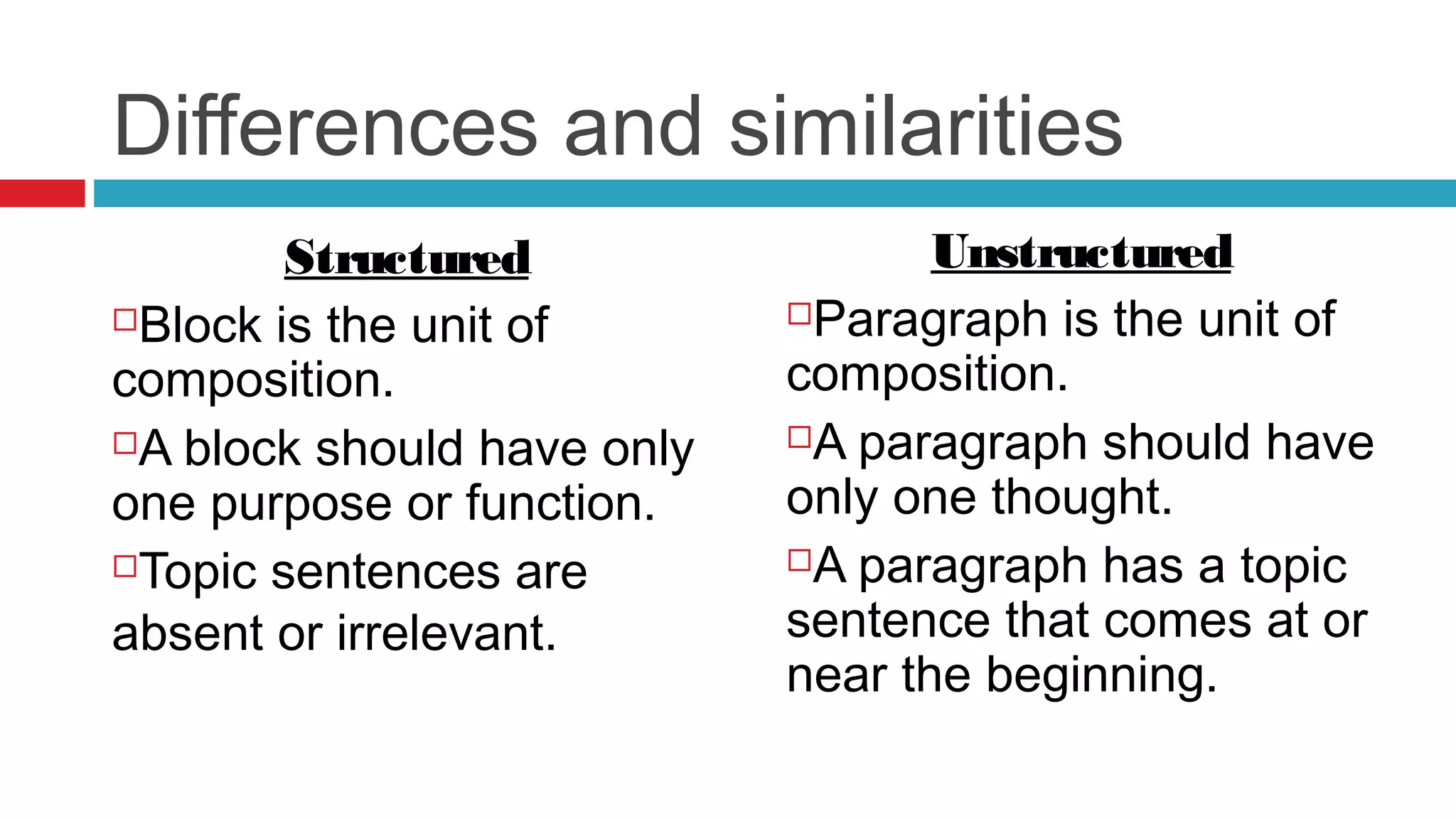
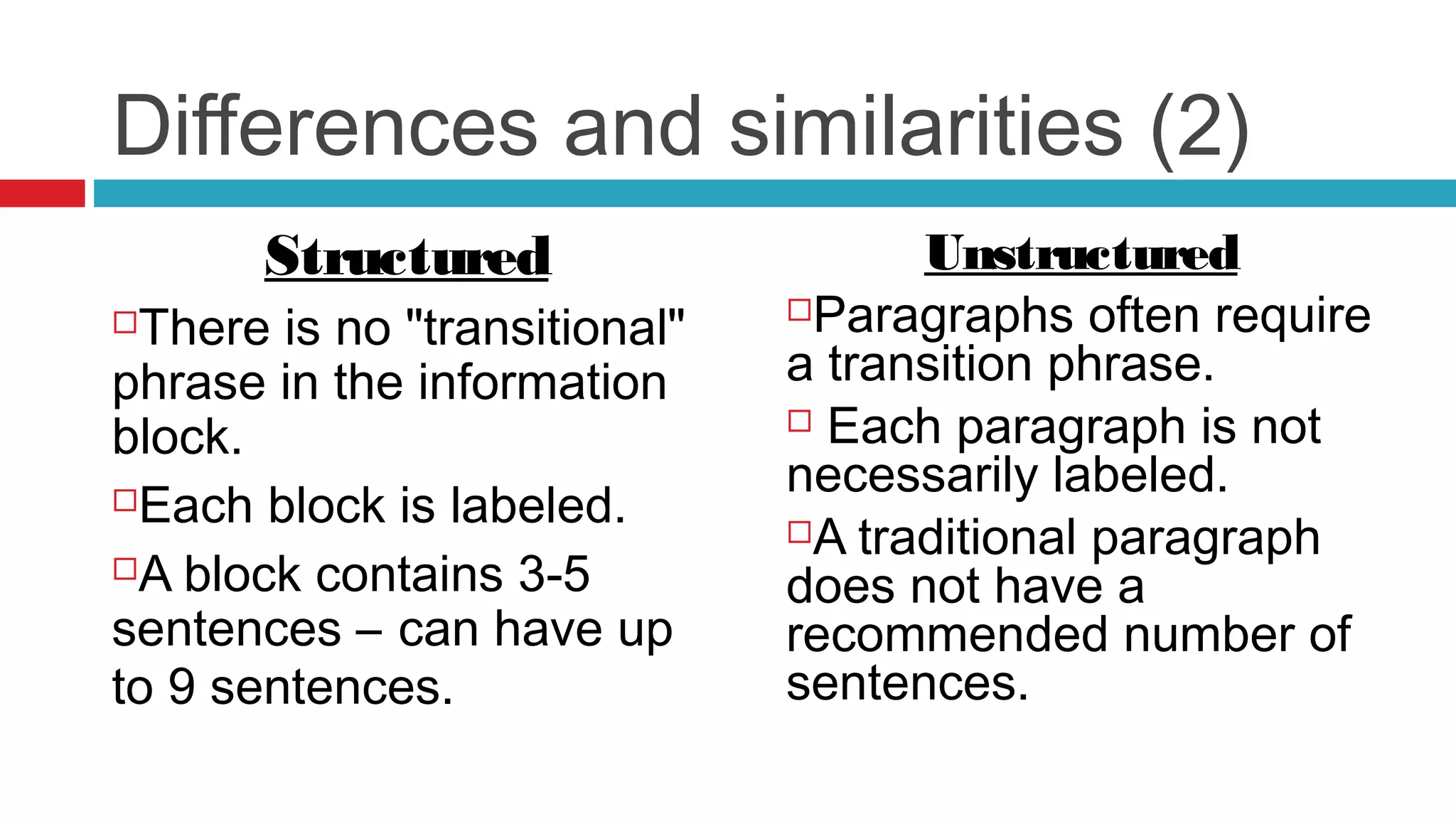
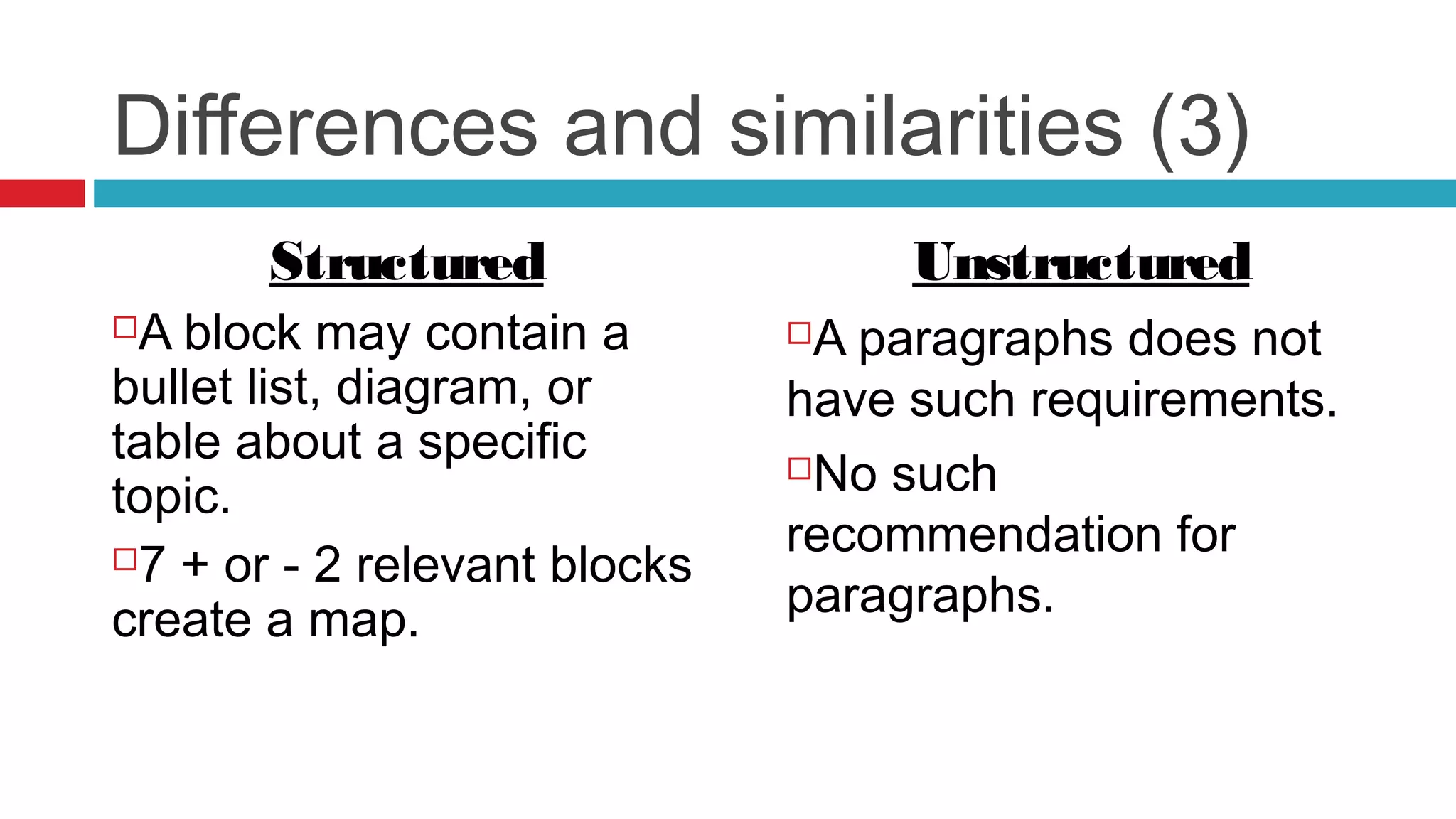
