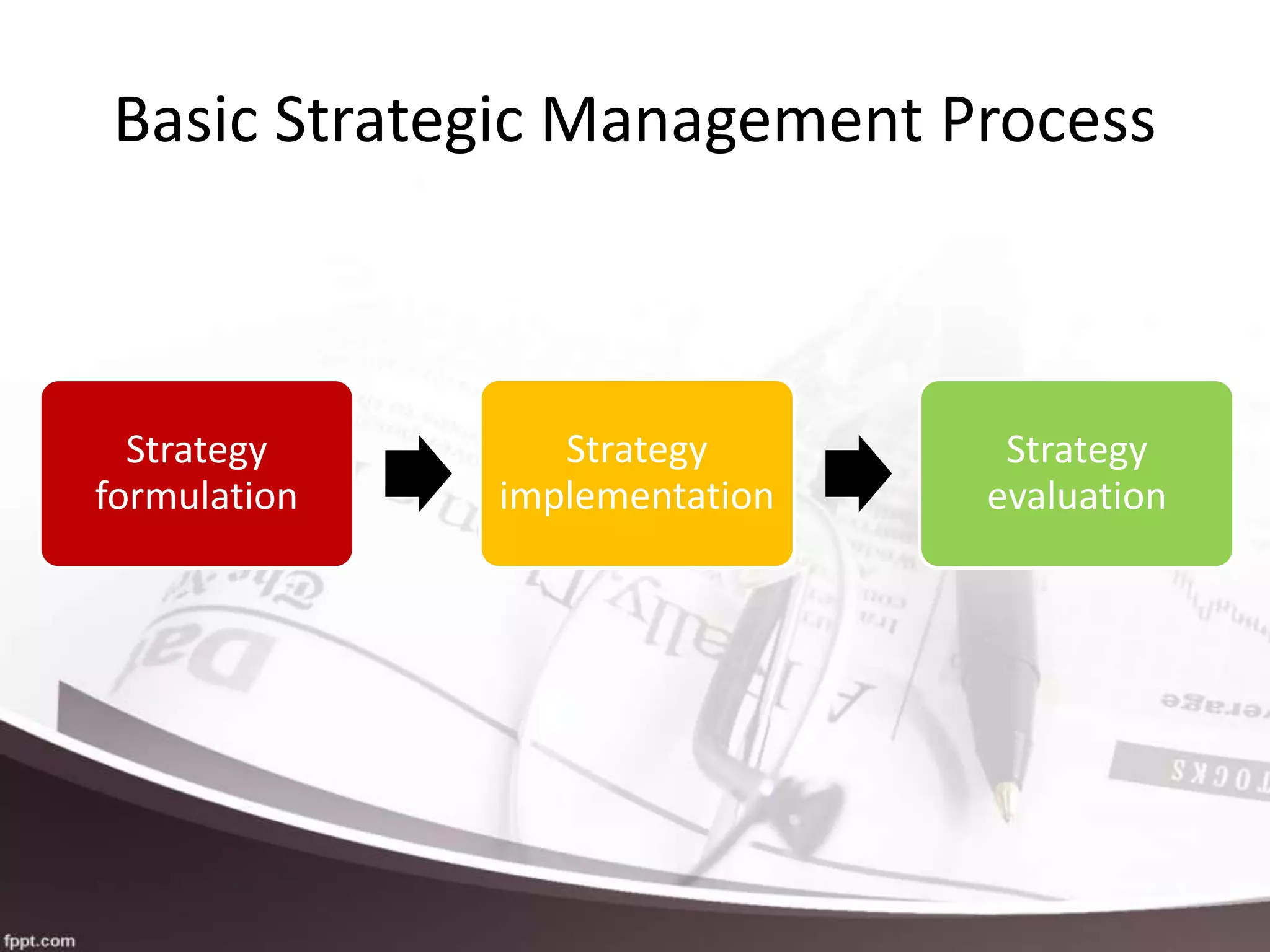
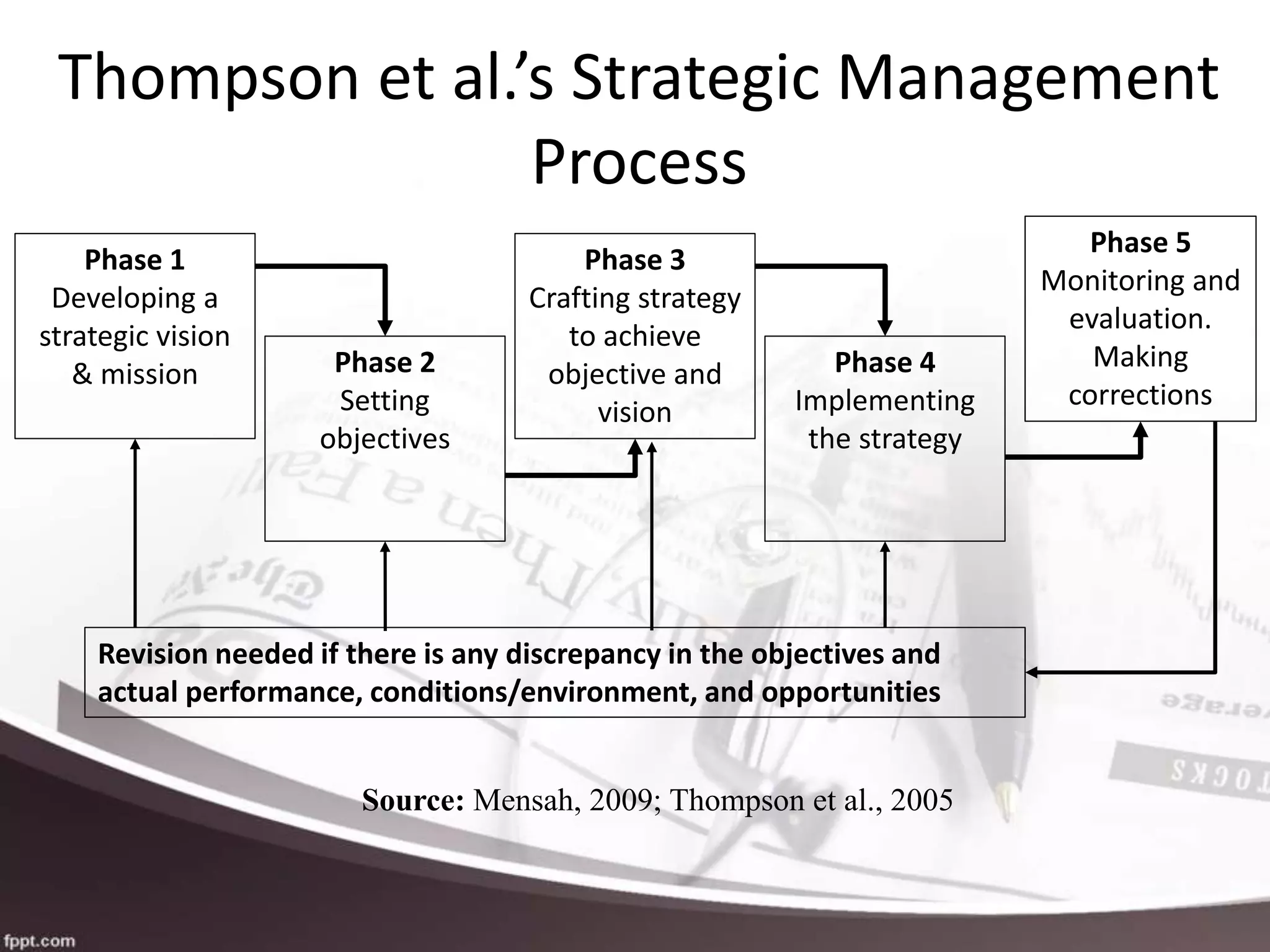
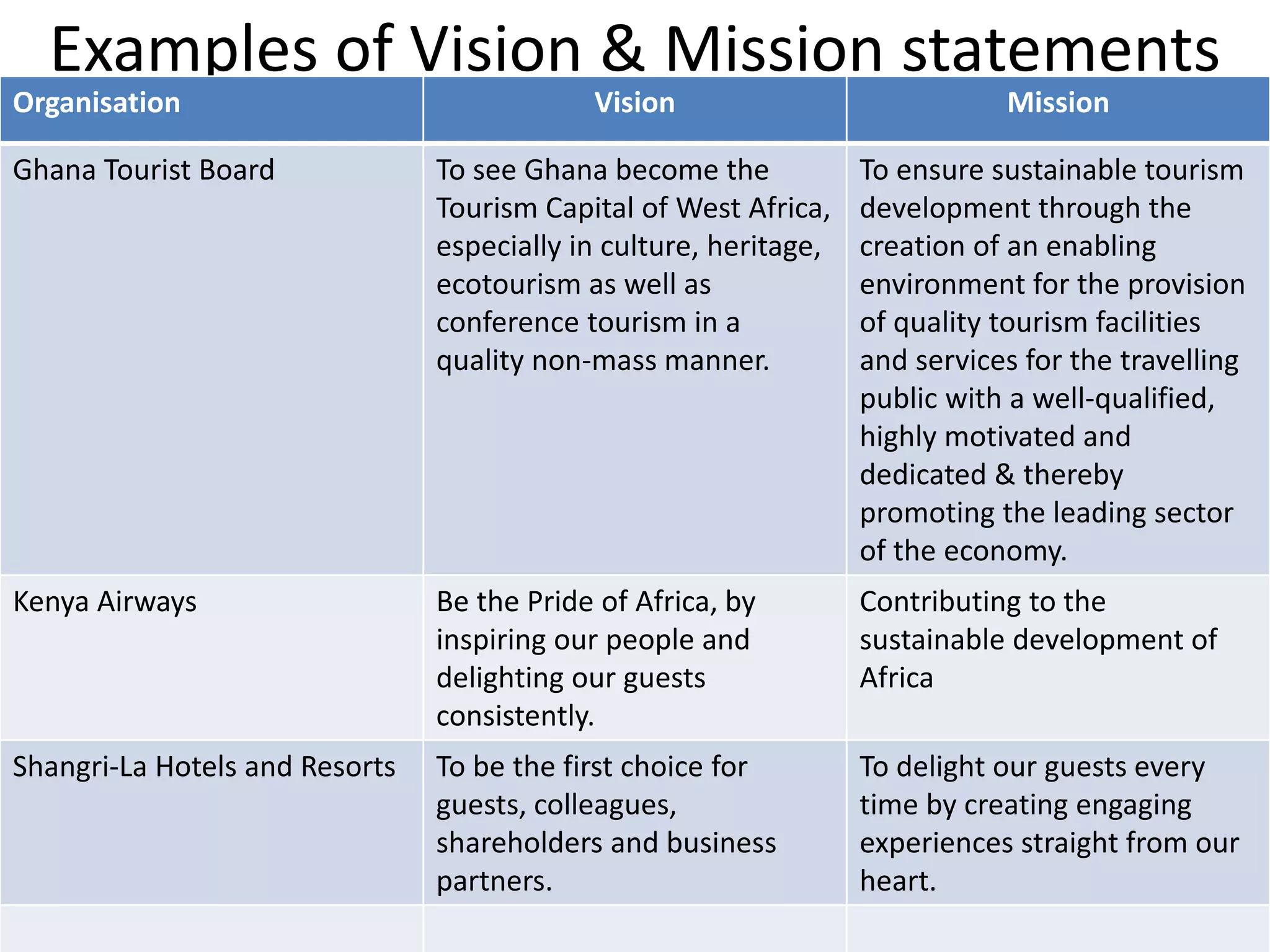
The document outlines the strategic management process for organizations in the hospitality and tourism industry. It discusses five key phases: 1) Developing a strategic vision and mission, 2) Setting objectives, 3) Crafting a strategy to achieve the vision and objectives, 4) Implementing the strategy, and 5) Monitoring performance and making corrections if needed. The process emphasizes setting specific, measurable goals and monitoring the environment to evaluate strategies and make adjustments to better achieve the organization's strategic goals.