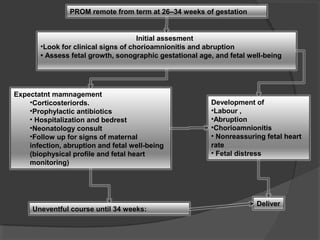
This document discusses prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), also known as premature rupture of membranes. It defines PROM and discusses frequencies. Consequences of PROM include preterm birth and associated complications like respiratory distress syndrome. It also discusses risks of infection to the mother and baby. Management approaches are provided for term PROM, preterm PROM, and PROM occurring at various gestational ages. Recommendations include expectant management with antibiotics for term PROM and delivery after 24 hours if no signs of infection. Preterm PROM guidelines include corticosteroids, antibiotics, and delivery by 34 weeks if uncomplicated.