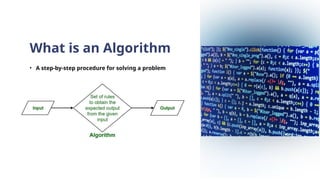
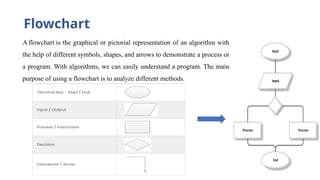
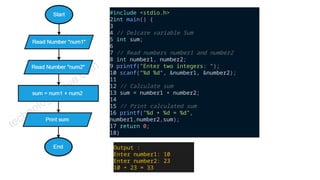
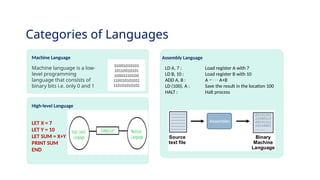
The document provides an overview of programming languages, their importance, and the concepts of algorithms and flowcharts. It covers the definition of programming language, the significance of learning to code, and examples of algorithms for tasks such as grade conversion and integer addition. Additionally, it distinguishes between system and application programming languages, highlights different categories of languages, and offers resources for further learning.