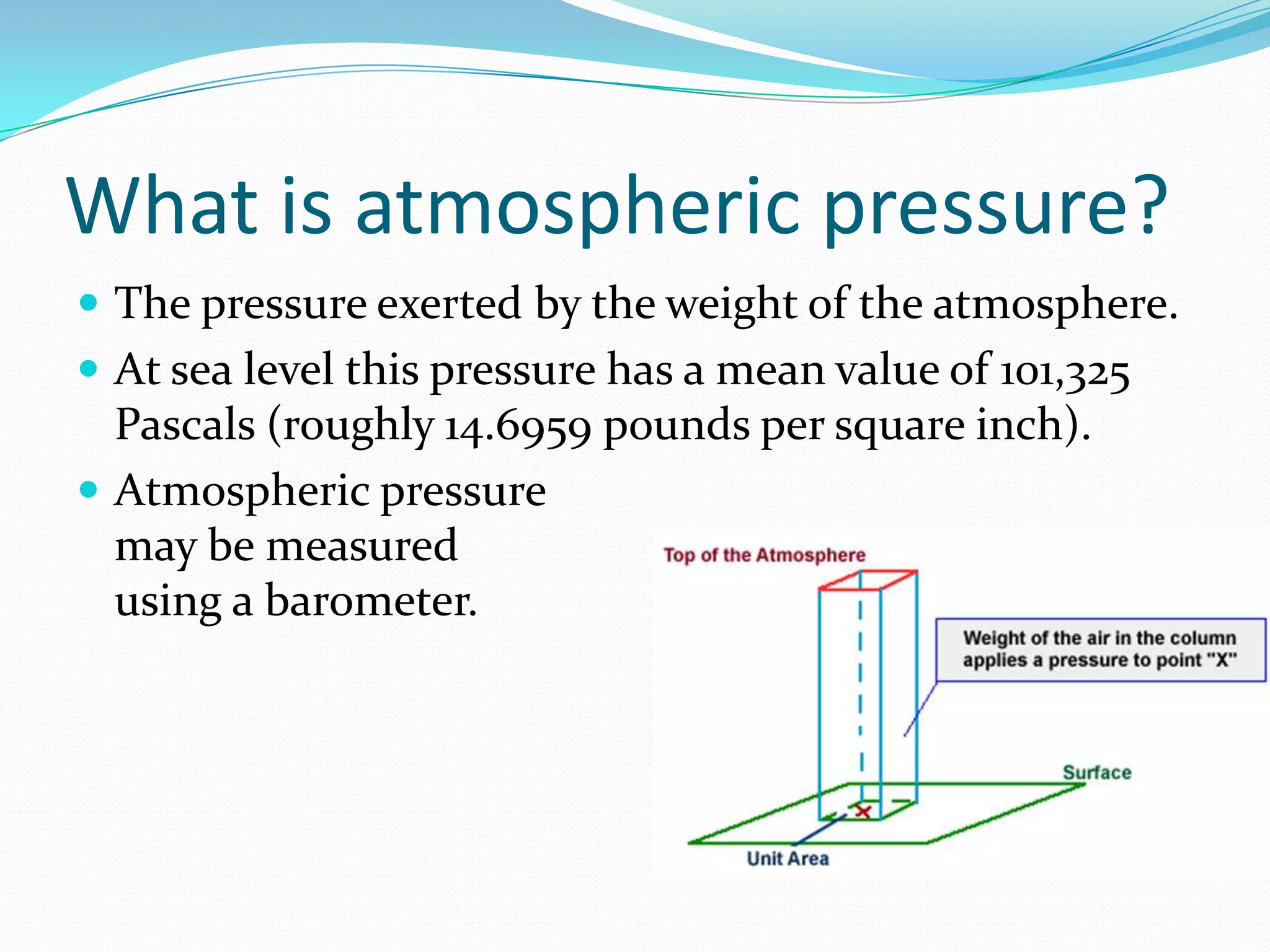
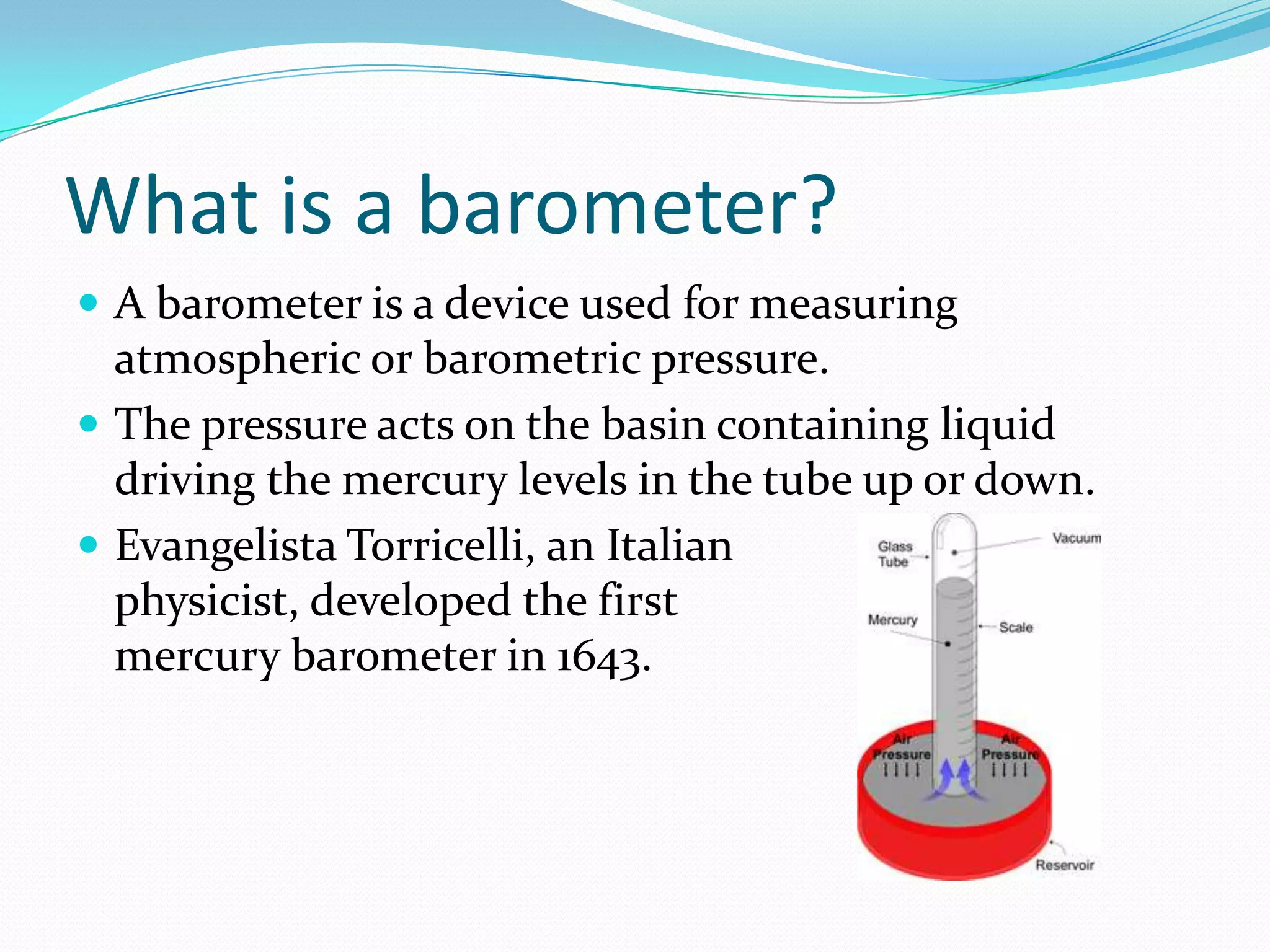
Atmospheric pressure can be measured using a barometer. The first mercury barometer was developed in 1643 by Evangelista Torricelli. Later, an aneroid barometer was invented in 1843 that functions without liquids. In 2004, Cold Energy obtained a patent for a device that generates electricity by exploiting differences in atmospheric pressure between geographic locations using a pressurized air pipeline. This concept could generate enough renewable energy to power 250,000 homes.