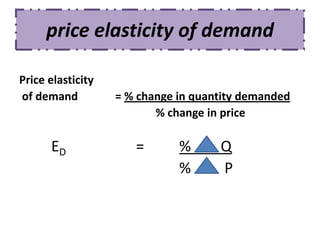
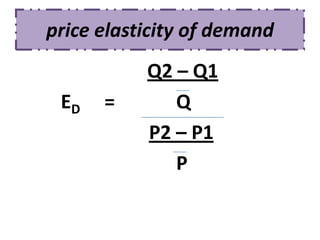
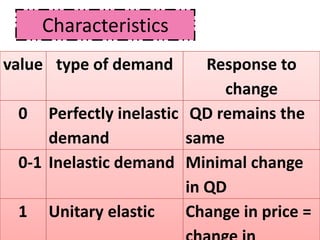
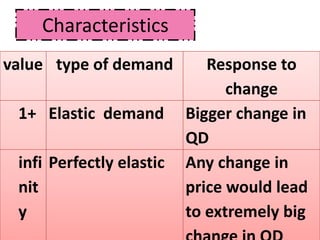
Here are the steps to solve the problems:
1. DEMAND FOR good Y
A. Q1 = 160; P1 = 110
B. Q2 = 240; P2 = 90
% change in Q = (Q2 - Q1)/Q1 = (240 - 160)/160 = 50%
% change in P = (P1 - P2)/P1 = (110 - 90)/110 = 18.18%
ED = % change in Q / % change in P = 50/18.18 = 2.75
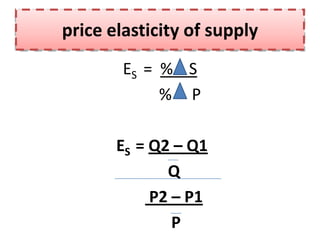
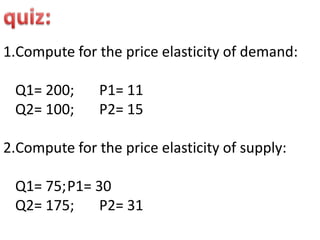
2. SUPPLY FOR good X
Q1 = 75; P1 = 30
Q2 = 175; P2 = 31
% change in