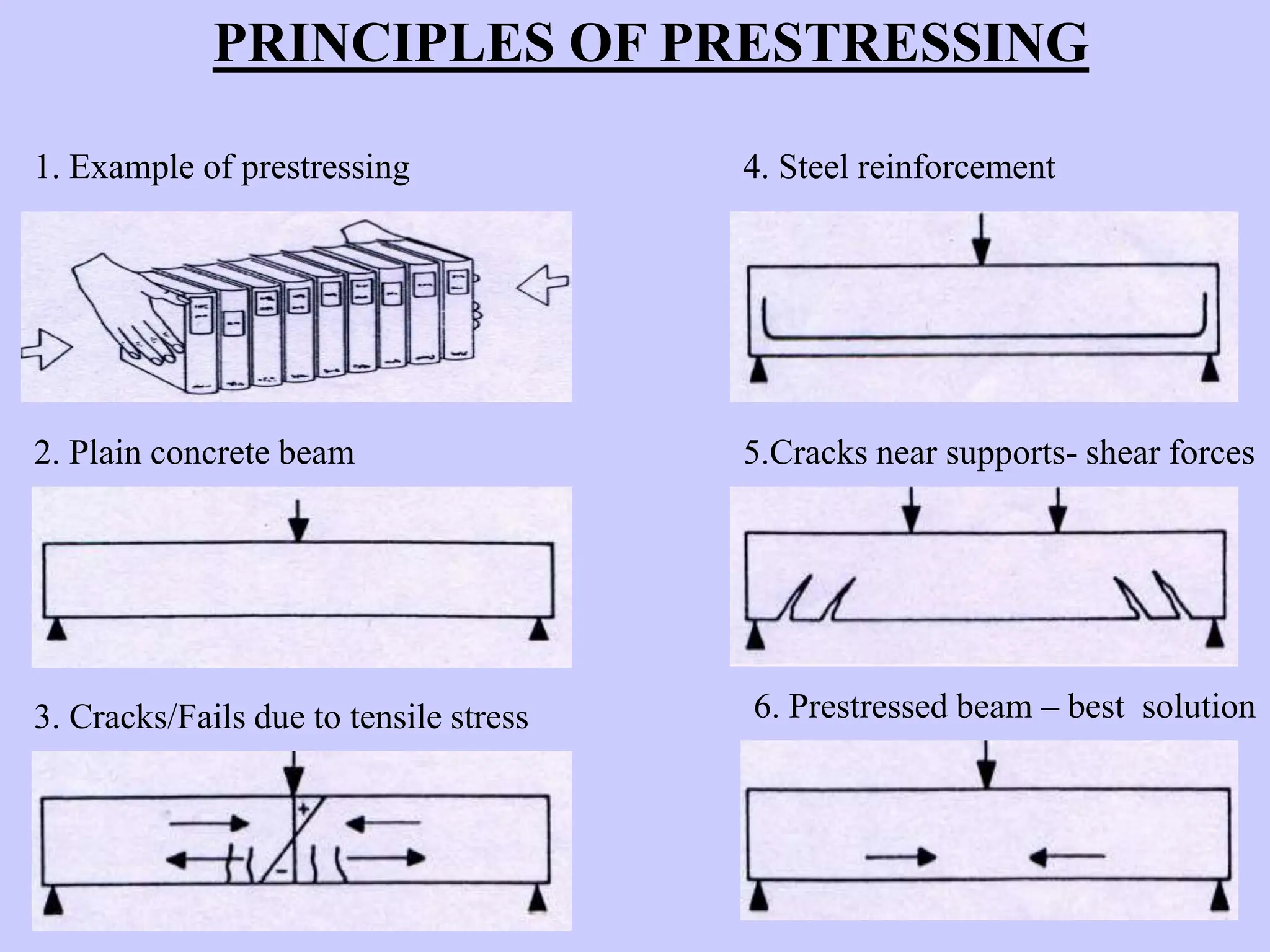
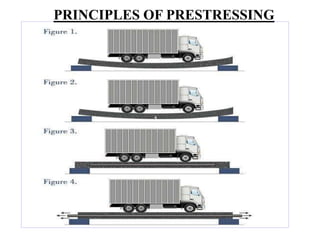
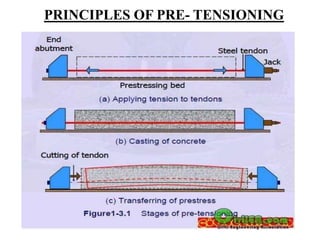
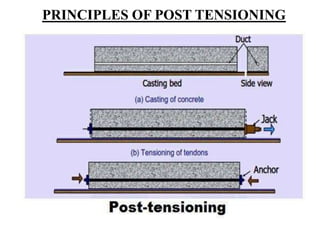
The document discusses the principles and applications of prestressing in construction. It describes how prestressing uses tensioned steel strands or wires to put concrete members into compression through pre-tensioning or post-tensioning. This counters the tensile stresses experienced by concrete and allows for longer spans, reduced member depth, crack control, and cost savings. Common applications of prestressing include bridges, flyovers, buildings, parking structures, and industrial structures.