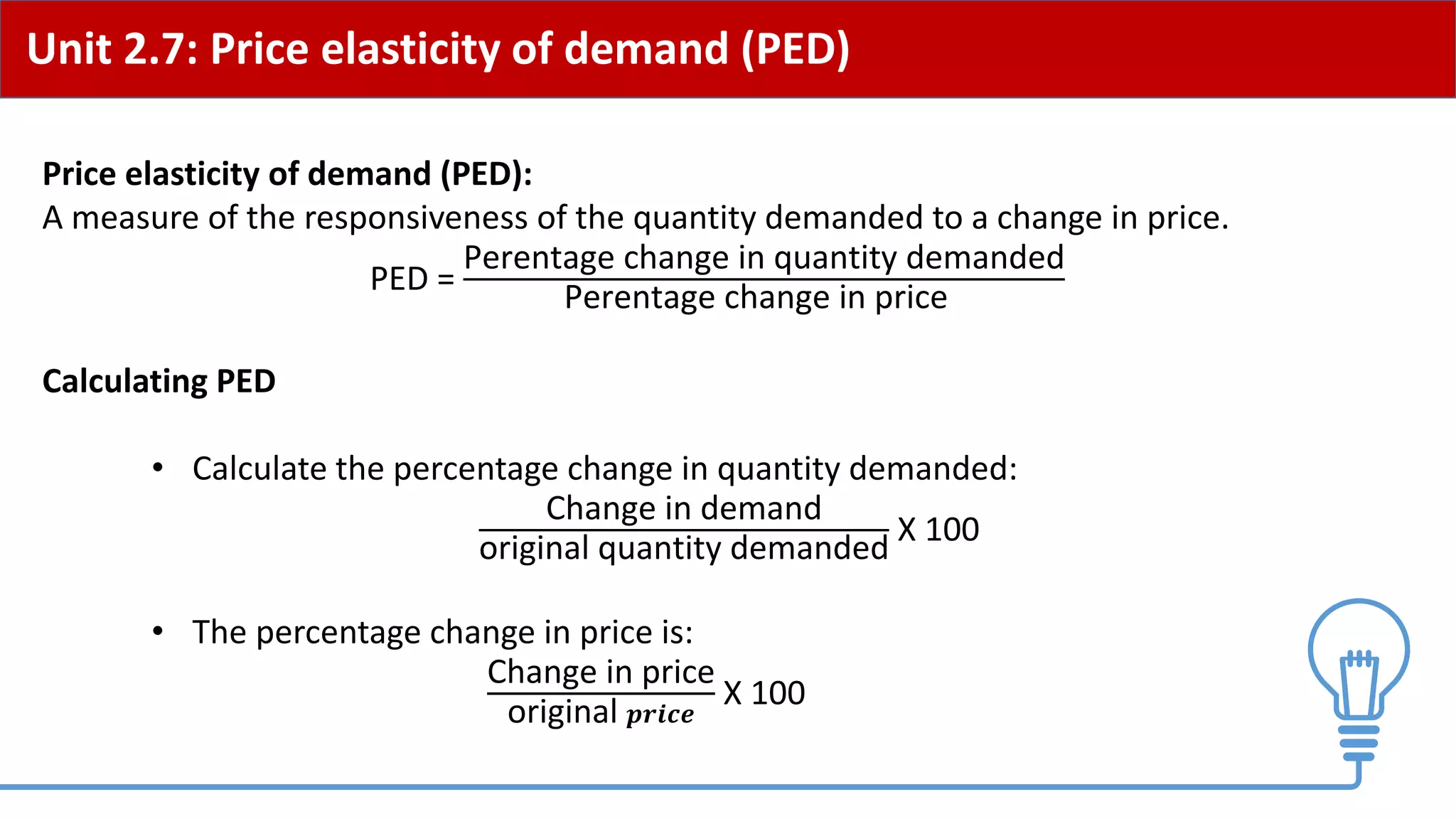
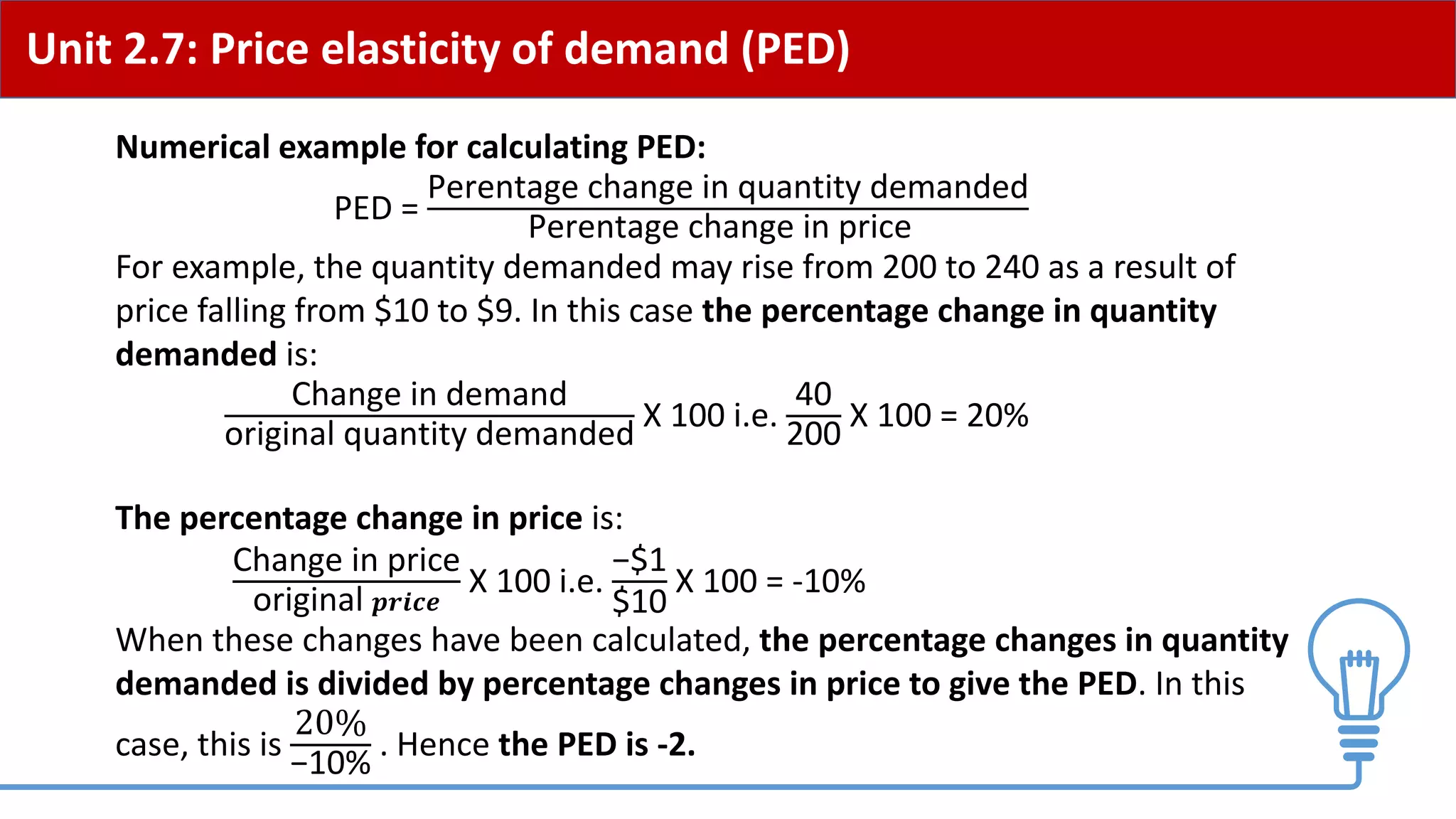
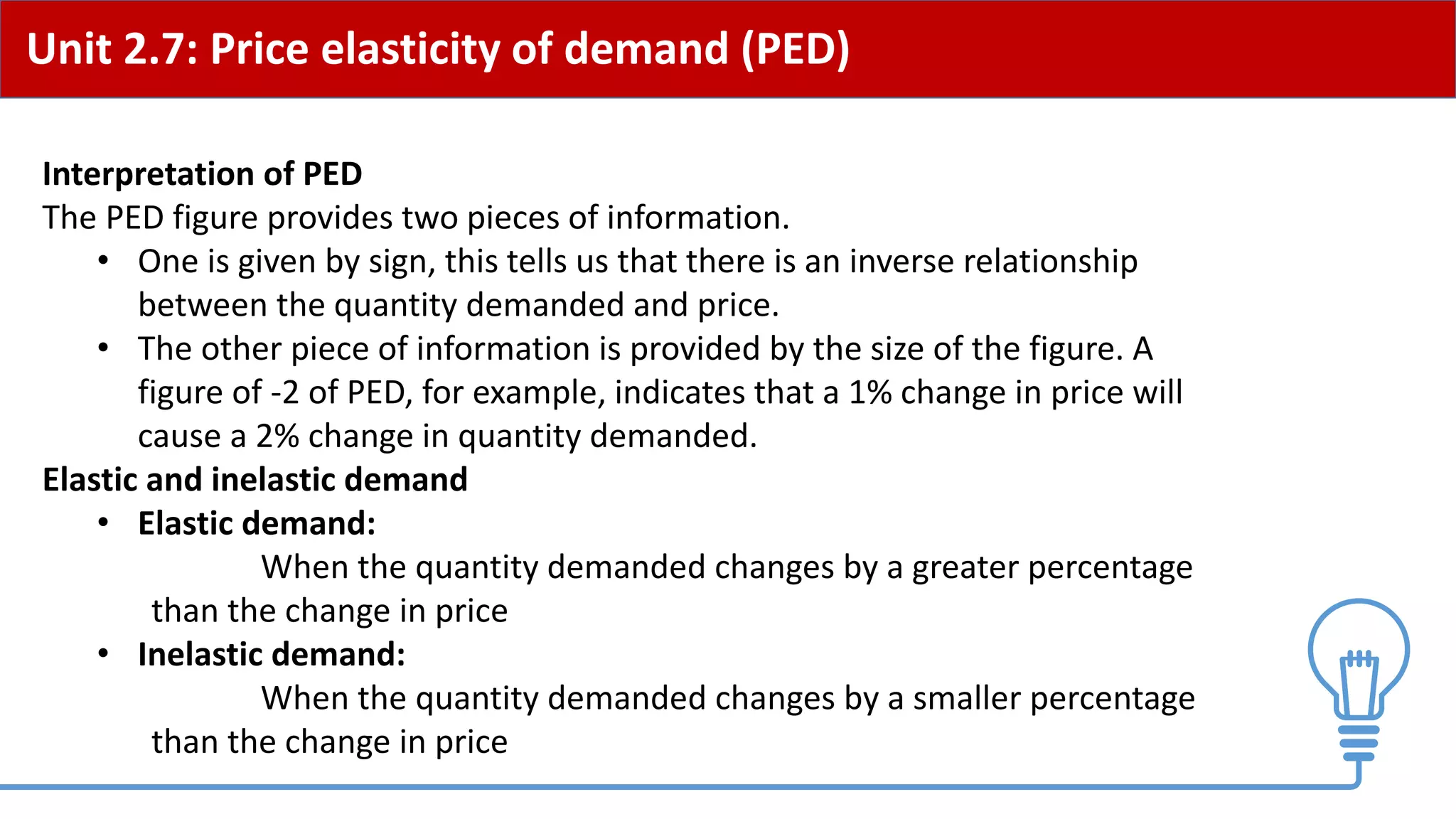
