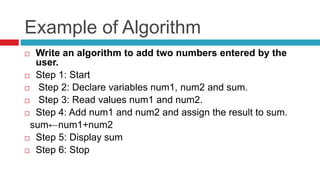
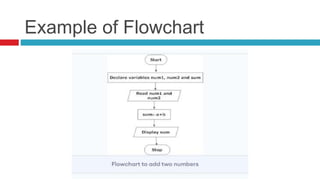
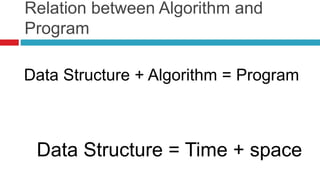
The document provides an introduction to programming concepts, including definitions of programming languages, algorithms, and flowcharts. It explains the relationship between data structures and algorithms in programming, along with a discussion of high-level programming languages and their applications, particularly emphasizing Python. Additionally, it covers how programs are executed and the environments in which Python can be developed and run.