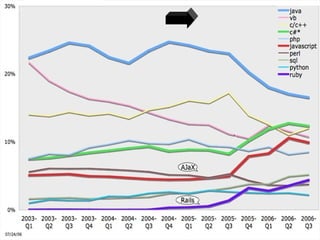
Programming involves writing computer programs and algorithms using programming languages. There are different types of programming languages from low-level machine languages close to hardware to high-level languages that are more abstract. Popular programming paradigms have evolved over time like structured programming, modular programming, object-oriented programming, and declarative programming to help manage complex programs. The most commonly used programming languages today include Java, Python, and JavaScript.