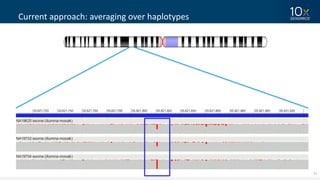
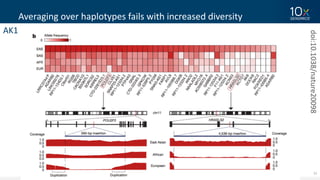
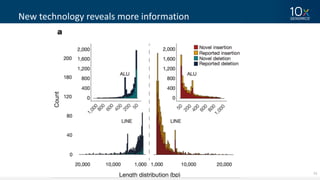
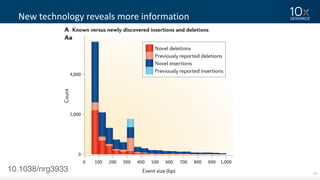
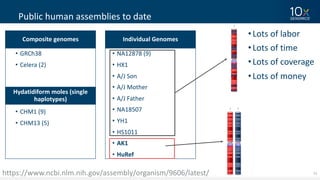
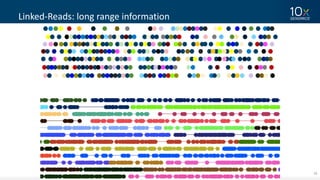
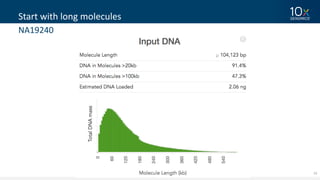
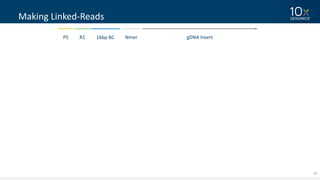
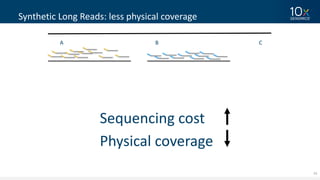
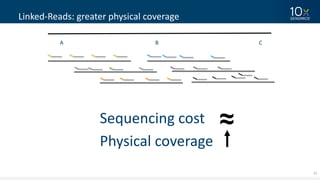
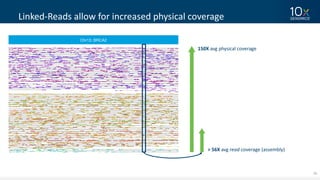
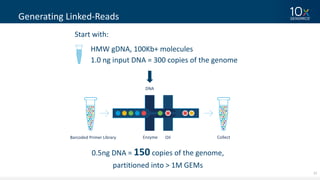
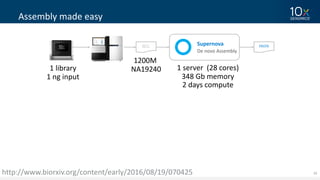
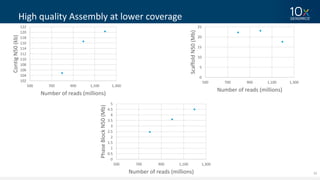
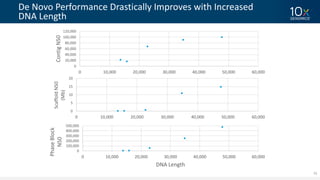
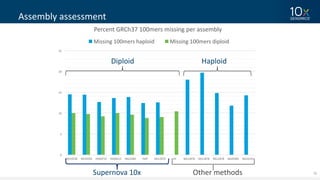
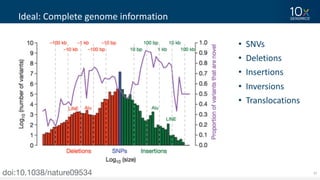
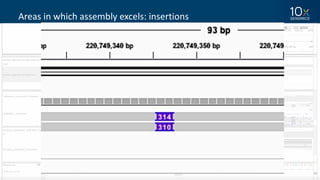
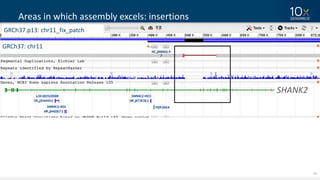
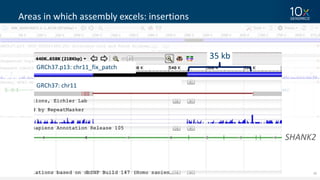
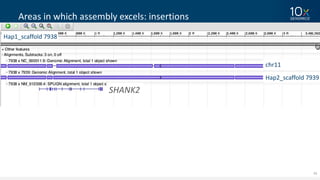
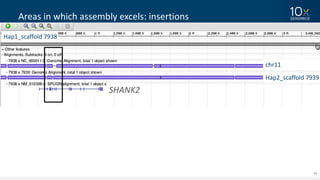
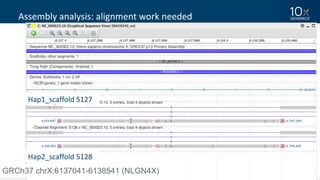
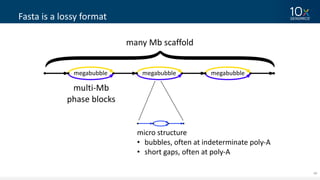
This document discusses how linked-read technology from 10x Genomics now enables routine de novo diploid genome assembly from individual human samples. Linked-reads generate long-range genomic information by barcoding DNA fragments derived from the same long input molecules. This allows for improved physical coverage compared to short reads or synthetic long reads. The document shows how a single 10x Genomics library with only 1 ng of input DNA and modest sequencing can generate high-quality human genome assemblies in 2 days. De novo assembly excels at resolving structurally complex and diverse genomic regions that remain difficult for short-read and alignment-based methods.