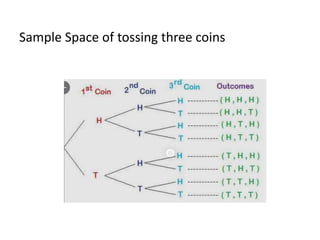
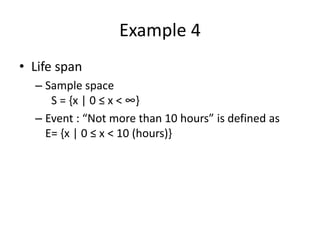
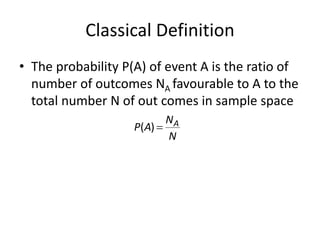
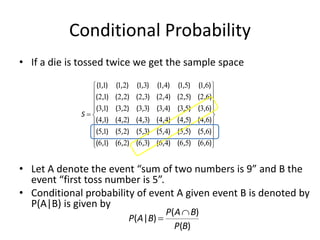
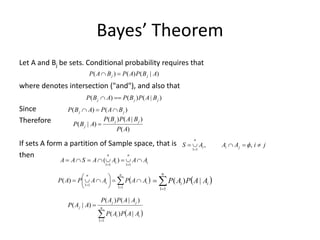
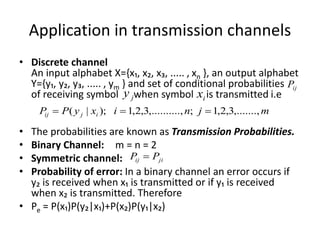
This document discusses probability theory and random processes. It defines key concepts such as random experiments, sample spaces, events, and probability. Random experiments are processes that can be repeated under the same conditions, with each repetition called a trial. A sample space contains all possible outcomes of an experiment. Events are subsets of outcomes from the sample space. Probability is defined axiomatically and through relative frequency. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating probabilities of events using the classical definition. Properties of probability like mutually exclusive and conditional probability are also explained.


























![• If A and B are independent events show that and B; A and ; and are also
independent events
Proof :
The events and are mutually exclusive and , therefore
A B A B
B
A B
A B
B
A
B
A
P(B)
B
A
P
B
A
P
B
A
P
-
P(B)
B
A
P
A)P(B
P
-
P(B)
B
A
P
P(A)]
-
P(B)[1
B
A
P
t.)
independen
are
B
and
A
(
)
A
P(B)P(
B
A
P
t.
independen
are
B
and
A
B
A
P
B
A
P
B
A
P
1 B)
P(A
P(B
A)
P
B
A
P
1
P(A)P(B)
P(B
A)
P
B
A
P
1 t.)
independen
are
B
and
A
(
P(A)]
P(B
A)]
P
[
B
A
P
1
[
1
)
B
)P(
A
P(
]
P(B
A)][1
P
[
B
A
P
1 t.
independen
are
B
and
A
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prp-unit1-230305182841-30105272/85/PRP-Unit-1-pptx-33-320.jpg)



![Combinations nCr or C(n, r) or
Example : There are m boys and n girls in a class. A team of k students is to be
selected.
(a) How many teams can be formed?
Answer: C(n+m, k)
(b) How many teams can be formed if there are i boys in each team?
Answer: C(n, i) C(m, k-i)
If we consider all teams as defined in (b) with i = 0, 1, 2, ......, k; then
If n = m = k
)
(n
r
!
)!
(
!
)
,
(
r
r
n
n
r
n
C
)
,
( r
n
n
C
k
i
i
k
m
C
i
n
C
k
m
n
C
1
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
.
..........
)
,
(
)
,
(
......
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
)
,
(
0
2
2
1
1
0
2
n
C
n
n
C
i
n
n
C
i
n
C
n
n
C
n
C
n
n
C
n
C
n
n
C
n
C
n
n
C
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
0
2 )]
,
(
[
.
..........
)]
,
(
[
......
]
)
,
(
[
)]
,
(
[
)]
,
(
[
)
,
( n
n
C
i
n
C
n
C
n
C
n
C
n
n
C
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prp-unit1-230305182841-30105272/85/PRP-Unit-1-pptx-37-320.jpg)

