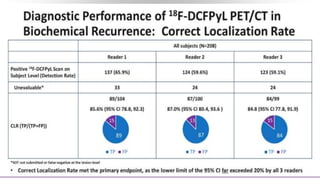
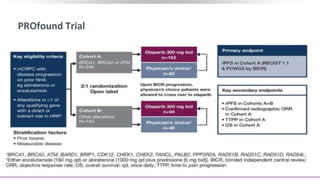
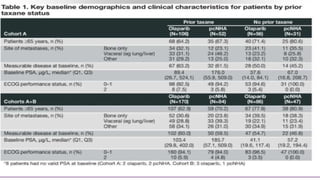
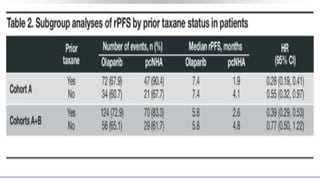
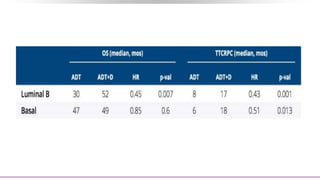
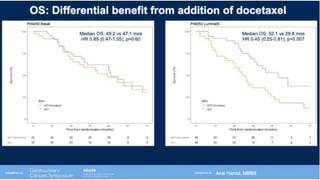
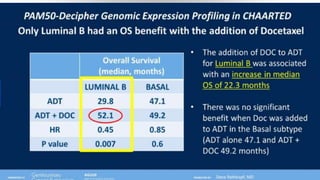
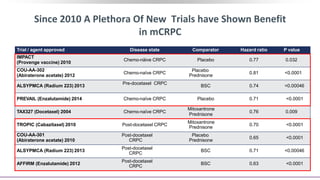
1) The document discusses several studies presented at the ASCO 2020 conference regarding prostate cancer treatment updates. These include studies on chemo-hormonal therapy, androgen signaling inhibitors, and immunotherapy combinations.
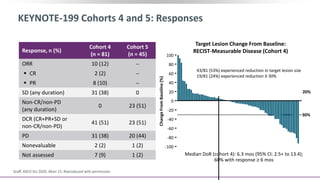
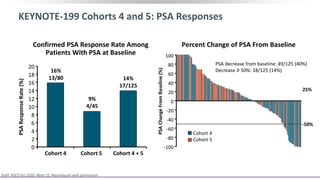
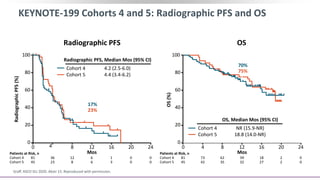
2) A key study found that combining pembrolizumab and enzalutamide showed activity in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer whose disease had progressed on enzalutamide, with an objective response rate of 12% and durable disease control.
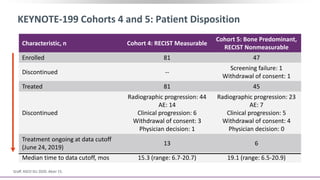
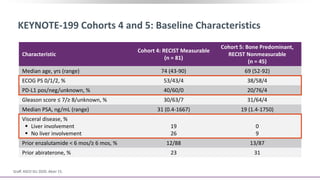
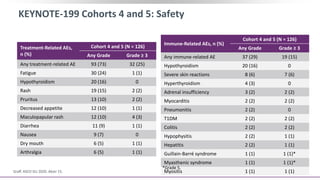
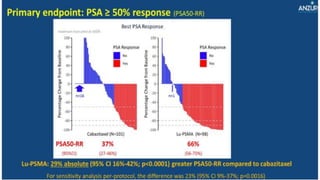
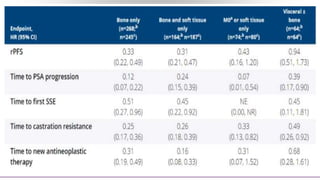
3) Additional results from the conference included findings on predictive biomarkers, outcomes based on site of metastasis, and safety data from combination immunotherapy and targeted therapy trials for advanced prostate cancer.








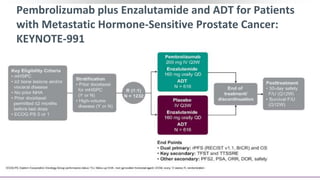

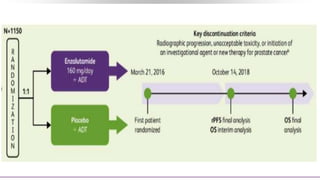


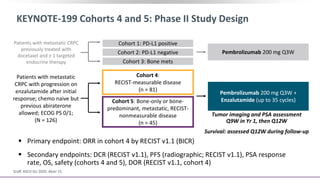
![Pembrolizumab + Enzalutamide for Enzalutamide-Resistant
mCRPC (KEYNOTE-199): Background
Pembrolizumab monotherapy active with durable response in PD-L1+ mCRPC[1,2]
Phase II study (N = 28): pembrolizumab + enzalutamide active in patients with PD on
enzalutamide[3]
Phase II KEYNOTE-199 study designed to evaluate pembrolizumab in multiple cohorts
of patients with mCRPC after disease progression on chemotherapy and/or targeted
endocrine therapy
‒ Cohorts 1-3: data previously reported for patients with RECIST-measurable PD-L1+,
PD-L1–negative, or bone-predominant disease previously treated with docetaxel and
≥ 1 targeted endocrine therapy[1]
‒ Cohorts 4 and 5 included in this report: RECIST-measurable disease and bone-
predominant metastatic, RECIST-nonmeasurable disease with progression on
enzalutamide after initial response[4]
1. Antonarakis. JCO. 2020;38:395. 2. Hansen. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:1807. 3. Graff. JCO. ASCO 2018. Abstr 5047. 4. Graff. ASCO GU 2020. Abstr 15.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prostatecancerasco2020updates-200905151412/85/Prostate-cancer-asco-2020-updates-26-320.jpg)