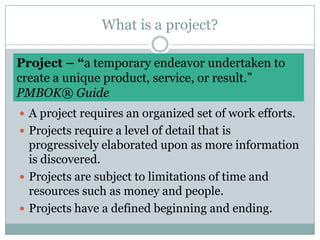
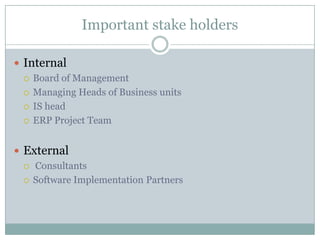
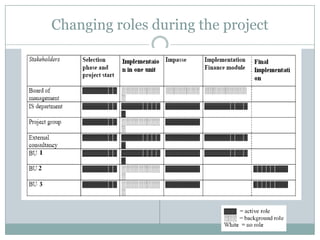
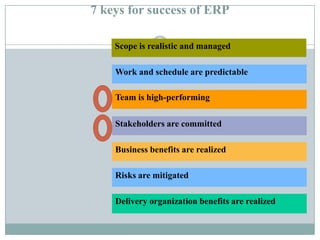
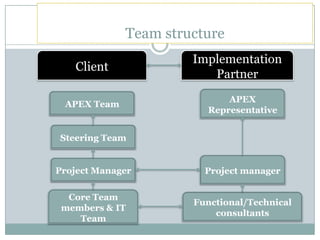
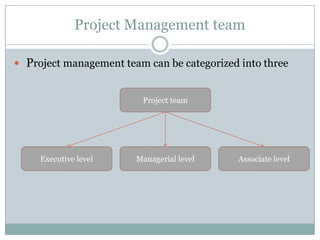
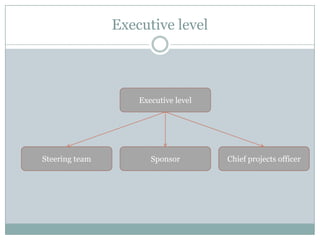
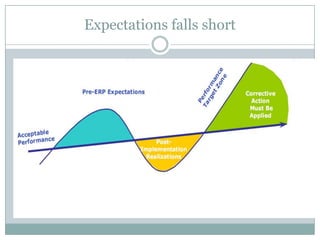
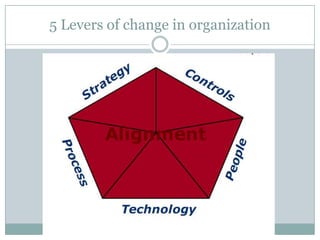
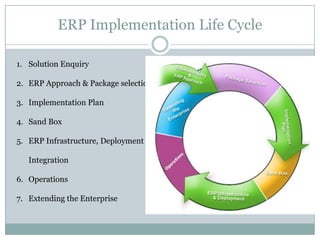
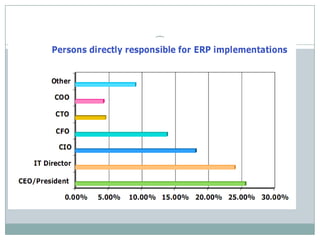
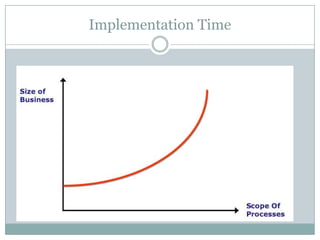
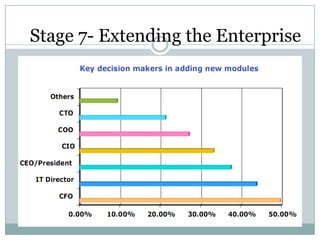
The document discusses project management and stakeholders in ERP implementation projects. It defines key terms like project, project management, and stakeholders. It identifies important internal and external stakeholders for ERP projects, like the board of management, business unit heads, IT heads, consultants, and software partners. It describes the roles and expectations of these stakeholders. It also discusses the importance of a project team and identifies the different levels in a project management team from executive to managerial to associate levels.