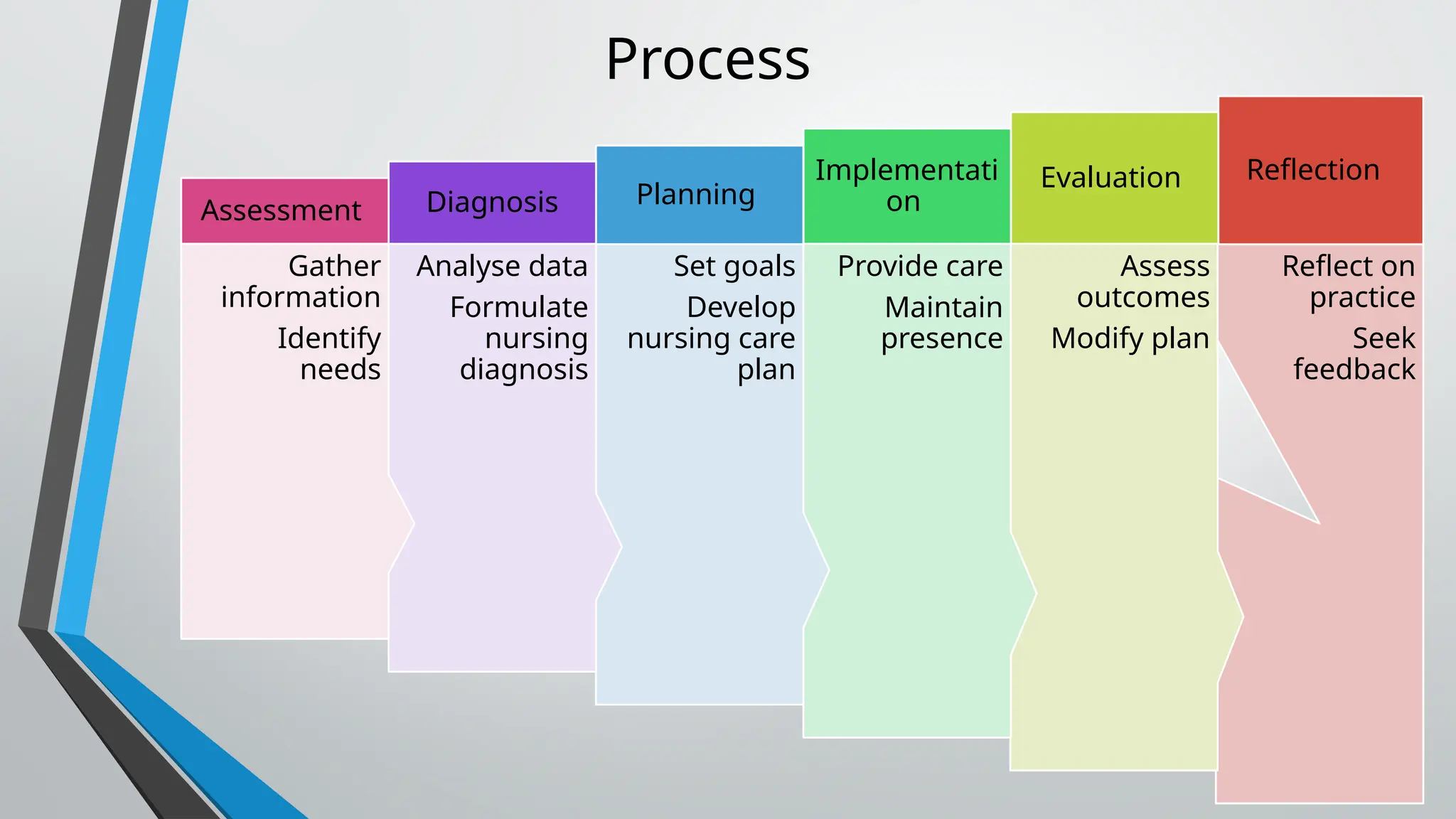
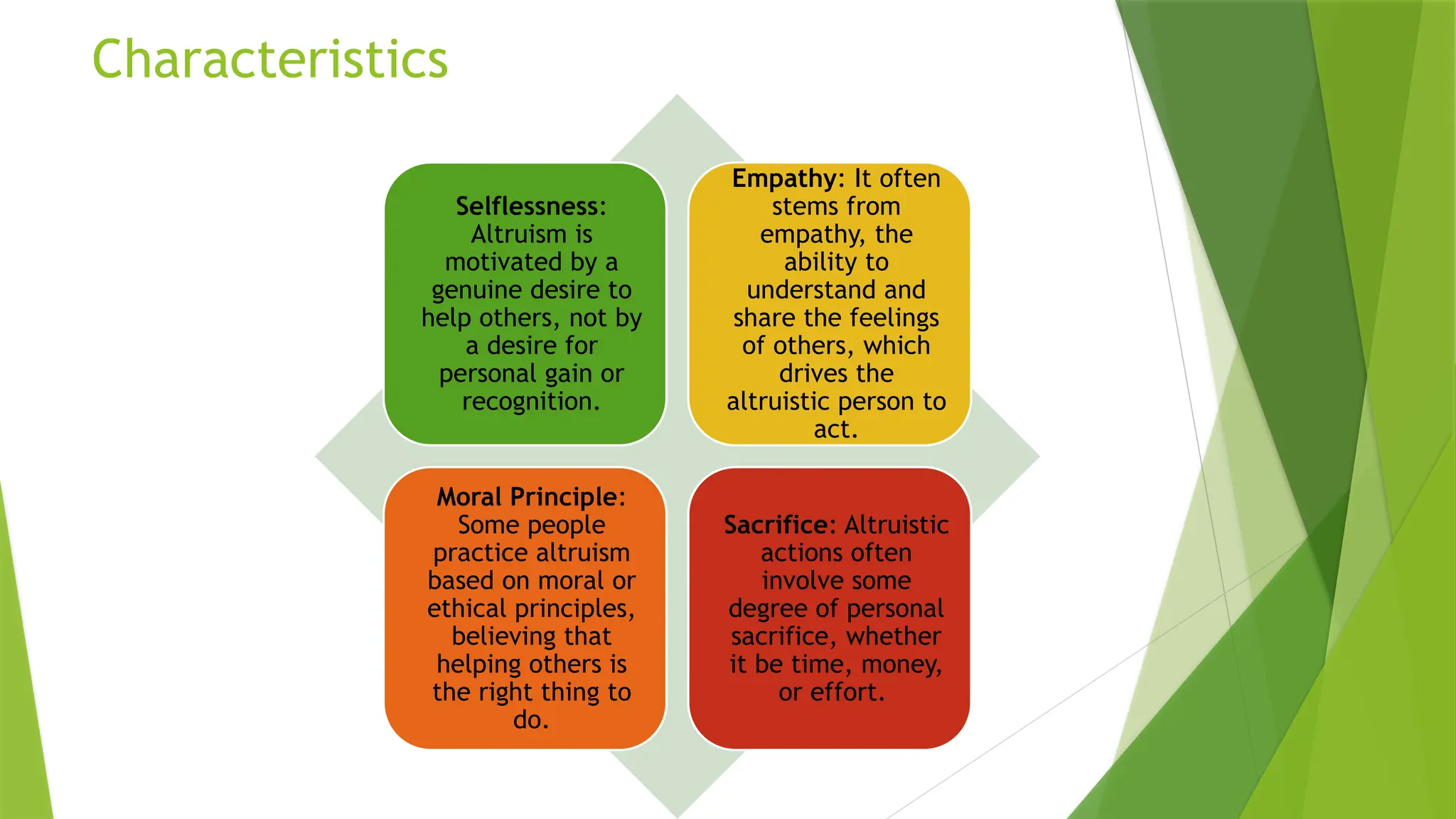
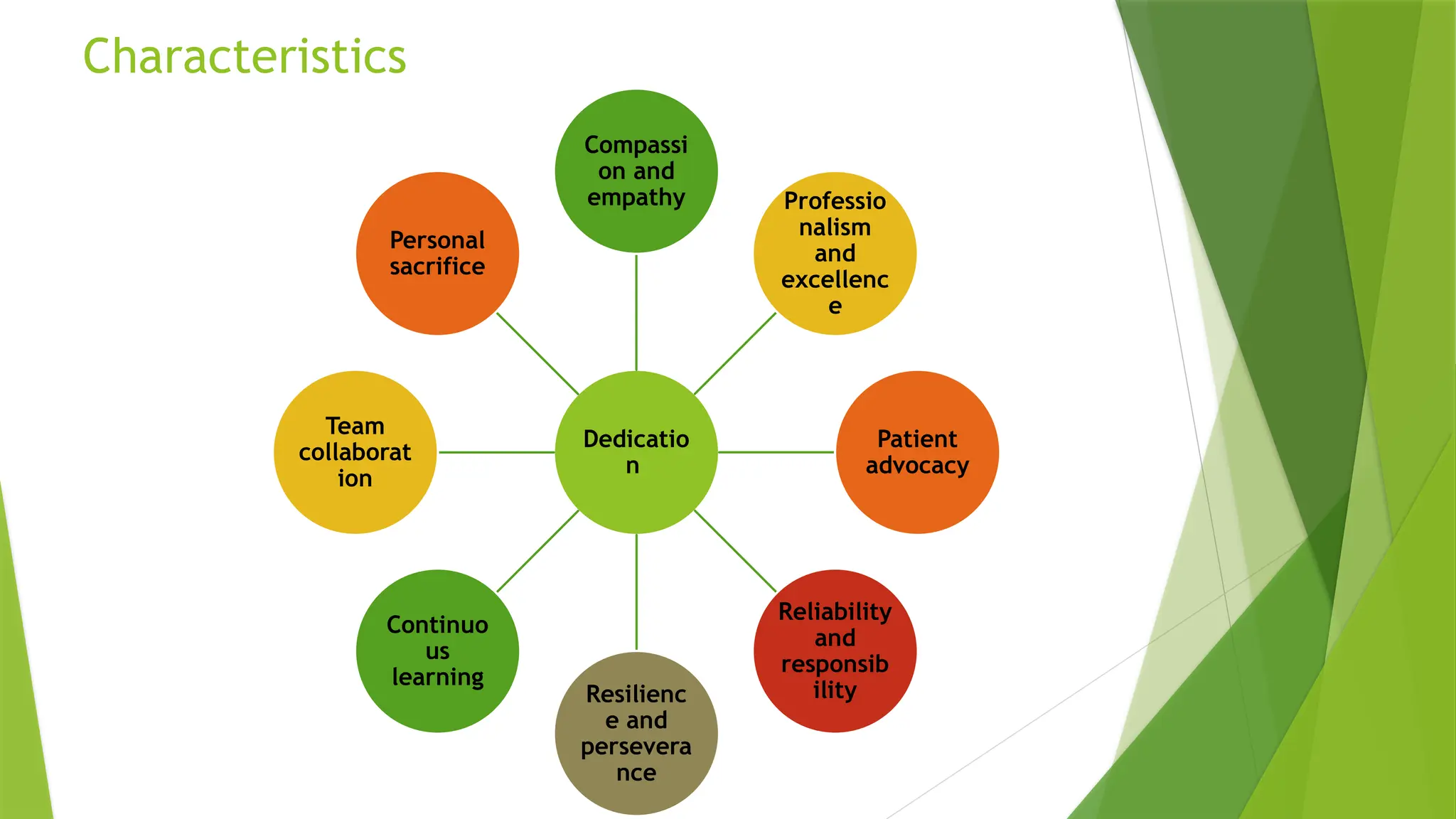
The document outlines the definition and criteria of professionalism in nursing, emphasizing characteristics such as competence, ethical behavior, and accountability. It also addresses challenges faced by nursing professionals, including ethical dilemmas and the balance between personal and professional identity, while detailing the importance of maintaining integrity and adherence to ethical standards. Additionally, it covers the roles of regulatory bodies, professional organizations, and the significance of continued education in ensuring high standards of nursing practice.