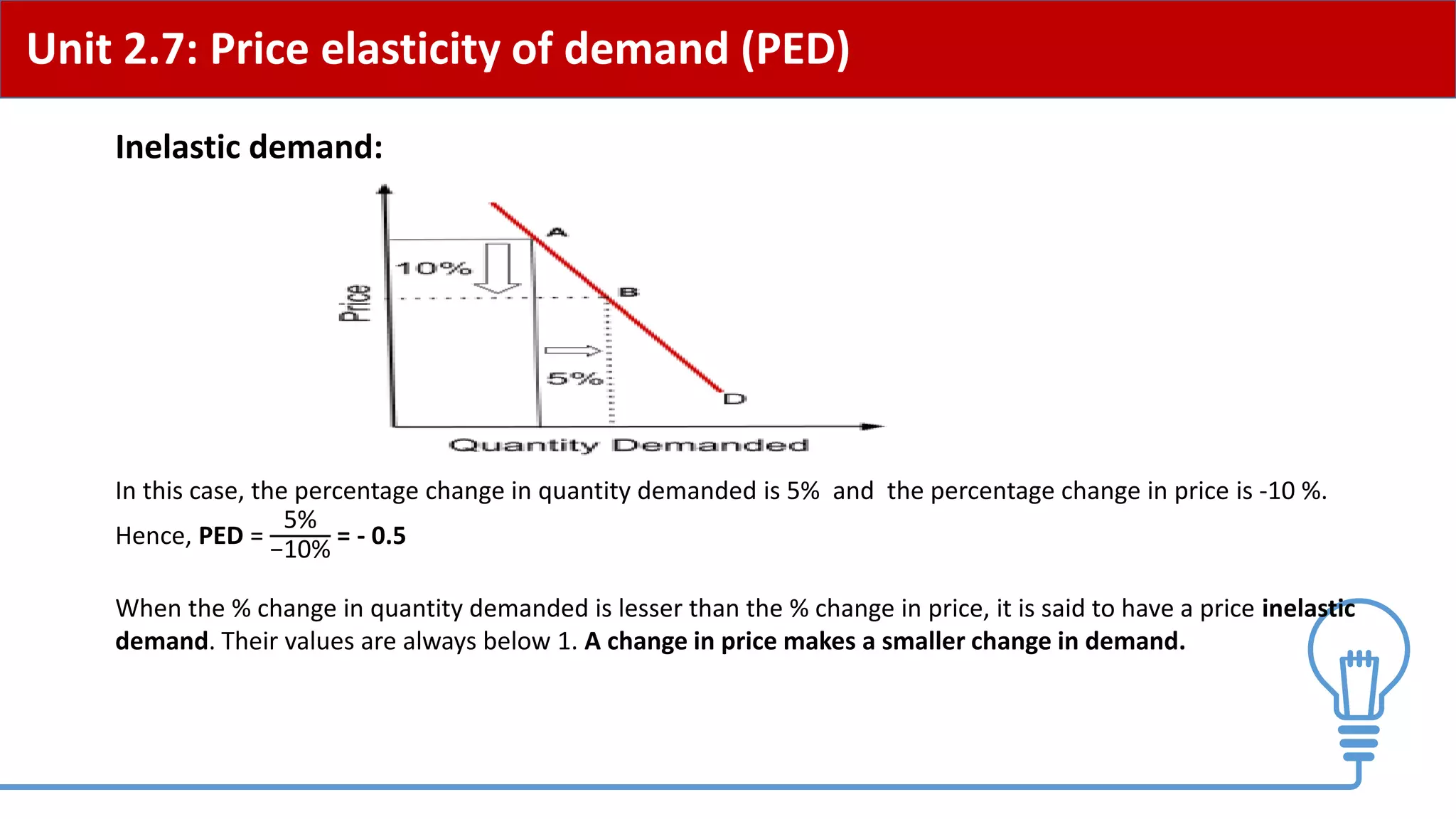
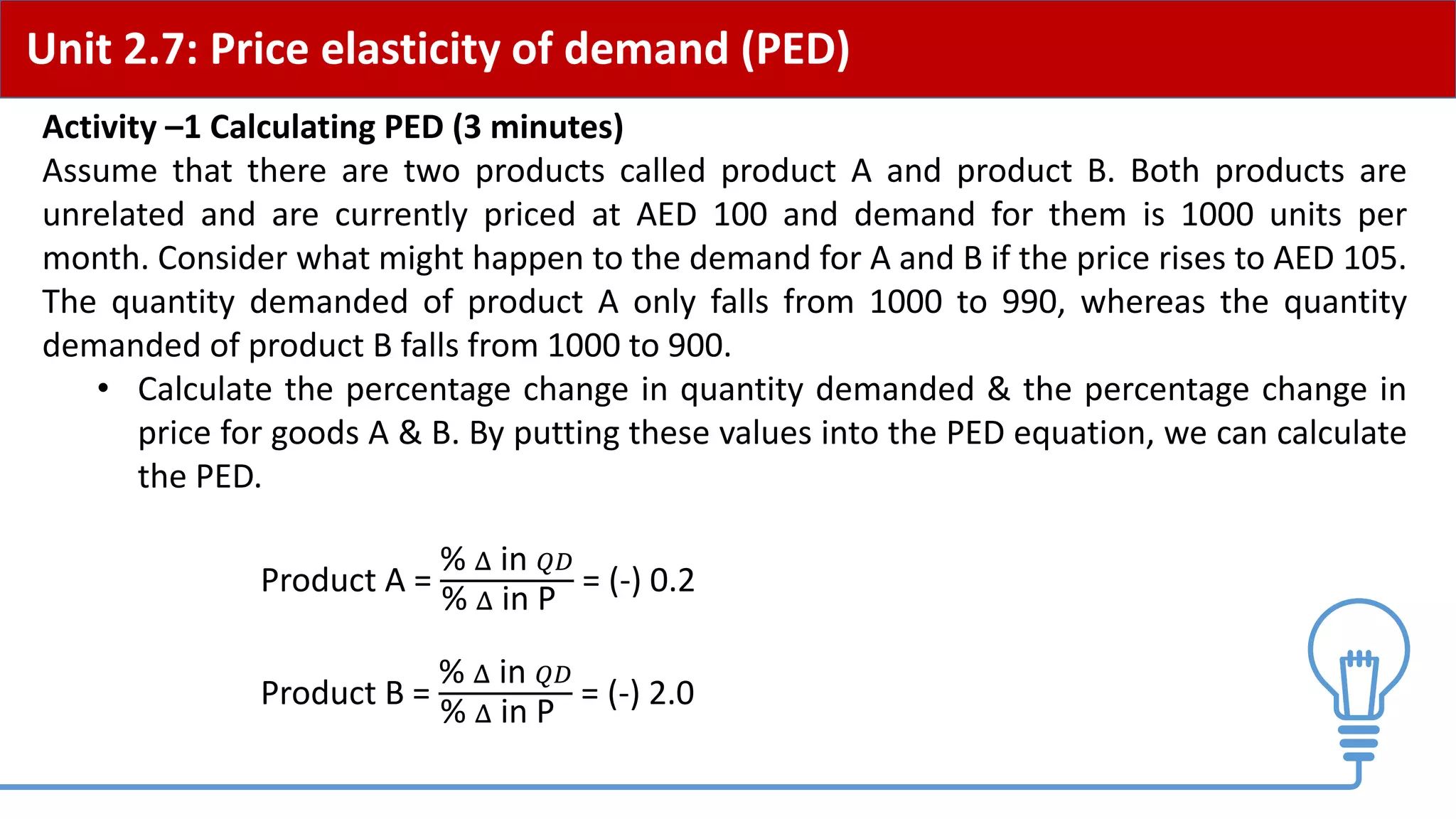
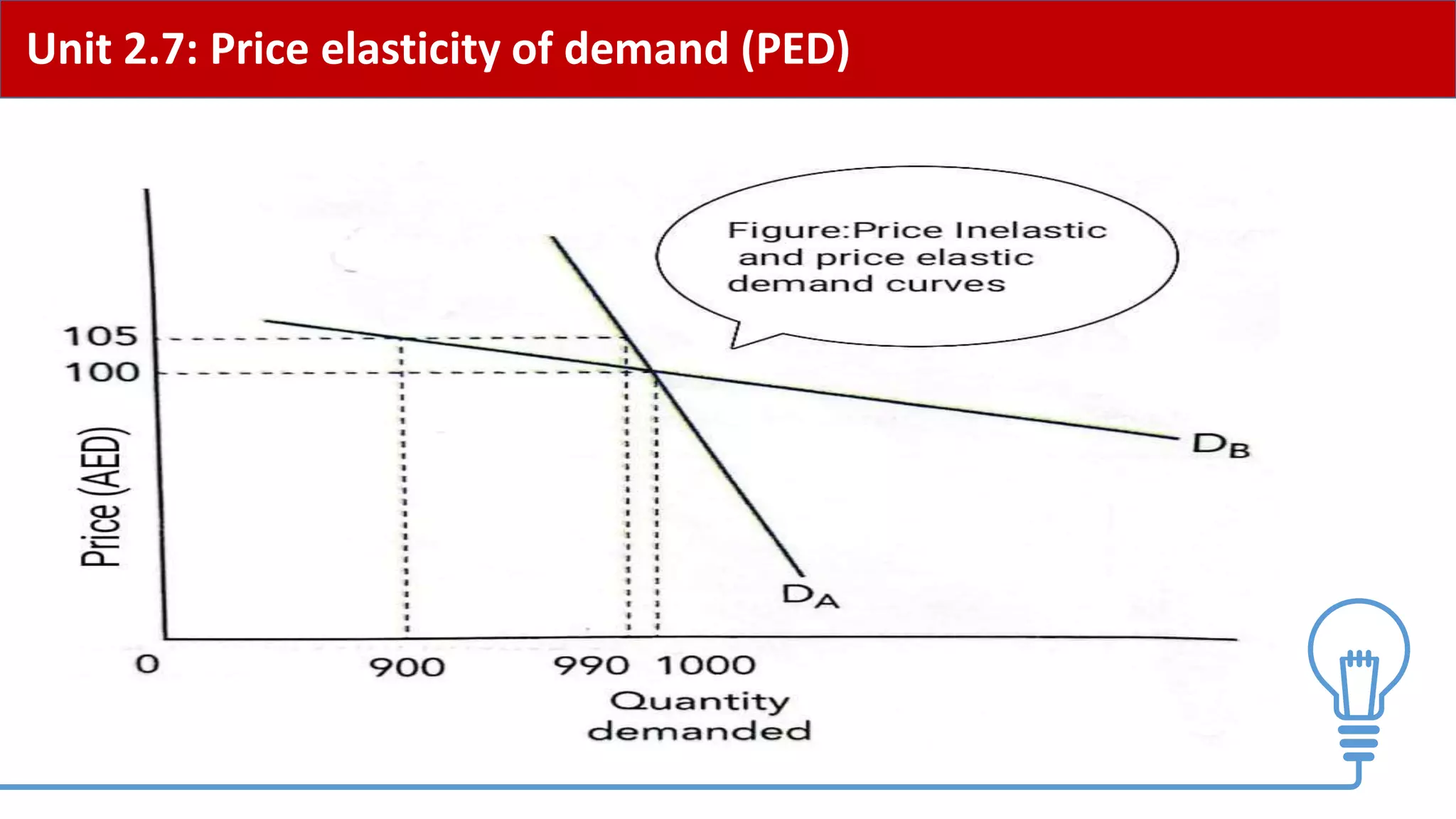
