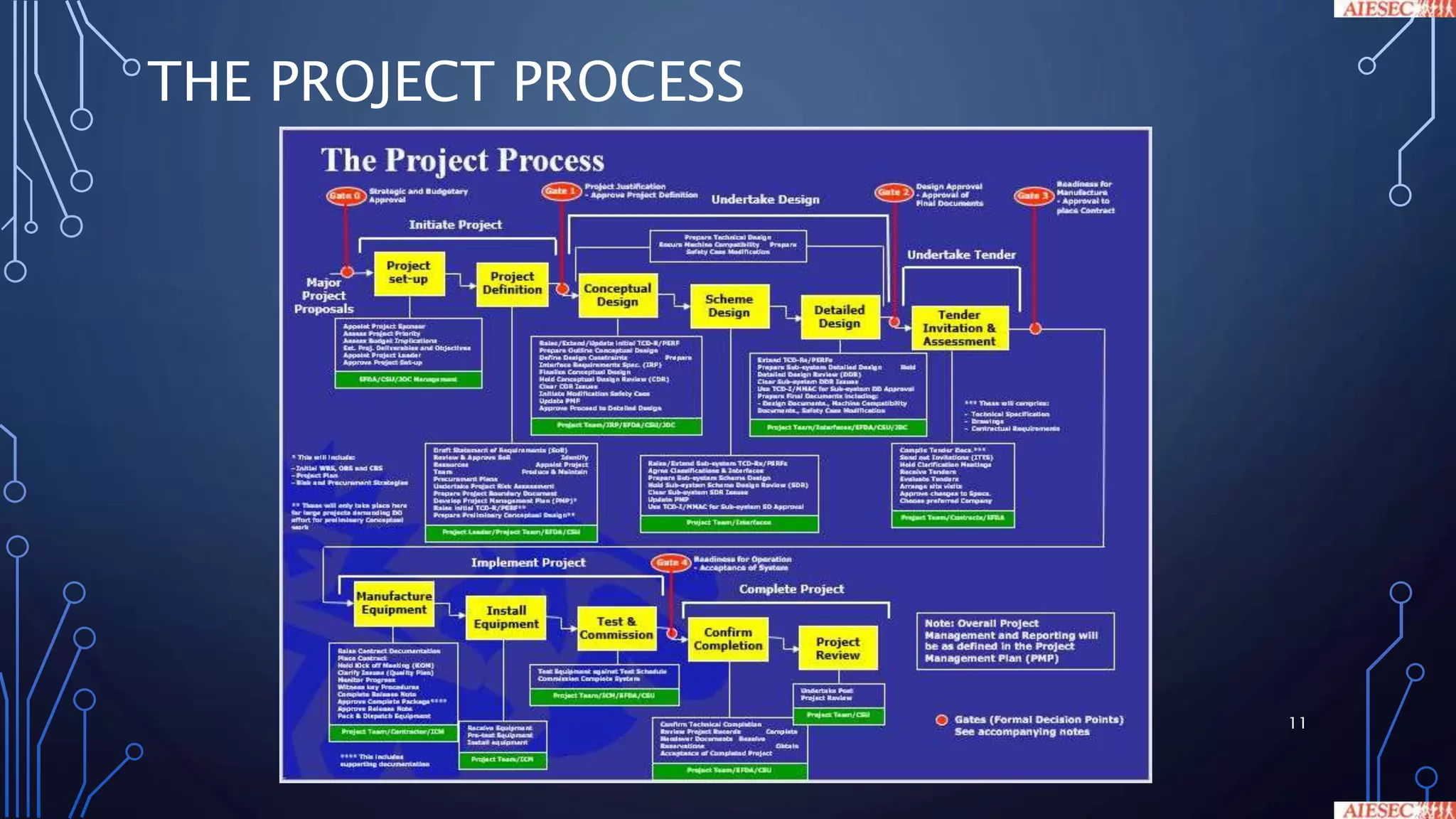
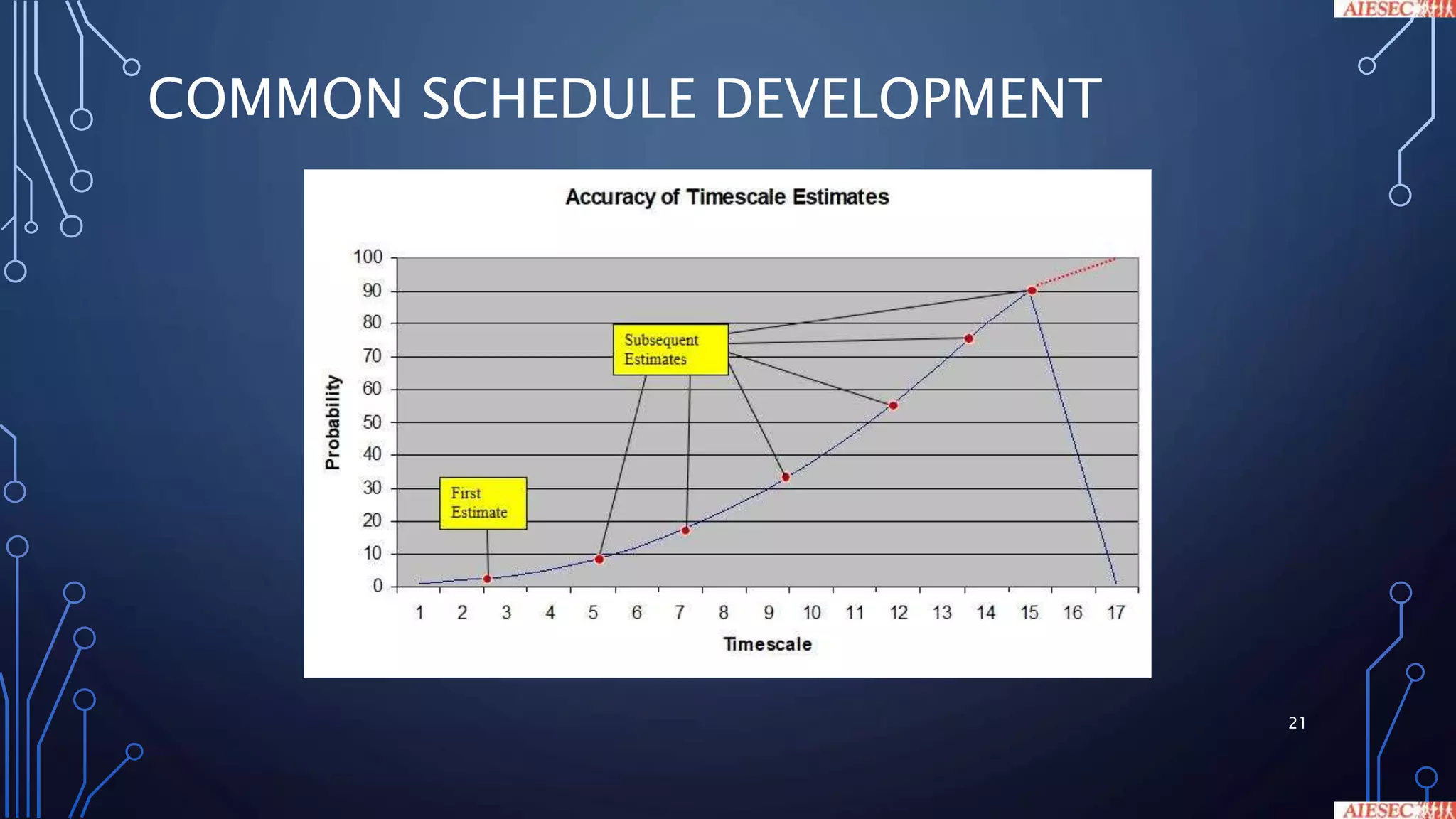
This document discusses key aspects of project management. It begins by outlining the objectives of project management, which include creating awareness of good practices, understanding essential elements like the project manager's leadership role and stakeholder engagement. It then defines what constitutes a project and project management. The document emphasizes the importance of planning, including developing a work breakdown structure and risk management process. It also covers the project manager's role, stakeholder engagement, and monitoring and control activities like progress reporting and corrective actions.