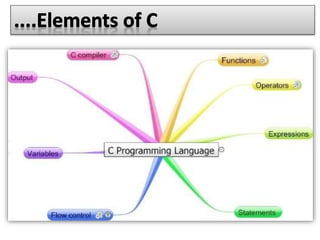
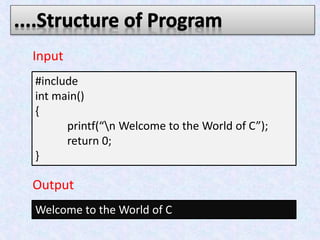
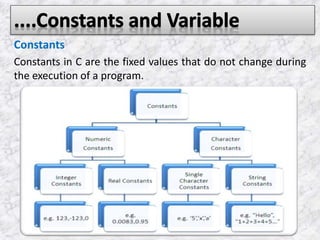
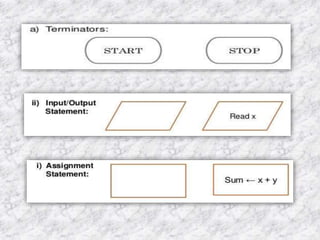
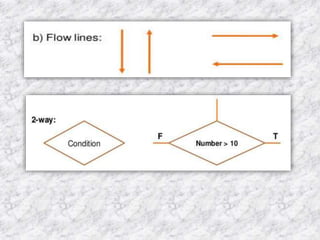
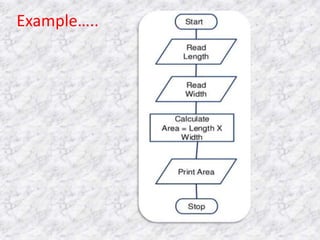
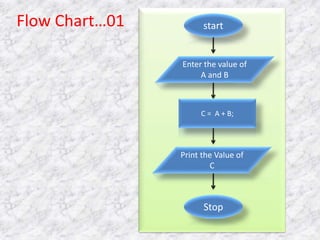
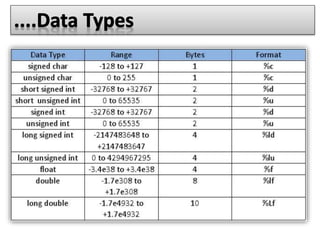
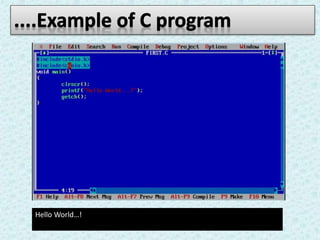
The document provides an overview of the C programming language. It states that C was developed in the 1970s at Bell Labs and became widely popular as it is efficient, powerful, and portable. It then discusses the basic components of a C program including header files, functions like main(), and library functions like printf(). It provides examples of simple C programs and explains the purpose and meaning of elements like #include, main(), braces {}, and return 0. Finally, it introduces concepts like variables, constants, and flowcharts to design algorithm logic.