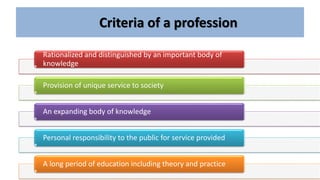
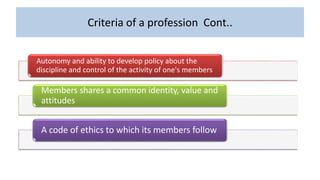
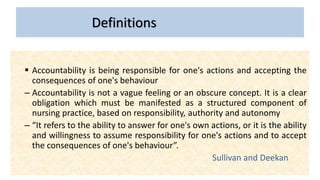
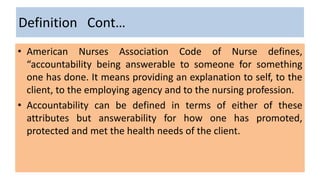
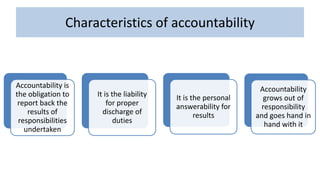
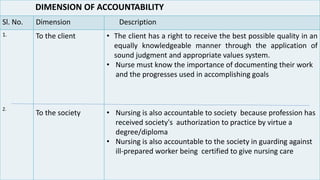
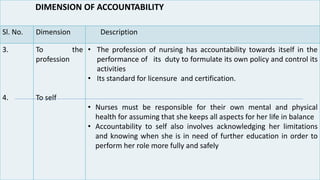
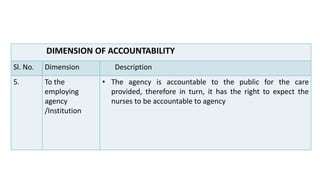
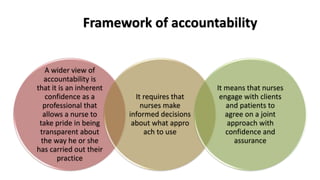
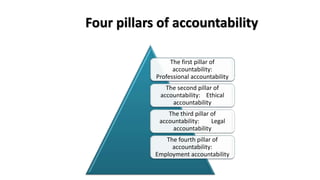
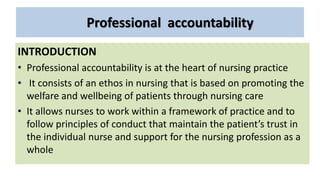
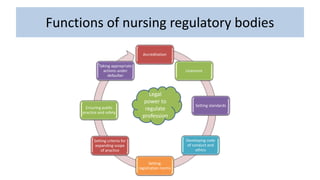
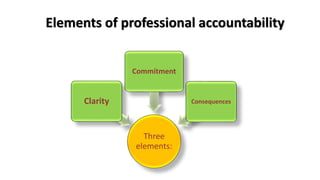
Professional nurses are accountable in several domains including professionally, legally, and ethically. They are accountable to themselves, clients, families, employers, regulatory bodies, and the general public for providing safe and effective care. Accountability involves being responsible and answerable for one's actions and decisions. Regulatory bodies set standards and codes of conduct to ensure accountability. The key principles of professional accountability are prioritizing patient interests, maintaining high standards, advocating for patients, and justifying all actions.