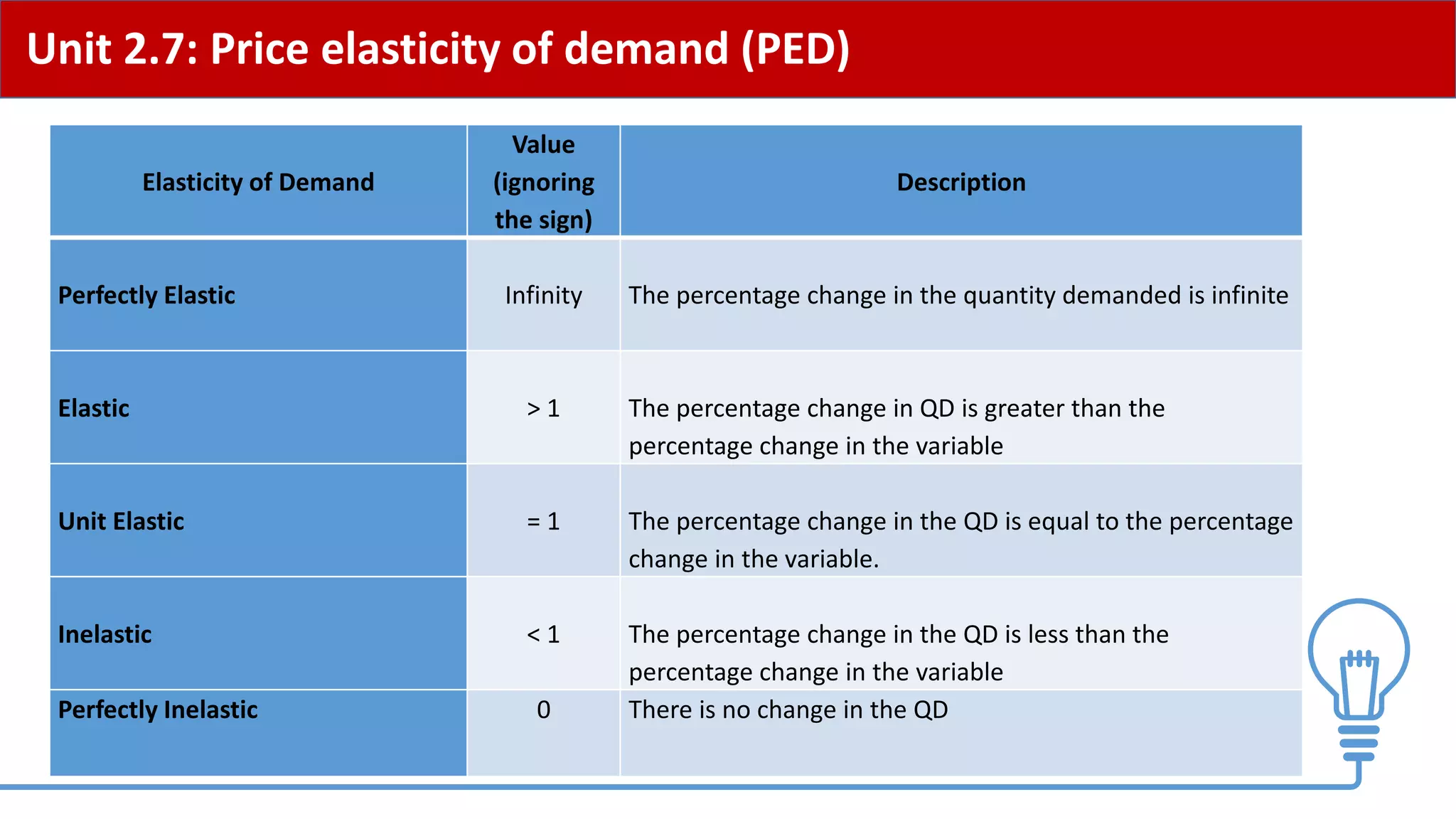
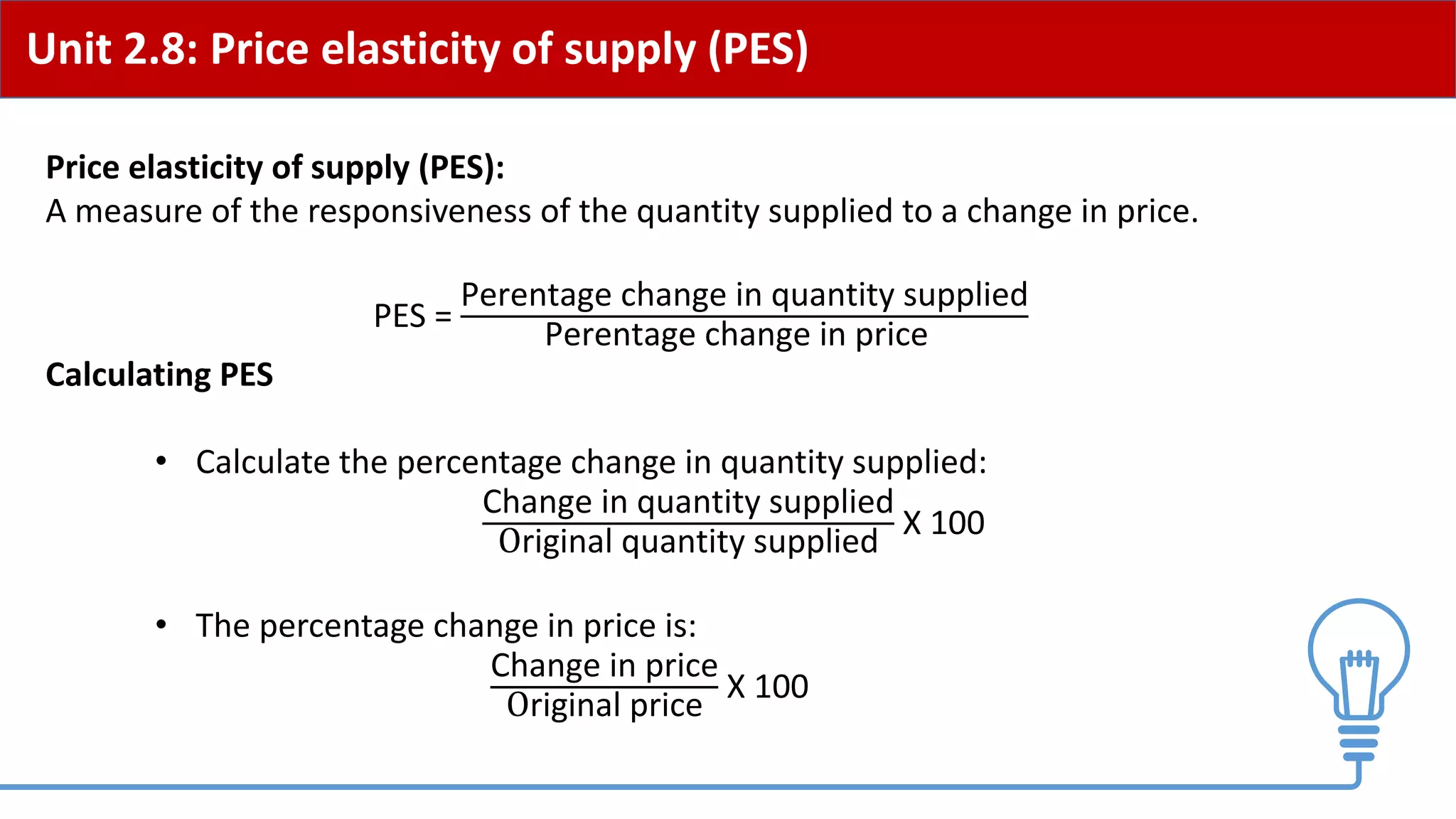
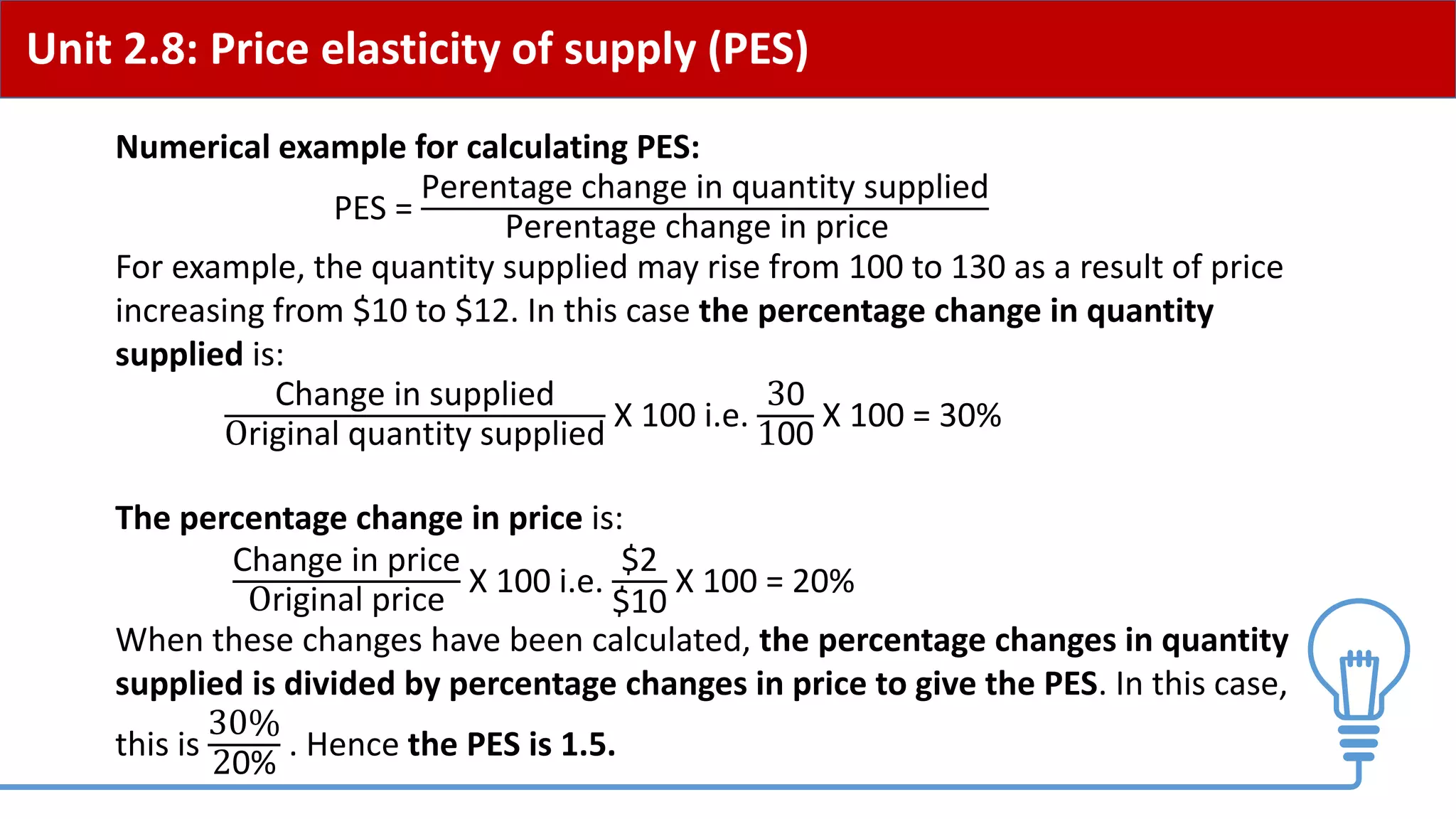
