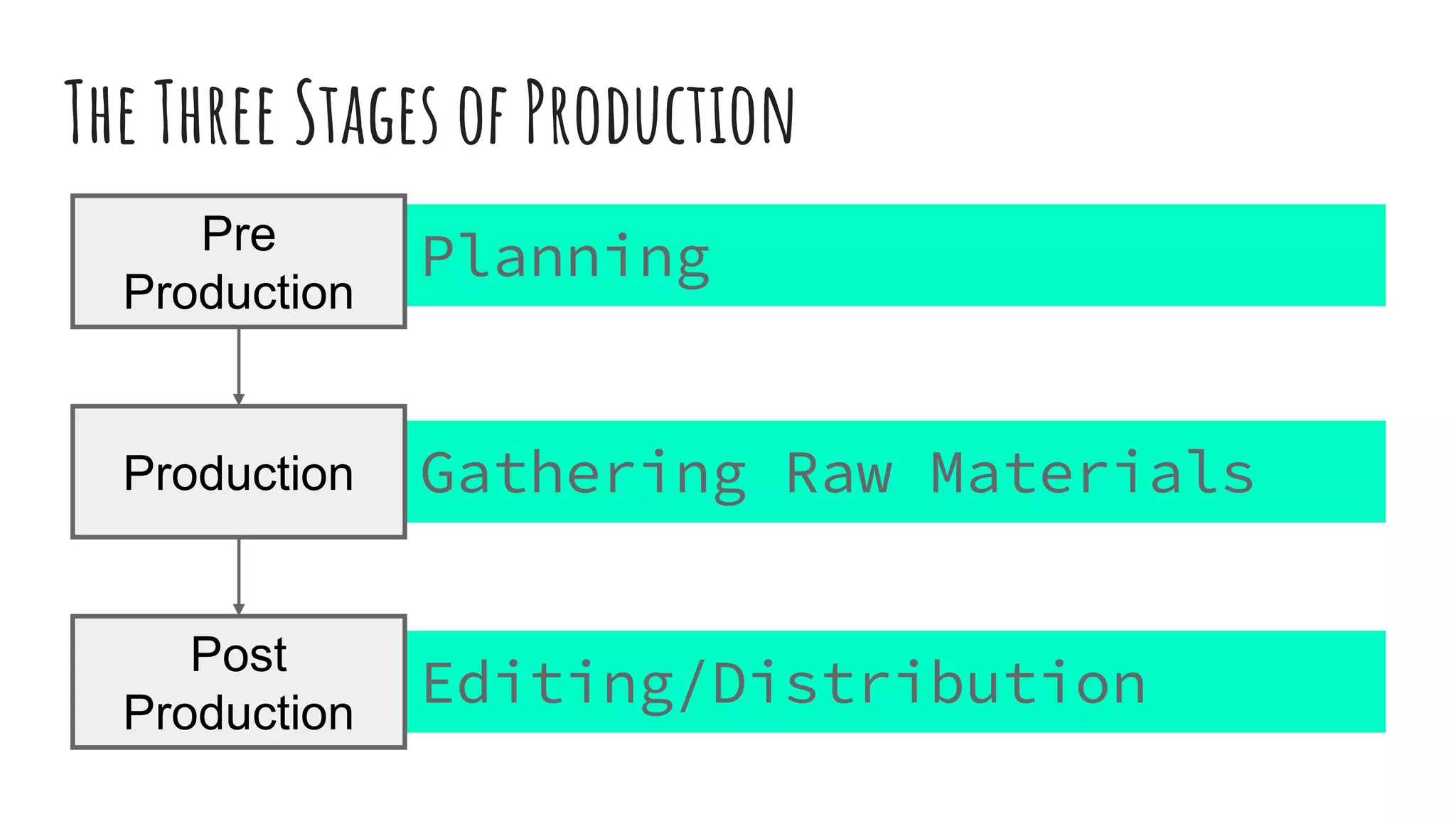
The document discusses the production process for media projects from inception through distribution. It describes the three main stages as pre-production, production, and post-production. Pre-production involves developing ideas, writing proposals and treatments, and planning through budgeting and scheduling. Production is the stage where raw materials like video, audio and images are gathered. Post-production is where the content is edited and prepared for distribution and promotion to audiences.