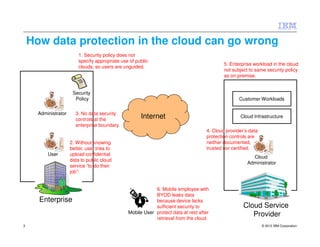
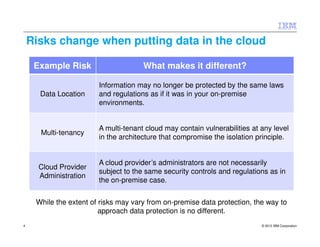
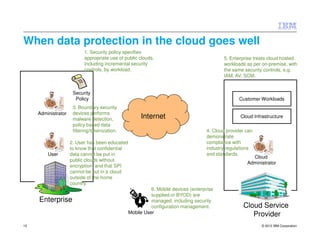
This document discusses protecting data in the cloud and outlines some of the risks and best practices. It notes that risks change when putting data in the cloud due to factors like data location, multi-tenancy, and cloud provider administration. However, the approach to data protection remains the same - through governance, policy, user awareness, technical security controls, and ensuring trust and compliance. The document provides examples of controls that can be implemented at different points from the enterprise boundary to the cloud infrastructure. It stresses the importance of a balanced approach and treating cloud workloads similarly to on-premise systems with the same security controls.