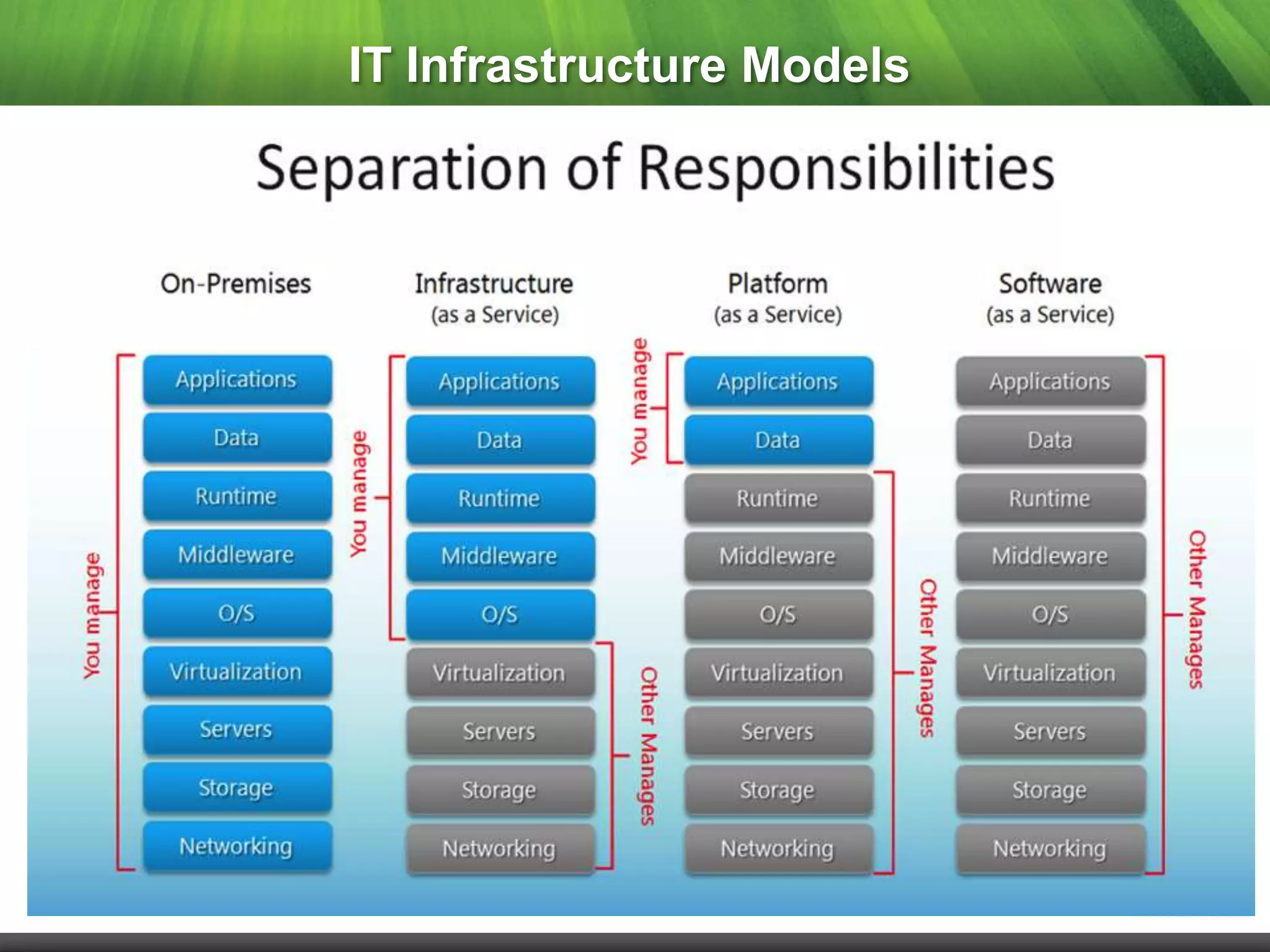
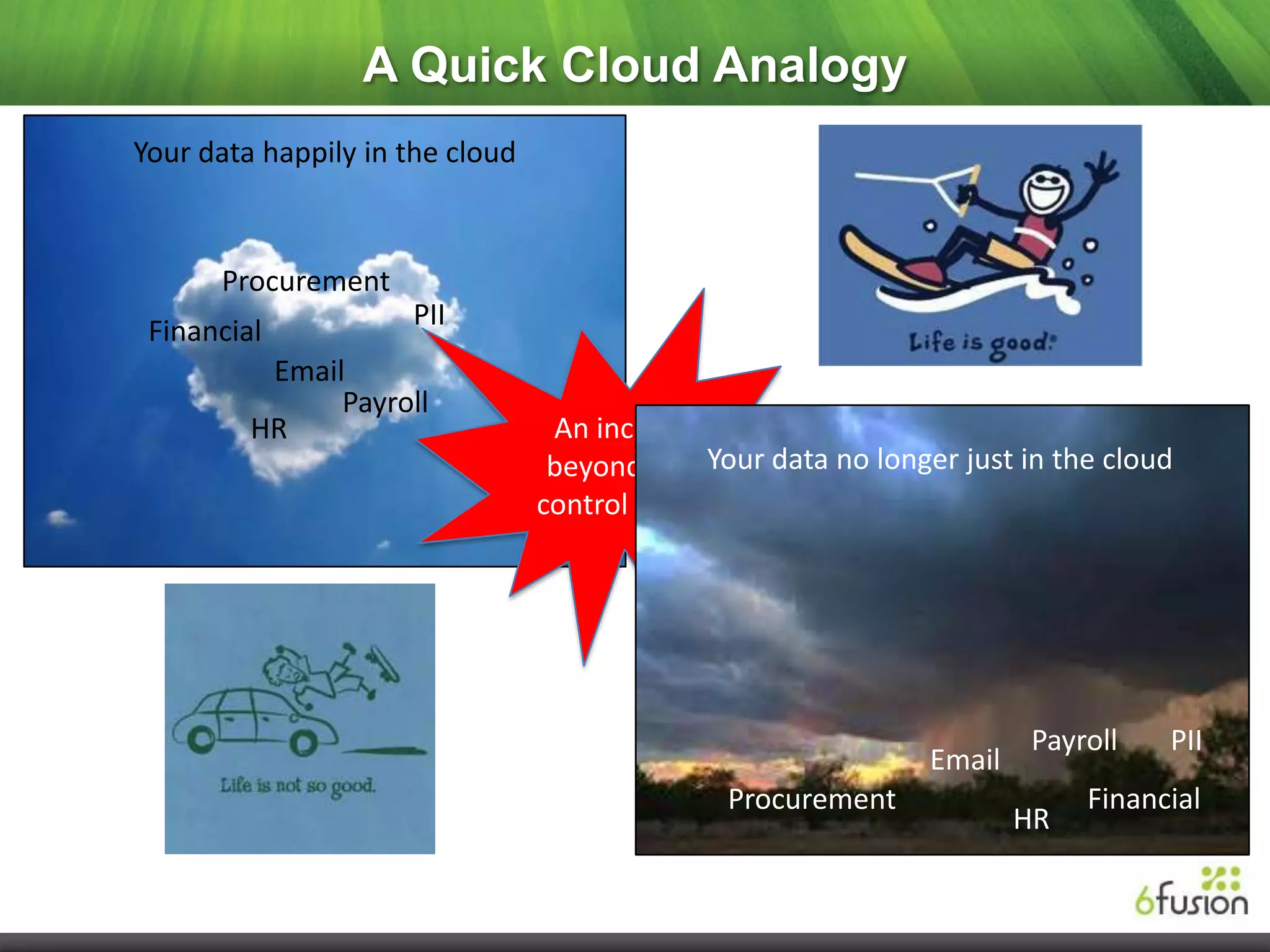
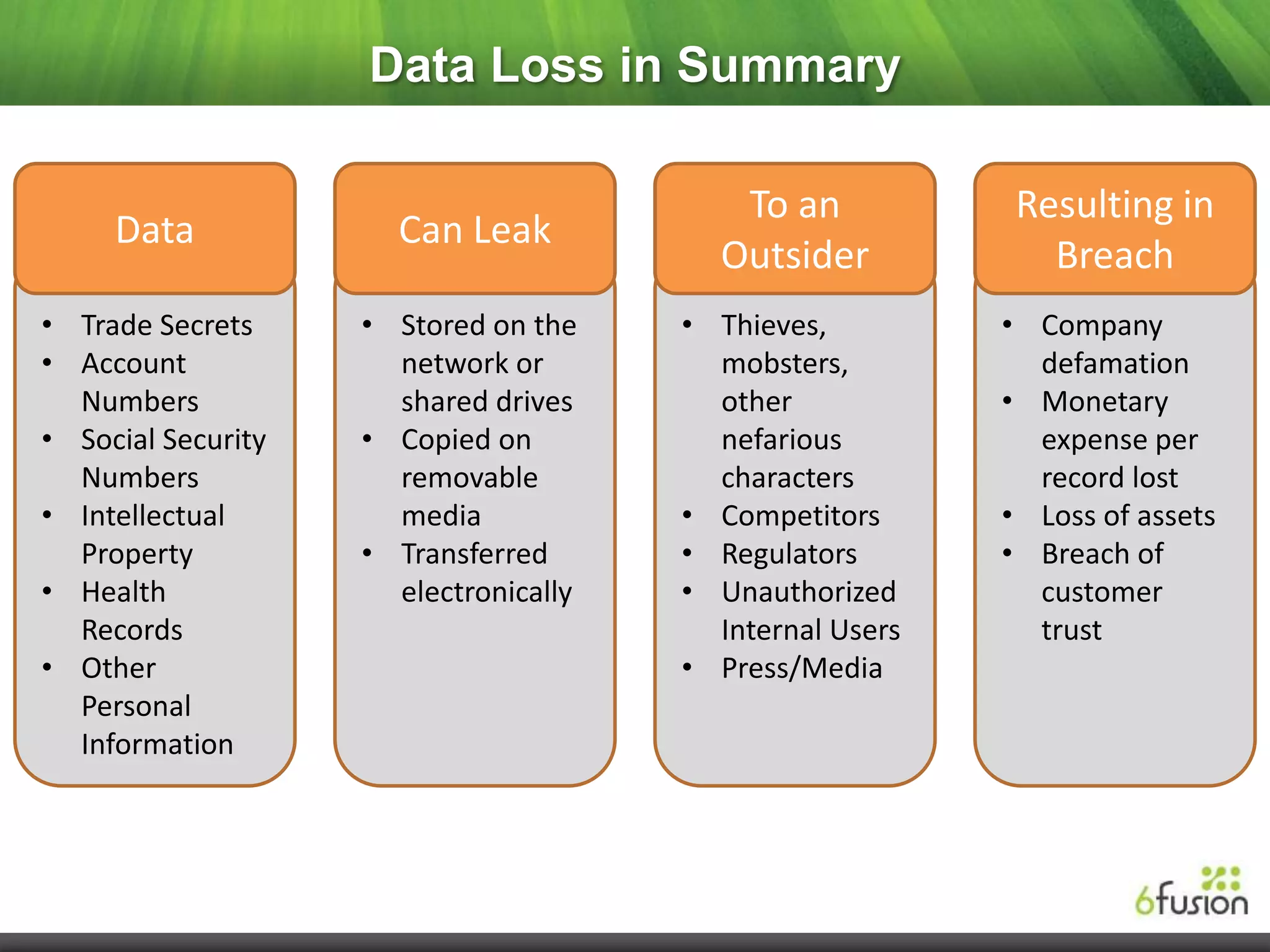
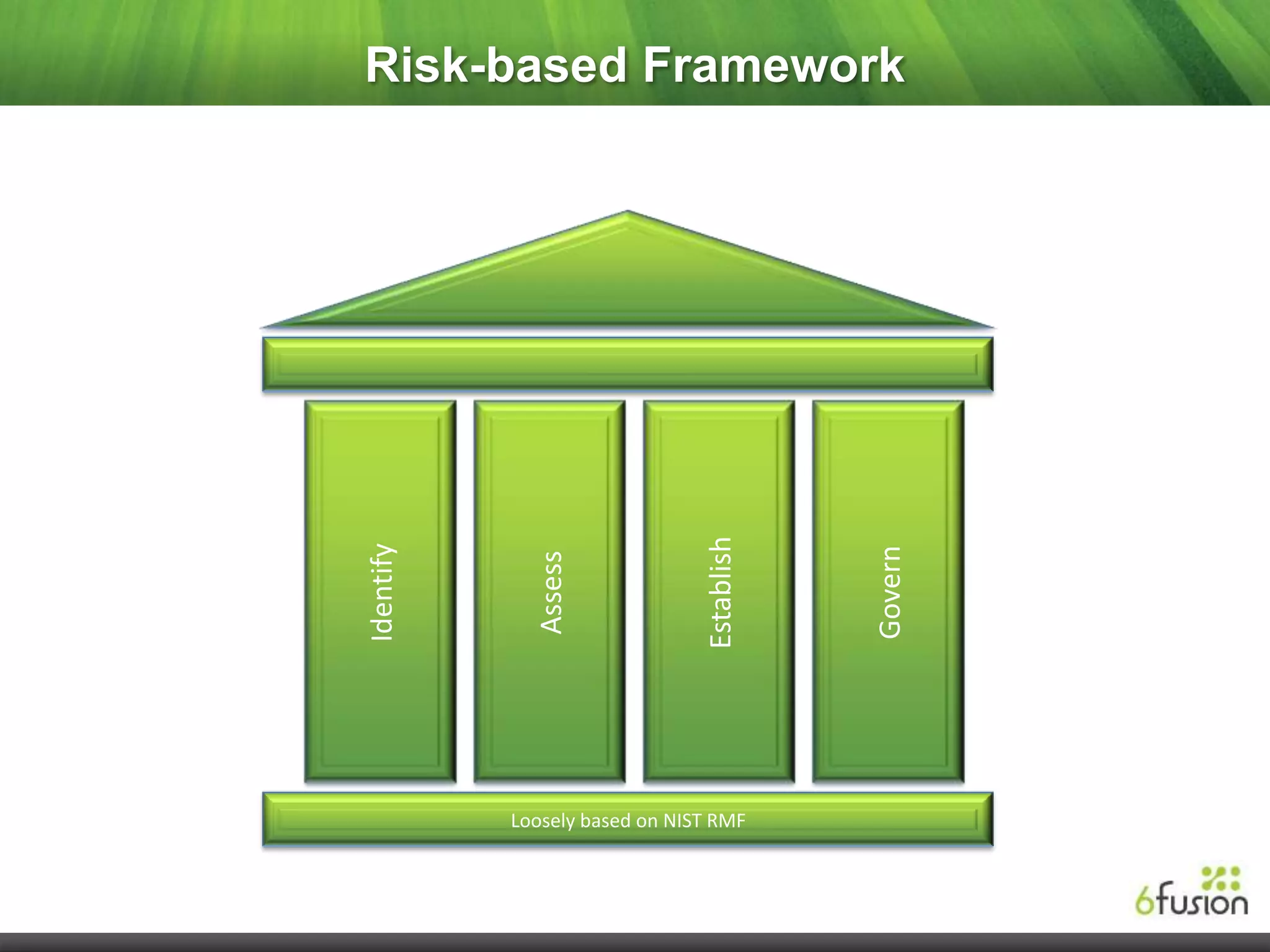
This document summarizes a webinar on cloud security presented by representatives from 6fusion and Network Box USA. It discusses common cloud security myths, challenges related to access, protection, segregation and recovery of cloud data, and best practices for cloud security including implementing security by design, active monitoring and having an incident response plan. The webinar concluded by discussing developing a risk-based security framework and taking questions from attendees.