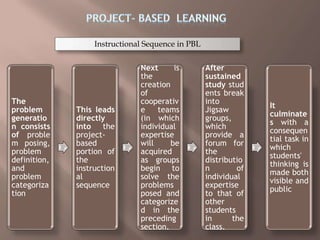
1. Project-based learning involves students shaping projects to fit their interests, conducting research from multiple sources, and presenting their results.
2. It requires critical thinking, collaboration, and communication across disciplines over an extended period of time.
3. Effective project-based learning starts with a real-world problem or question, allows active student investigation using various representation methods, and involves collaboration within a learning community.