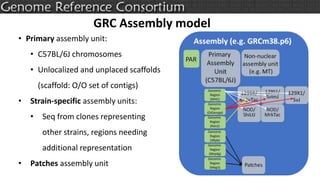
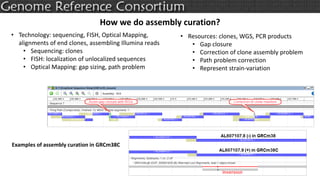
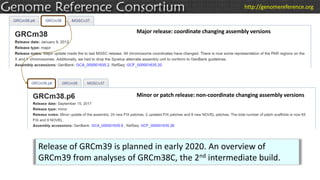
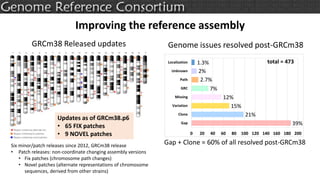
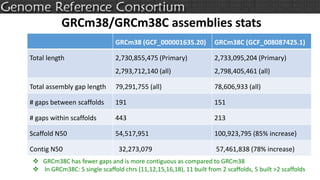
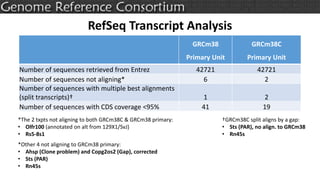
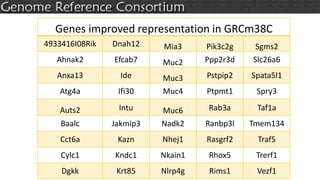
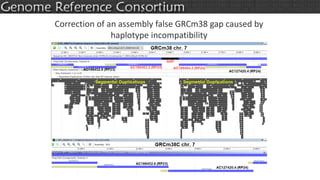
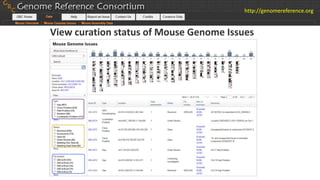
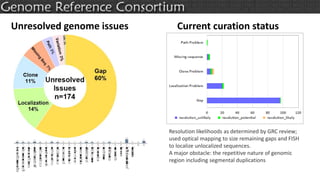
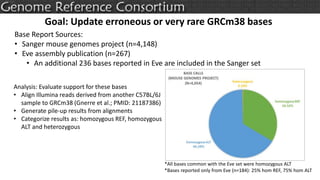
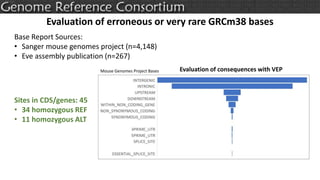
The document discusses the upcoming release of the GRCm39 mouse genome assembly, scheduled for early 2020, following the analysis of the intermediate build GRCm38c. It highlights updates, improvements, and the assembly curation process, including strategies for gap closure and the representation of strain variations. Additionally, it outlines the changes made between GRCm38 and GRCm38c, demonstrating enhanced contiguity and reduced gaps in the genome assembly.