevent leakage of location information in sensor networks from a global eavesdropper. Periodic collection provides high location privacy while source simulation provides tradeoffs between privacy, communication cost, and latency. The techniques are efficient and effective at providing source and sink location privacy compared to existing methods that only defend against local adversaries.