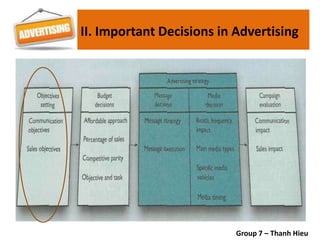
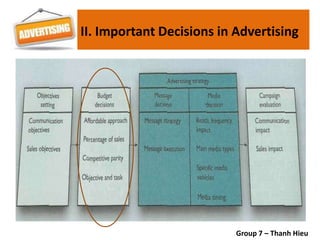
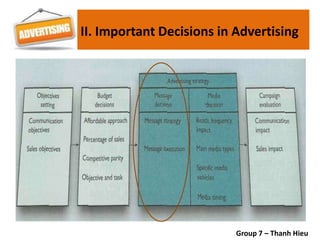
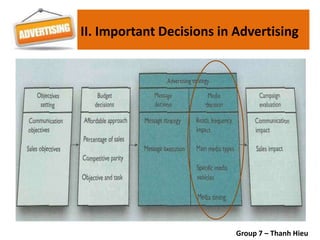
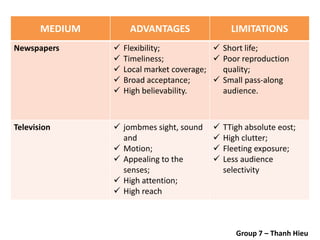
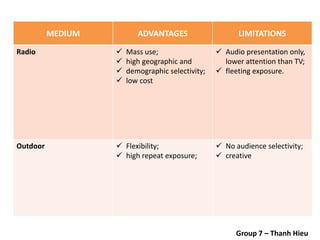
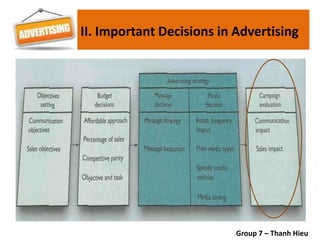
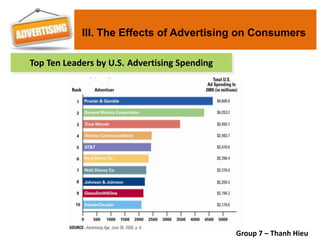
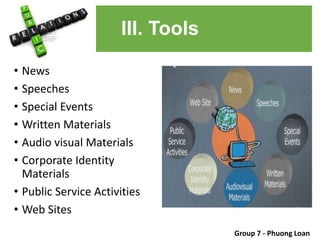
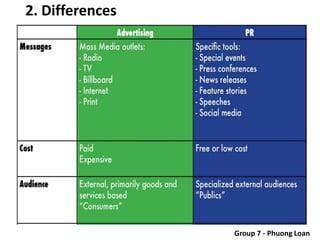
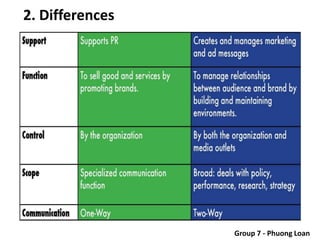
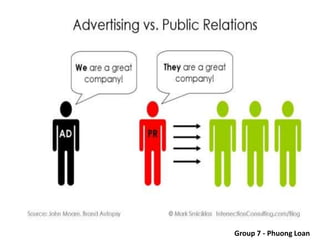
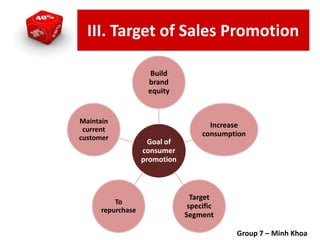
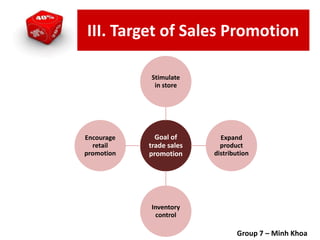
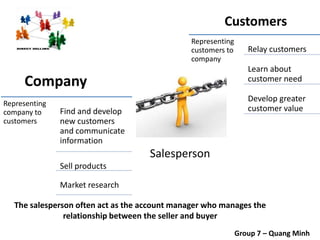
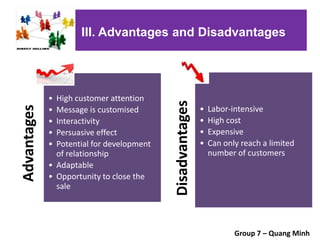
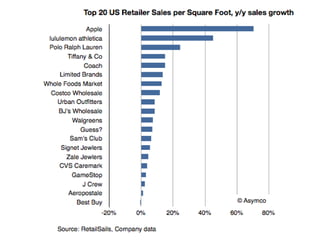
The document covers various promotional strategies including advertising, public relations, sales promotion, personal selling, and social media, emphasizing their definitions, important decisions, advantages, and limitations. It highlights the roles and effects of these strategies on consumer behavior and brand perception. Additionally, it presents a case study of Apple's promotional mix, analyzing its advertising, public relations, sales promotion, and personal selling efforts.