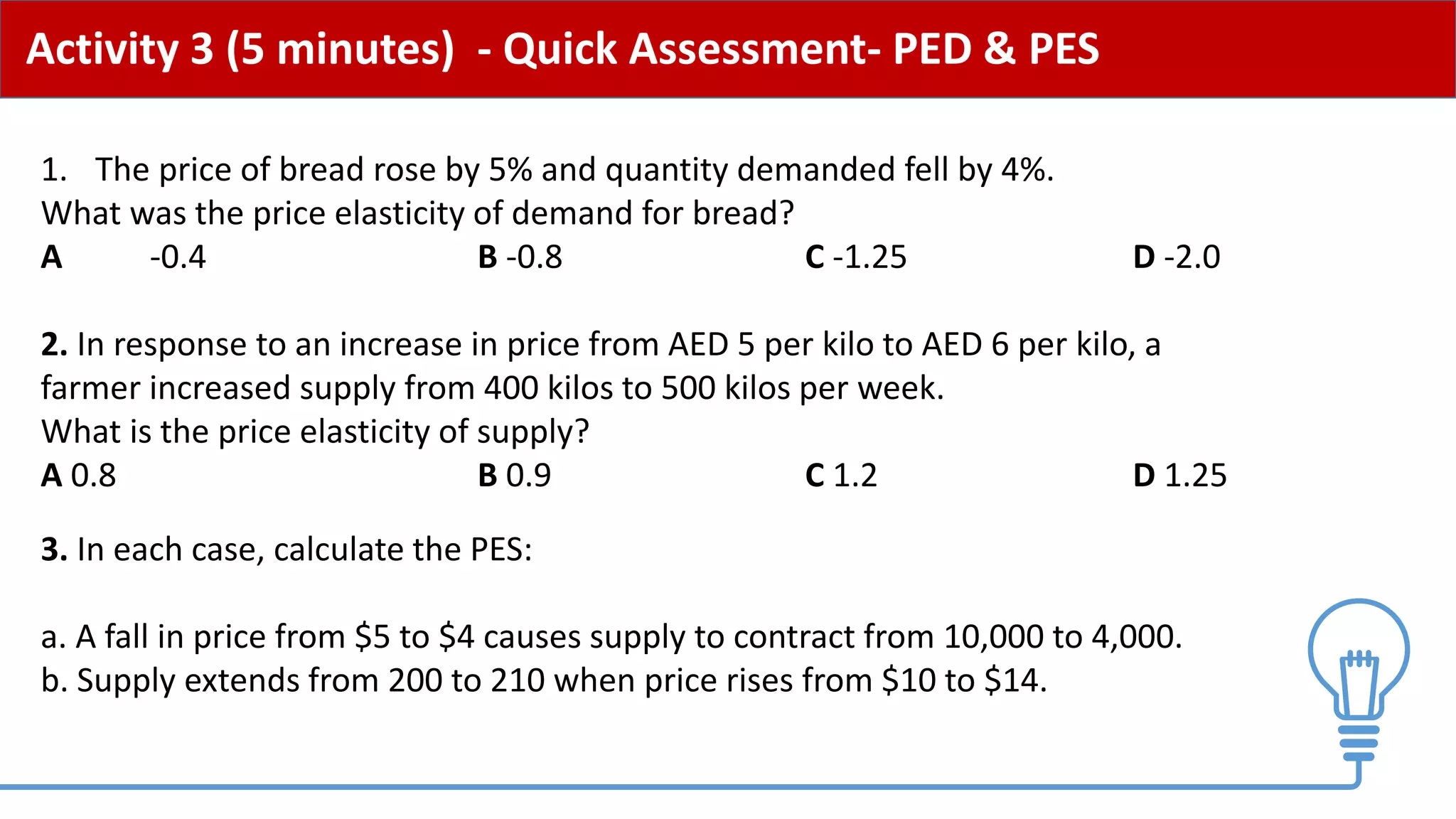
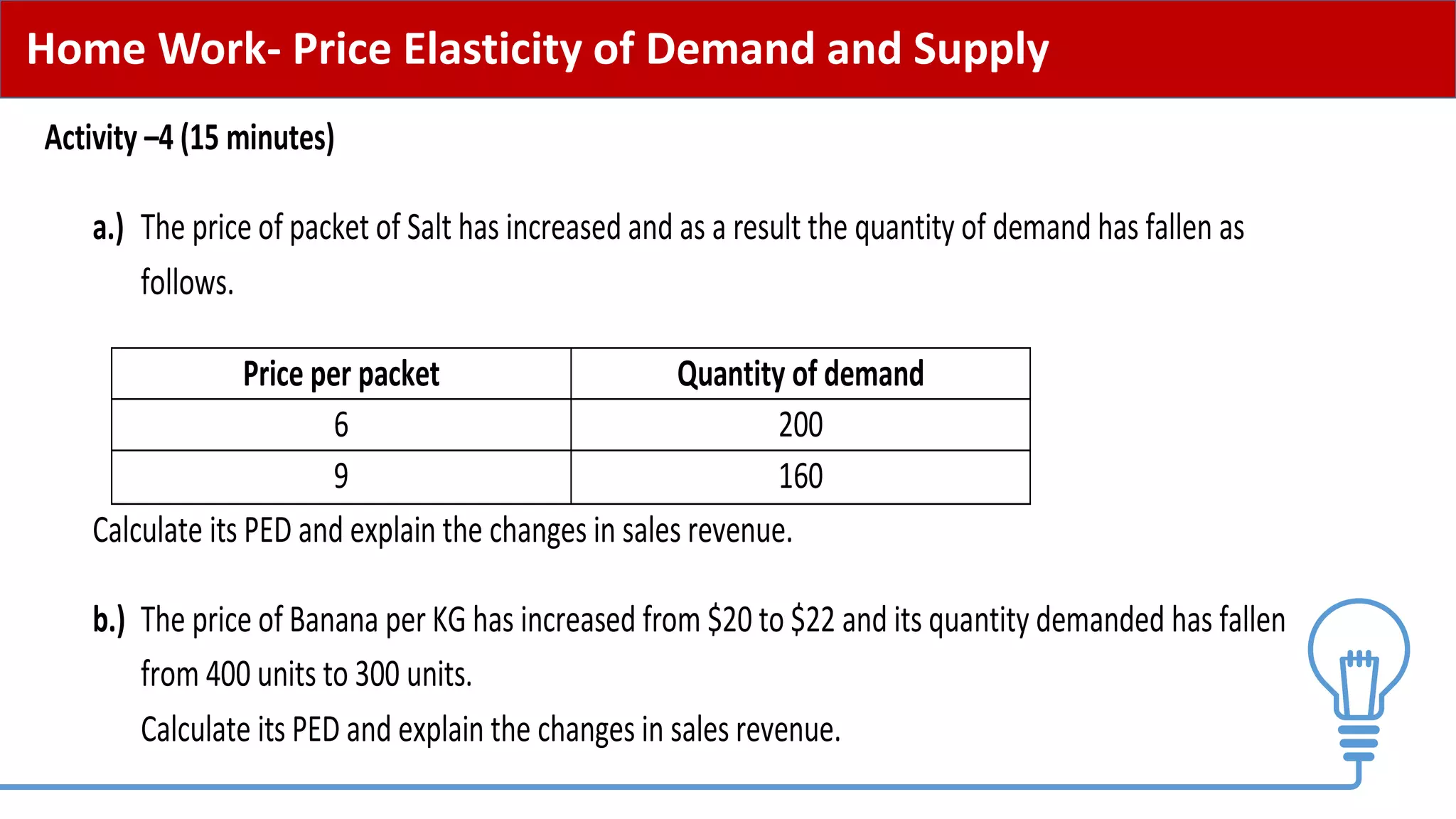
This document provides an overview of price elasticity of demand (PED) and price elasticity of supply (PES). It defines these concepts and explains how to calculate PED and PES values. The key determinants of PED are also outlined. Examples are provided to illustrate elastic versus inelastic demand and supply. The implications of elasticity for revenue and pricing decisions are discussed. Students are provided with a self-evaluation checklist and homework assignments involving elasticity calculations.