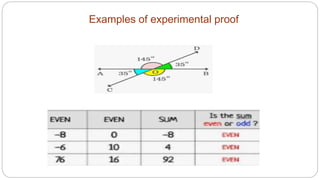
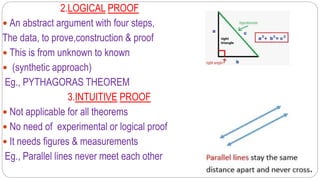
This document discusses the meaning, nature, and types of mathematical proofs. It defines a proof as a rigorous argument used to establish the truth of a mathematical statement. Proofs can be direct or indirect. Direct proofs establish a conclusion logically by moving from the known to the unknown. Indirect proofs establish a conclusion by assuming it is false and reaching a contradiction. The document provides examples of different types of direct proofs like experimental, logical, and intuitive proofs. It also discusses types of indirect proofs like proof by contradiction, proof by exhaustion, and non-constructive proofs.