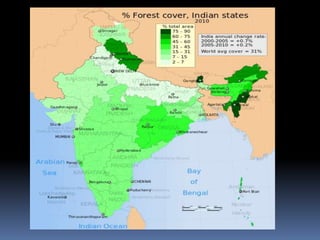
Protected forests in India were introduced in 1927 to protect forests and resident species from further depletion. There are two types of protected areas - reserved forests where all activities are banned unless permitted, and protected forests where some local community access is allowed. India has over 100 national parks, 440 wildlife sanctuaries, 48 tiger reserves, and 18 biosphere reserves to protect forests and wildlife. The Indian Forest Act of 1927 provides legal guidelines for declaring and managing reserved and protected forests throughout India.