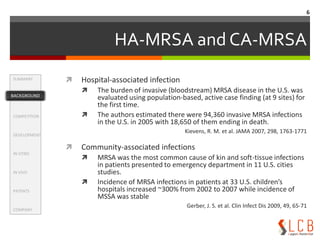
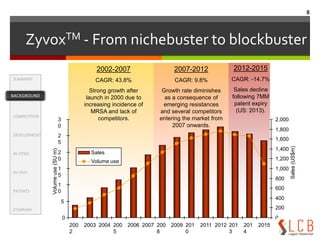
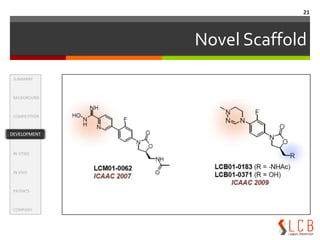
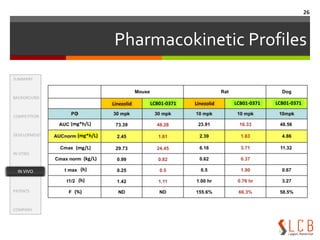
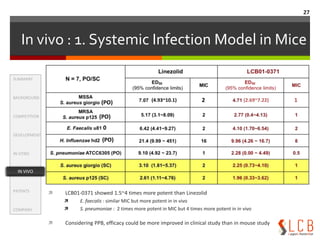
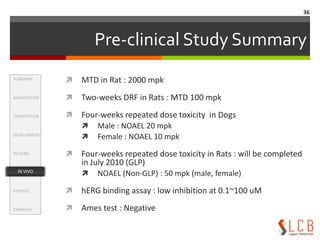
This document summarizes an oxazolidinone analogue developed as a novel antibiotic with improved potency and safety over linezolid. The analogue, LCB01-0371, showed superior potency to linezolid against MRSA, VRE, and H. influenzae in vitro and in animal studies. It has a good safety profile with comparable or less bone marrow toxicity and significantly less MAO inhibition than linezolid. The document provides background on the need for new antibiotics to treat MRSA and reviews linezolid's mechanism of action, effectiveness, safety concerns, and market performance. It also discusses clinical stage oxazolidinone competitors to linezolid like torezolid, radezolid, and