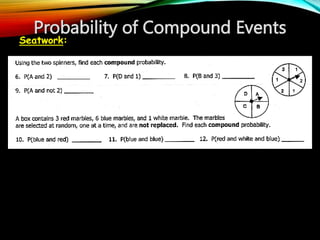
This document discusses probability and compound events. It defines key probability terms like experiment, outcomes, sample space, and events. It also covers unions and intersections of events. Examples are provided to illustrate finding the union and intersection of events. The document concludes with assignments, including answering practice problems on unions and intersections of events, and generating additional problems involving the probability of compound events.