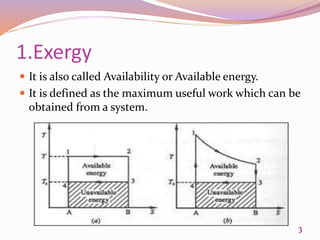
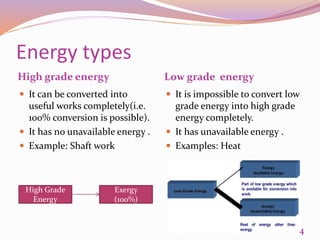
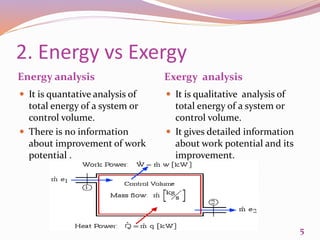
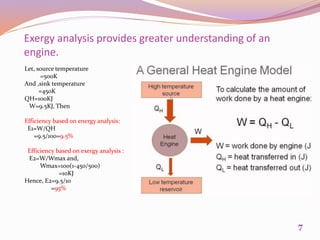
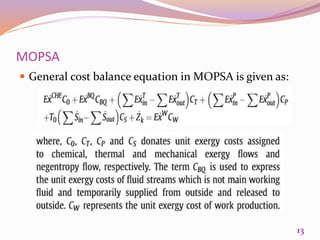
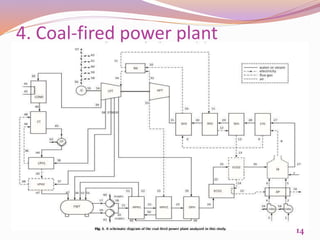
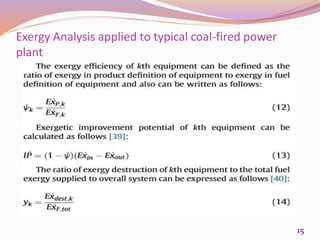
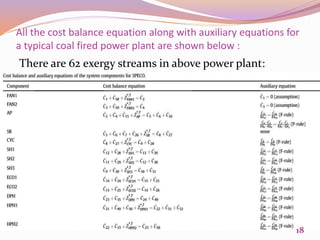
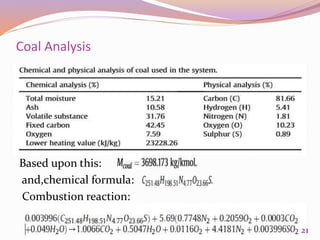
This document discusses exergetic and thermoeconomic analysis of a coal-fired power plant. It begins with definitions of exergy as usable work and explanations of energy and exergy analysis. It then describes various thermoeconomic analysis methods including Specific Exergy Costing (SPECO) and Modified Production Structural Analysis (MOPSA). SPECO and MOPSA are applied to a sample coal-fired power plant model to determine the unit exergy costs of each stream. The results of exergy and economic analyses of the plant are presented, identifying locations for potential efficiency improvements.