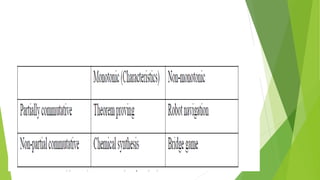
This document discusses characteristics that can be used to analyze problems for heuristic search methods. It identifies key dimensions such as decomposability, recoverability of solution steps, and consistency of knowledge. These dimensions can help determine appropriate search methods. The document also provides examples of different types of production systems, including monotonic, non-monotonic, commutative, and partially commutative systems.