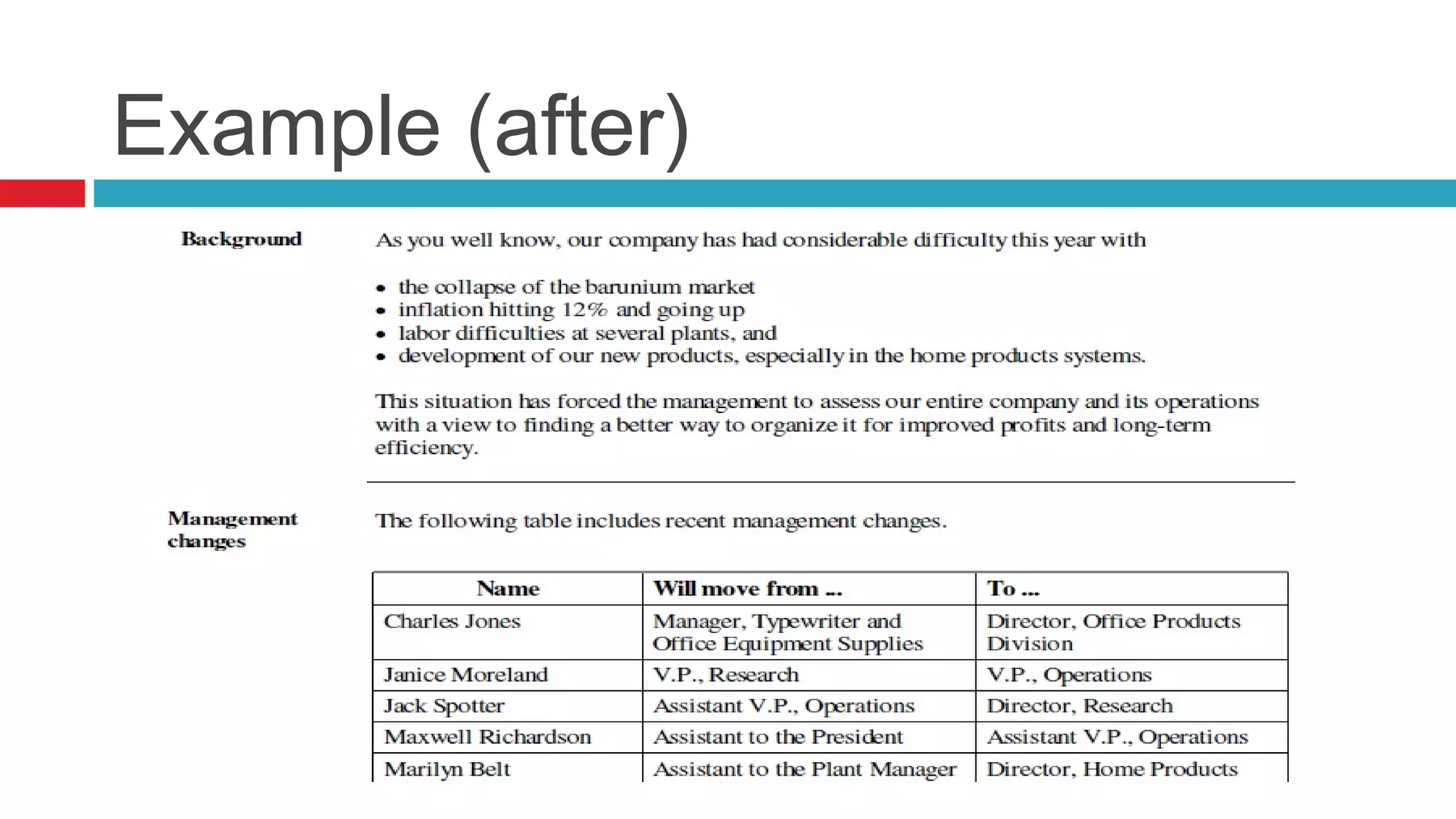
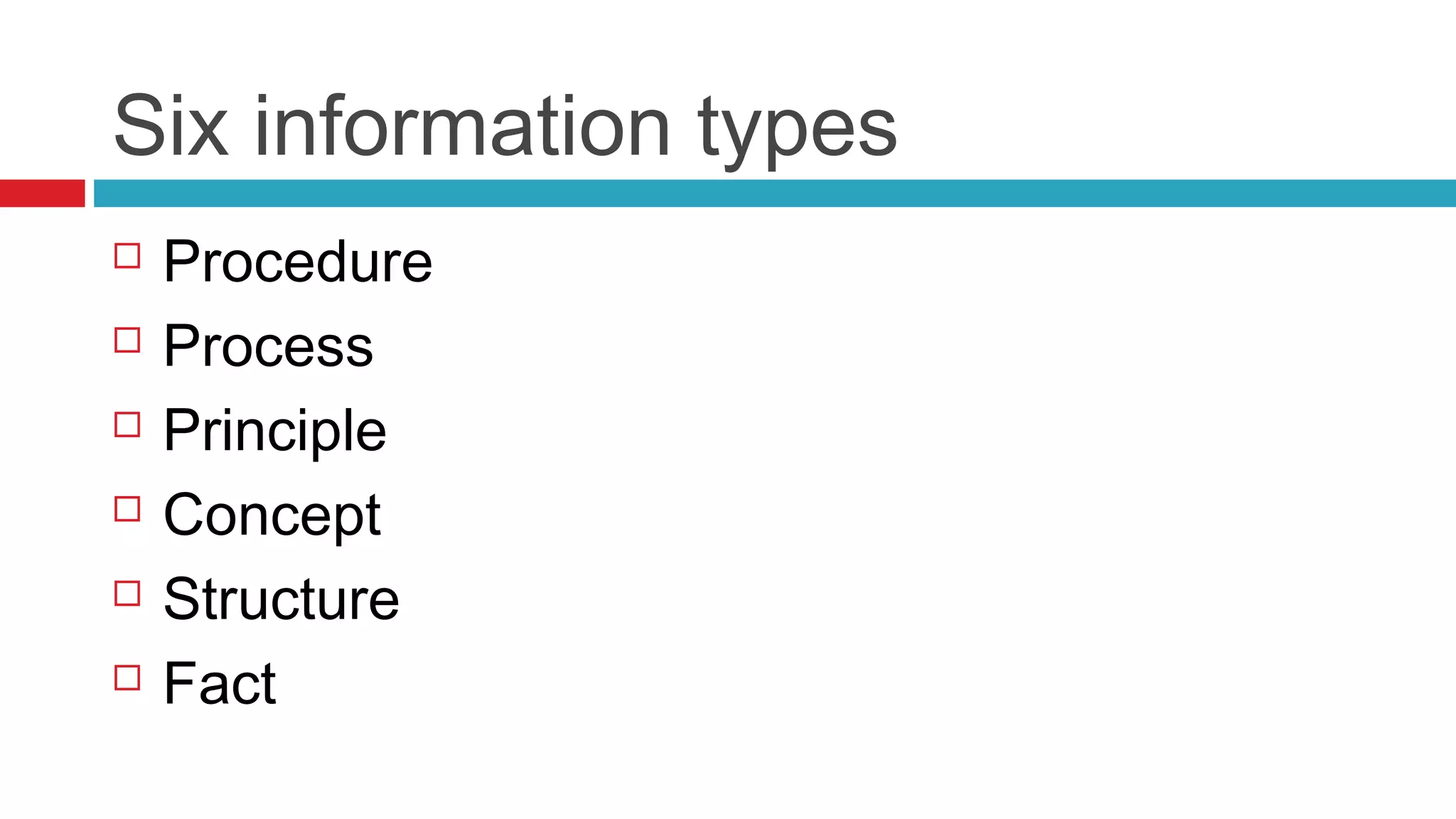
This document introduces the concepts of structured and unstructured writing, highlighting key differences and benefits of structured writing. It describes structured writing as creating independent information blocks for better accessibility, while unstructured writing typically involves paragraphs with topic sentences. The document also outlines principles of structured writing and types of information that can be organized using this method.