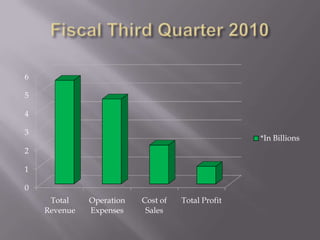
Starbucks has relatively high production costs due to costs of goods like dairy and labor. However, Starbucks has been able to remain profitable through measures like periodic price increases to offset rising costs of inputs. Starbucks also aims to lower production costs through its ownership of coffee farms and long-term contracts with suppliers. While price increases can reduce demand, Starbucks has seen continued customer loyalty as many view Starbucks drinks as inelastic.